NOTE: Some content may not display correctly, including tables and figures. See PDF for full details.
Details on the Carbon Tax (Tax for Climate Change Mitigation)
In order to realize a low-carbon society, strengthening climate change mitigation(energy-related CO2 emissions control measures),namely the deployment of renewable energy and energy-saving measures,“Tax for Climate Change Mitigation” is to be gradually enforced from October 1, 2012. Specifically, it asks wide and fair burdens for the use of all the fossil fuels such as oil, natural gas and coal, depending on environmental load (CO2 emissions).
In order to solve the pressing issues of energy and climate change, we would thank all the citizens very much for the understanding and cooperation in suppressing CO2 emissions associated with the use of energy much as possible.
Introduction of CarbonTax 【Contents】 1. Background and Purpose of CarbonTax 2. Mechanism of CarbonTax 3. Household Burden due to CarbonTax 4. Efforts to Reducethe Economic Burden and CO2 5. Revenue of Carbon Tax 6. CO2 Reduction Effects of CarbonTax 7. Considerable Measures Related to CarbonTax |
|
1. Background and Purpose of Carbon Tax
Climate change is an important and urgent global issue. To realize a low-carbon society, Japan is aiming to curb its greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 80% by 2050.
Approximately 90% of GHG emissions in Japan is carbon dioxide deprived from the energy use (energy-related CO2). For the drastic reduction of Japan’s GHG, it is essential to strengthen energy-related CO2 emissions control measures in the medium to long term.
In addition, as to reduce reliance on nuclear power, further promotions of energy-related CO2 emissions control measures, such as the promotion of energy-saving and renewal energy, are becoming more important than before the Great East Japan Earthquake (happened on March 11, 2011).
Given this background, in order to limit energy-related CO2 emissions by leveraging the economic incentives through taxation and to strengthen energy-related CO2 emissions control measures such as renewable energy and energy-saving measures by utilizing the tax revenue, “Tax for Climate Change Mitigation” was founded in FY 2012 Tax Reform.
2. Mechanism of Carbon Tax
(1) Summary
Tax for Climate Change Mitigation (hereinafter referred to as “Carbon Tax” asks the burden widely and thinly for the use of fossil fuels such as petroleum, natural, gas, and coal depending on environmental load.
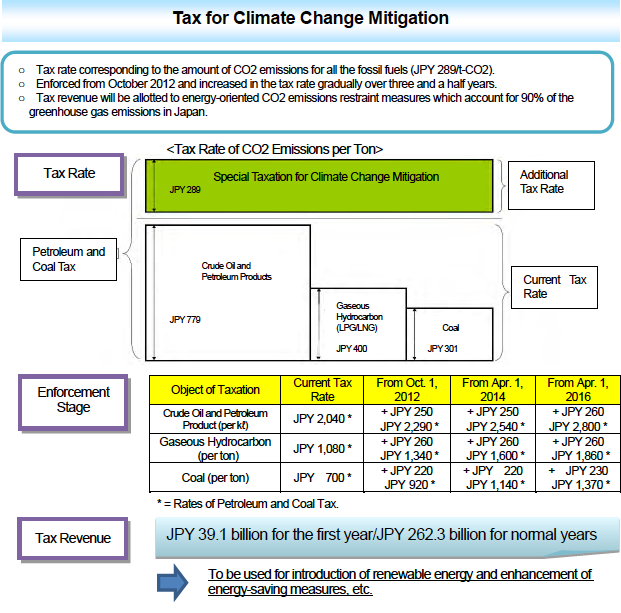
Specifically, by using the CO2 emissions factor of each fossil fuel, the tax rate per unit quantity (kilo litter or ton) is set in order that each tax burden to be equal to JPY 289 per ton of CO2 emissions. Moreover to avoid the rapid increase in burden, tax rates will be raised in three stages over three and a half years.
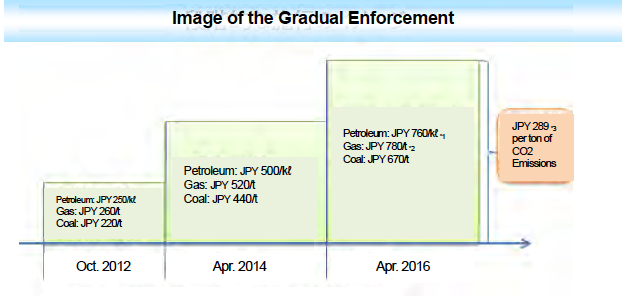
In addition, Carbon Tax takes advantage of the taxation scheme of the current petroleum and coal tax which tax base covers all the fossil fuels and is levied in the form to add the above tax rates to the petroleum and coal tax.
3. Household Burden due to Carbon Tax
According to the simple calculations based on the current energy usage, an additional household burden caused by Carbon Tax is expected to be about JPY 100 a month, and JPY 1,200 a year for an average household. Since this assumes the state after all the three enforcement stages, the monthly burden in FY 2012 or 2013, for example, is supposed to be approximately one-third of that (JPY 30/month).
The amount of energy price hike with the tax | Annual energy consumption | Burden per household |
Gasoline | JPY 0.76/ℓ | 448ℓ | |
Kerosene | JPY 0.76/ℓ | 208ℓ | JPY 1,228/year |
Electricity | JPY 0.11/kWh | 4,748kWh | (JPY 102/month) |
Natural Gas | JPY 0.647/Nm3 | 214Nm3 | |
LPG | JPY 0.78/kg | 89kg | |
Note 1: Estimated on the basis of Family Income and Expenditure Survey (FY 2010) by Statistics Bureau, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications and et al.
Note 2: In the above estimate, a variety of measures to reduce the burden associated with the introduction of this tax is not considered. As all the tax burden is assumed to be passed on to all customers, the amount of price increase and burdens vary depending on the circumstances of the actual price shift. Also, the amount of price increase and burdens of electricity may vary depending on the amount of fossil fuels used for power generation in practice.
4. Efforts to Reduce the Economic Burden and CO2
Although burdens will be incurred by Carbon Tax depending on the amount of fossil fuels consumption, it is possible to reduce the economic burden as well as CO2 by actively promoting the energy-saving efforts and renewable energy use.
For example, in efforts for daily energy-saving,
・Bylowering the temperature of 1 degree Celsius in cooling equipment or increase 1 degree Celsius in heating, approximately JPY 1,800 can be saved annually (about 33kg of CO2 reduction).
・By stopping idling for 5 minutes everyday, approximately JPY 1,900 can be saved annually (about39kgof CO2 reduction).
In addition, it is possible to reduce economic burden and CO2 by utilizing household equipment such as,
・Purchase of energy-savinghome appliances, LEDlightening and environmentally friendly vehicle such as hybrid and electric vehicles
・Installation of insulation and double-glazed glass
・Installation of solar powergenerators, solar water heaters and fuel cells for home use
Tax burden can be reduced by these various efforts while reducing CO2 as well.
Note: It is assumed that tax burden of JPY 289 could be reduced by the reduction of 1 ton of energy-related CO2, but it may vary depending on the actual situation of the price shift of the tax.
5. Revenue of Carbon Tax
Revenue of Carbon Tax is estimated to be JPY 39.1 billion for the first year FY 2012 and JPY 262.3 billion for each normal year after FY 2016.
By utilizing this tax revenue, it is planned that various measures of energy-related CO2 emissions control, such as energy-saving measures, promotion of renewable energy, and clean and efficient use of fossil fuels, will be steadily implemented. For instance, various promoting measures are to be conducted for:
- Promotion of domestic business location for innovative low-carbon technology-intensive industries, namely, lithium-ion butteries
- Installation of energy-saving equipment by small and medium-sized enterprises
- Introduction of financial assistance for local governments to promote energy-saving and renewable energy so-called “Green New Deal Funds” in accordance with local characteristics.
6. CO2 Reduction Effects of Carbon Tax
As for the CO2 reduction effects by Carbon Tax, mainly the followings are expected: [1] “Price Effect”: CO2 emissions control effect through taxation, and
[2] “Budget Effect”: CO2 reduction effect by inflecting tax revenue for measures for energy-related CO2 emissions control
In addition, [3] “Announcement Effect” is expected namely:
- Prior Announcement Effect: CO2 emissions control effects through preventive actions for emissions control before tax enforcement
- Signaling Effect: CO2 emissions control effects through raised awareness across all the society against climate change by the fact of the tax introduction
The price effect and budget effect of Carbon Tax were estimated as approximately -0.5% to
-2.2% of CO2 reduction in 2020 compared to 1990 (about 6 million tons to 24 million tons in quantity).
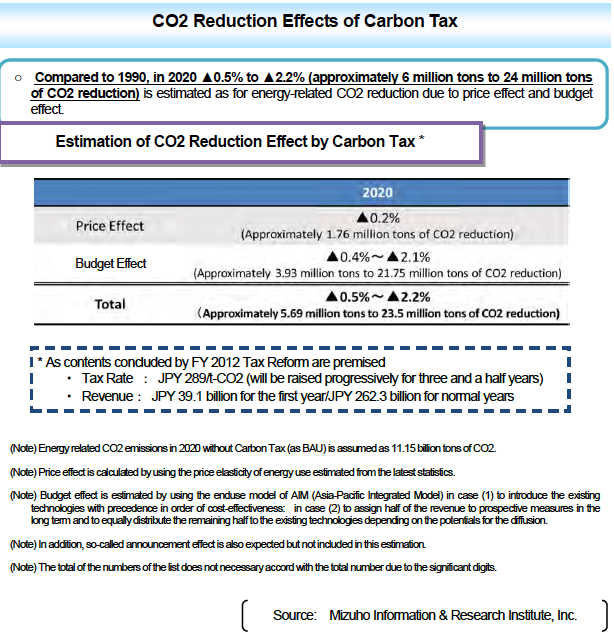
(Note) Energy related CO2 emissions in 2020 without Carbon Tax (as BAU) is assumed as 11.15 billion tons of CO2.
(Note) Price effect is calculated by using the price elasticity of energy use estimated from the latest statistics.
(Note) Budget effect is estimated by using the enduse model of AIM (Asia-Pacific Integrated Model) in case (1) to introduce the existing technologies with precedence in order of cost-effectiveness: in case (2) to assign half of the revenue to prospective measures in the long term and to equally distribute the remaining half to the existing technologies depending on the potentials for the diffusion.
(Note) In addition, so-called announcement effect is also expected but not included in this estimation.
(Note) The total of the numbers of the list does not necessary accord with the total number due to the significant digits.
Source: Mizuho Information & Research Institute, Inc.
In addition, further CO2 reductions are expected by performing additional efforts thanks to the spreading effects of the tax. Moreover, as the induction effects upon industrialization and innovation, CO2 reduction by infiltrating low-carbon technology and actions into the whole economy and society are also expected.
7. Considerable Measures Related to Carbon Tax
Carbon Tax is designed to avoid excessively heavy burdening for specific fields and industries and to secure its equitableness by asking “wide and thin” burdens. In addition, so as not to increase burdens drastically, Carbon Tax is to be enforced progressively in three and a half years and the exemption and refund measures are to be provided for the certain fields.
For the following a.to e., exemption and refund measures are provided for the ratesaddedby“Special Taxation for Climate Change Mitigation”.
a. Imported and domestic volatile oil for petrochemical products production
b. Imported specific coal
c. Specific coal for electric generation in Okinawa
d. Imported and domestic bunker A heavy oil for agriculture, forestry and fishery
e. Domestic oil asphalt
For the following a. to f., exemption and refund measures are provided only for the tax rates added as “Special Taxation for Climate Change Mitigation”.
a. Imported coal used for home generation of electricity for caustic soda production in caustic soda manufacturing industry
b. Heavy oil and light oil used for domestic cargo ships and passenger ships
c. Light oil used for railway
d. Aviation fuel for domestic flight
e. Imported coal used for home generation of electricity for salt production in salt manufacturing industry by the ion exchange membrane method
f. Light oil used for agriculture, forestry and fishery
In addition, the following measures are to be conducted:
- Supportive measures for cost reduction in fuel production and distribution, stabilization of fuel supply and energy-savings in logistics and transportation sectors
- Supportive measures for depopulated and cold areas
Please feel free to contactus about this web site:
Environmental TaxationTeam
Environment and Economy Division
Environmental Policy Bureau
Ministry of the Environment, Japan
(E-mail: [email protected])
(DialNumber: +81-3-5521-8230)