NOTE: Some content may not display correctly, including tables and figures. See PDF for full details.

Over the period of 1990 to 2010, Thailand’s energy consumption continuously
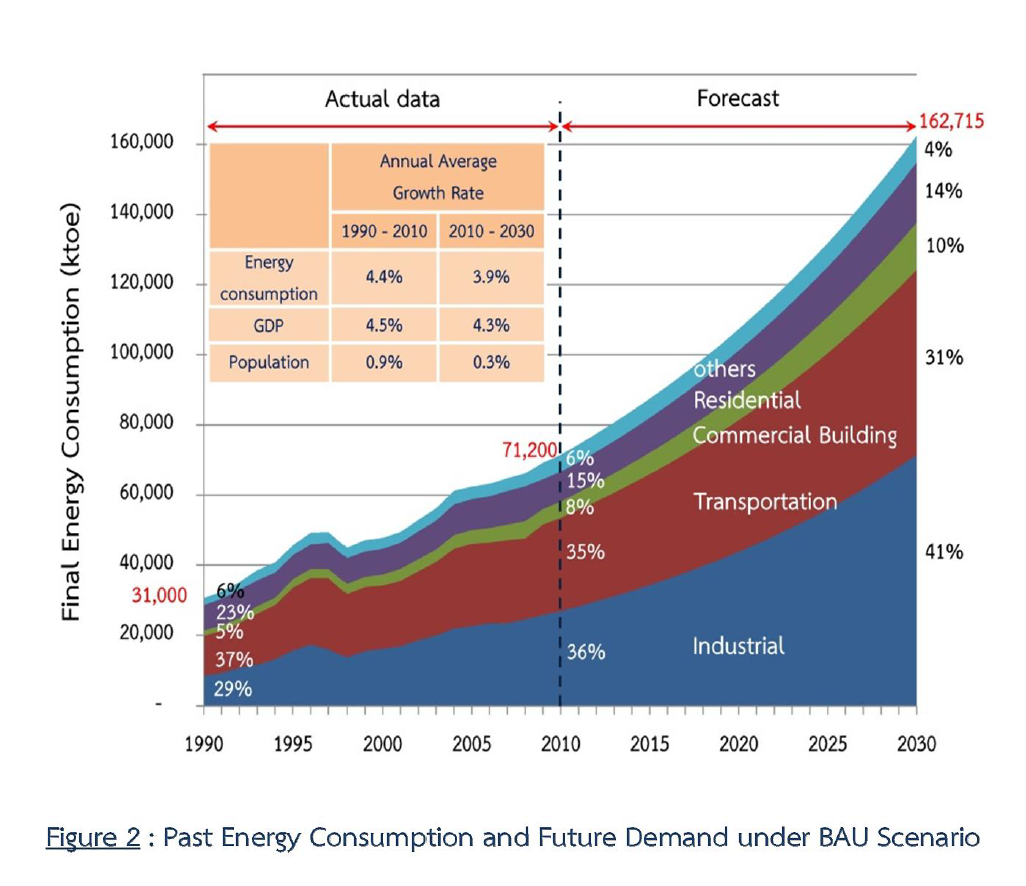
increased by average at the annual rate of 4.4 percent. In the year 2010, final energy consumption amounted to 71,200 kilotons of oil equivalent (ktoe) or 2.32 times of the amount in the year 1990 while the annual economic growth rate during the period was at 4.5 percent. Measuring as the percentage change in energy consumption to achieve one percent change in national GDP, the energy elasticity ratio accounted for 0.98, which deemed high, compared with that in other developed countries having well energy efficiency.
According to the 2010 study on the future energy consumption over the next 20 years (2011 - 2030), based on the “Business as Usual” (BAU) scenario with the annual average economic and population growth rate at 4.3 and 0.3 percent respectively, the energy demand during the period is forecasted to increase annually by average at 3.9 percent. The energy consumption in the year 2030 will rise to 162,715 ktoe or 2.3 times as much of the amount in the year 2010.
Based on historical energy data and statistical review, the growth of energy consumption in commercial and industrial sectors considerably surpassed the economic growth. In 2010, the economic growth achieved 2.36 times as much of the amount in 1990 while the energy demand growth of commercial and industrial sectors during the period were recorded by 3.7 and 3.0 times as much respectively. The causes of such soaring energy demand in commercial sector were the robust economic growth, together with rapid urban expansion, real estate and condominium development. In industrial sector, the energy
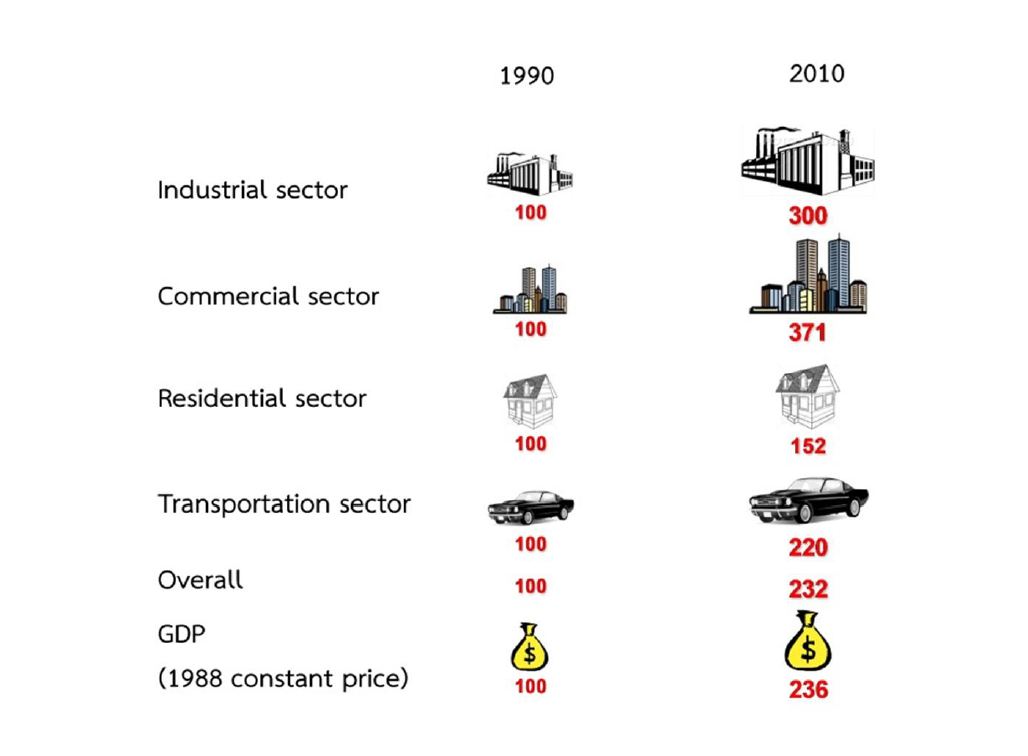
Figure1 : Energy Demand Growth by Sector and Energy Growth in 1990-2010 |
|
demand rose annually by average at 7.1 percent. Its consumption share rose from 26 percent of total energy consumption in 1986 to 36 percent in 2009 which was very close to the transportation sector, occupying 35.6 percent in 1986 and slightly increasing to 35.8 percent in 2009. Residential sector reduced its share from 28.2 percent in 1986 to 14.9 percent in 2009, due to more efficient home appliances.
Figure2 : Past Energy Consumption and Future Demand under BAU Scenario |
|
StrategiesFormulation Framework |
|
The Energy Conservation Act, which has been enacted in Thailand since 1992, has enforced only industrial and commercial sectors, including efficient appliances and equipment. Nevertheless, transportation sector, which consumed one-third of the total energy demand, has not been enforced by the Act. Neither definite strategy nor action plan aimed at significantly materialization. As such, the past achievement has not been substantial as intent. In 2010, the Energy Policy and Planning Office (EPPO), assigned by the Ministry of Energy, had formulated the long term 20-year (2011 - 2030) energy efficiency strategies and was endorsed by the Cabinet in May 2011. This 20-year (2011 - 2030) Energy Efficiency Action Plan (EEAP) was the framework for all stakeholders being integrated and steered to fulfill the national and international commitment under the same umbrella and goal of energy use efficiency and climate change alleviation.
- World Energy Council’s 4 A’s Policies aim at achievement of energy implementation in analyzing and formulating strategies and implementation activities under the Plan.
- The concepts to improve the quality of public sector management under The Office of the Public Sector Development Commission, Thailand’s formatting the Plan.
Figure 3 : Concepts to improve the quality of public sector management.
Energy efficiency to mobilize national production and consumption toward low carbon and environmental friendly society.
Strengthen energy security, reduce household expenses, cost of product and service, trade deficit. Increase competitiveness and reduce emission of greenhouse gas which affects climate change.
Reduce energy intensity (EI), measured as energy consumption per unit of GDP, in the year 2030 by 25 percent from the year 2010.
(1) Employ integrated compulsory measures through laws, regulations and standards, together with promotion through various incentives.
(2) Employ energy measures which create widespread effects on awareness, behavior change of consumers, decision-making of entrepreneurs, and market transformation, via campaigns and public relation activities relevant with energy and climate change.
(3) Promote public private partnership for supporting and implementing energy conservation measures.
(4) Distribute promotion activities to various public and private organizations which possess resources and experiences readiness, such as power utilities and industrial associations with Ministry of Energy supports.
(5) Employ professionals and Energy Service Company (ESCO), as vital mechanisms, in terms of consultation and implementation of energy efficiency projects requiring high technology.
(6) Increase self-reliance on energy technology to cut costs and to foster technology accessibility, together with promoting high energy efficient products, manufacturers, and businesses.
The strategies of the 20-year EEAP, the following World Energy Council 4 A’s approach was applied, i.e.
AVAILABILITY :
EEAP targets all energy sectors, including producer and consumer sectors, under the definition of energy conservation stipulated under 1992 Energy Conservation Act, and compliance with the terms of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Convention in reducing carbon dioxide emission. Producer sector consists of power generation, transmission and distribution while consumer sector comprises of industrial, commercial, residential and transportation.
ACCESSIBILITY :
Facilitate access to all mechanisms which will enhance achievement, namely, investment, technology, and knowledge on operation and implementation.
ACCEPTABILITY :
Provide satisfaction to all stakeholders, i.e. significant energy savings as expected by the government, reasonable return on investment for entrepreneurs and environmental issues in public. In this regard, the implementation will be carried out through public - private participation approach.
ACCOUNTABILITY :
Strengthen the government roles in both effective enforcement of compulsory measures (PUSH) and the provision of wide incentive measures (PULL). They are to ensure the law compliance of all designated implementers and to promote the climate of investment. Compulsory measures consisting of Energy Management, Building Energy Code (BEC), and Minimum Energy
Performance Standards (MEPS) are to deter the use of inefficient energy appliances and to encourage the use of equipment and appliances with High Energy Performance standards (HEPS).
20- year EEAP divides into 3 phases of implementation, i.e. 6 year short-term (2011 - 2016), 6 year medium term (2017 - 2022) and 8 year long-term (2023 - 2030). Based on the concept of execution short-term infrastructure programs, the master road map’s directions will lead towards the successful implementation in the medium and long terms.
The short-term programs emphasize on existing proven projects as well as new projects with quick achievement potential, R&D, law and regulation amendment, institutions strengthening, and the study on raising funds for investment in industry restructure for medium and long terms through public private participation approach whilst the medium and long-term programs are the continuity of the successful projects in the short-term phase.
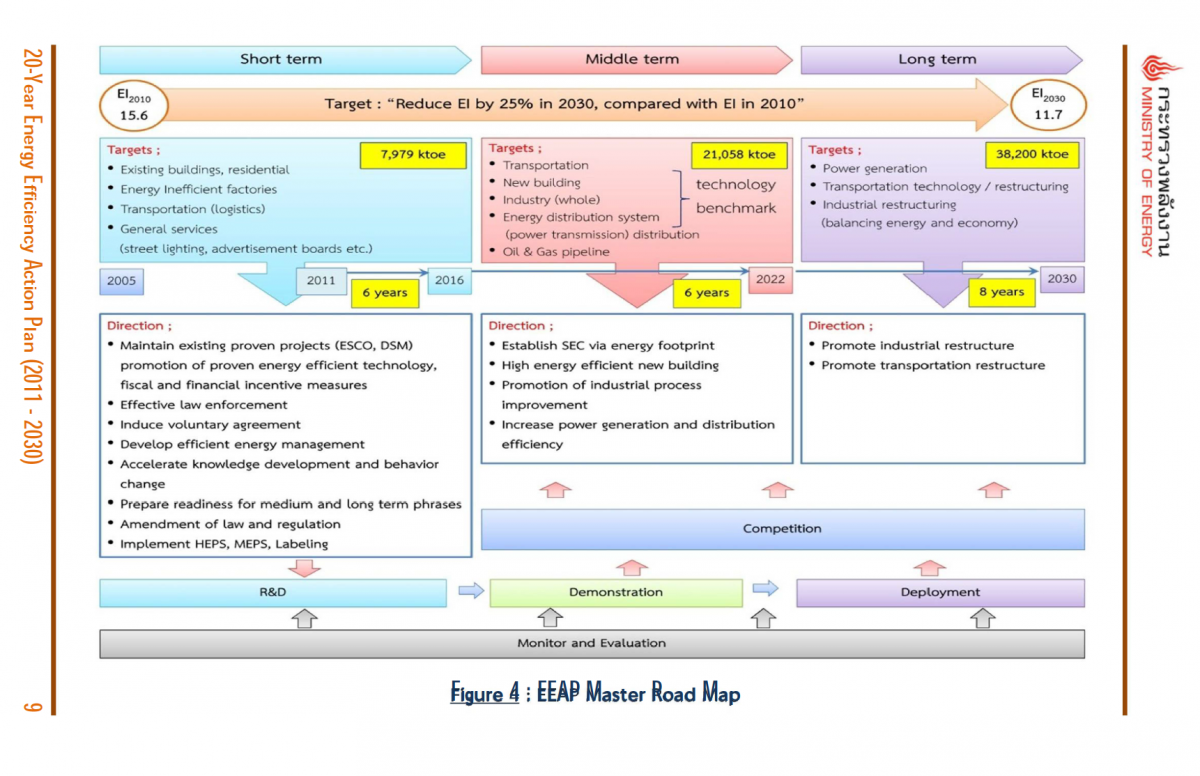
Figure 4 : EEAP Master Road Map
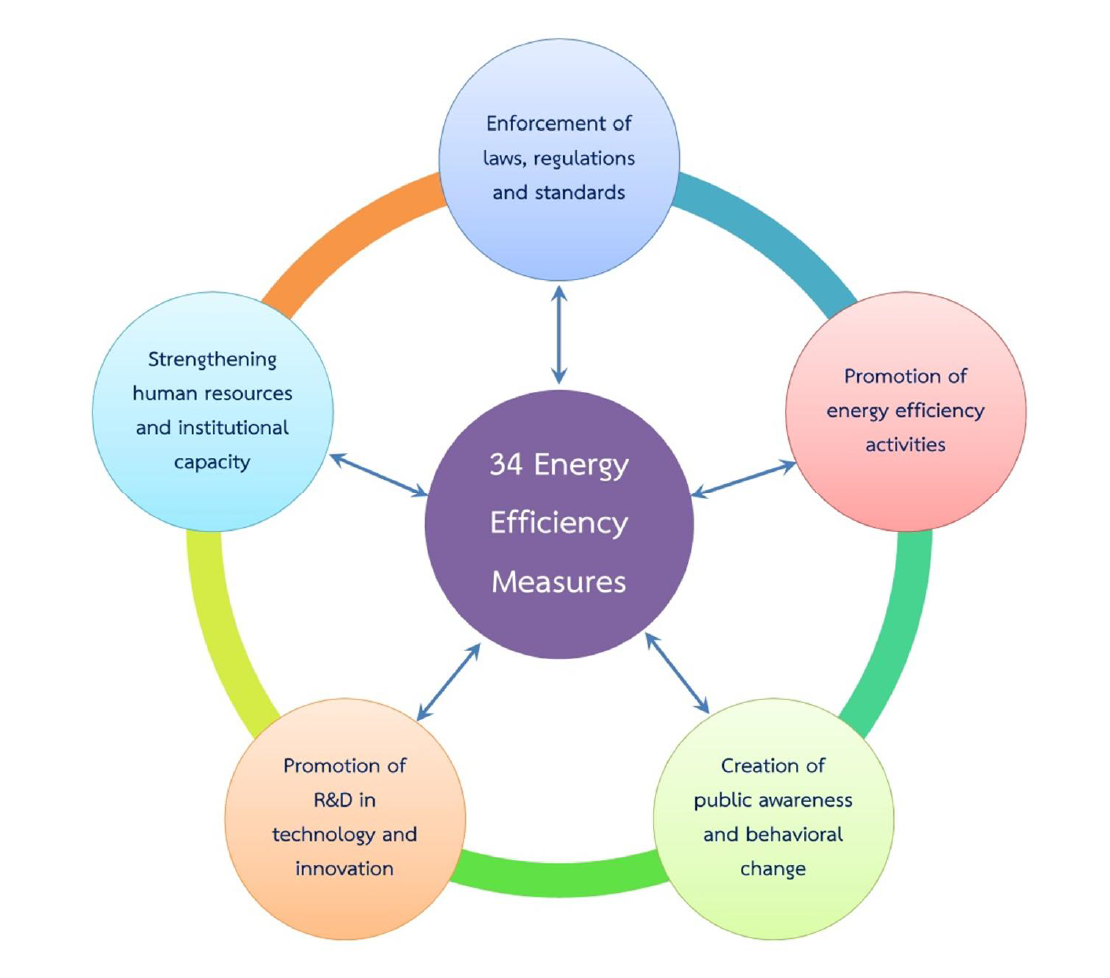
Figure 5 : 5 Strategic Approaches and 34 Measures |
|
Intensified enforcement of laws, regulations and standards |
|
Past record on inefficient use of energy was the effects of ineffectiveness of law enforcement resulting from unclear role of law enforcers, outdated law, and rapid technology development. Investment promotion in energy inefficient industries relocated from industrially developed countries. Additionally, the influx of cheap imported inefficient appliances worsened the situation. Intensified enforcement of laws, regulations, measures, and energy performance standards are the effective instruments to handle such inefficient practices.
Sector | Measures / Programs |
Cross cutting | - Intensify enforcement of Energy Conservation Act
- Mandatory labeling
- Minimum energy performance standards (MEPS)
- Energy efficiency resource standards (EERS) for large energy businesses
|
Industry | 5. Specific energy consumption benchmarking (SEC) |
Large commercial building | - Energy performance standards
- Mandatory energy performance labeling
|
Transportation | - Mandatory energy performance labeling
- Minimum energy performance standards (MEPS) for vehicles
- Fiscal measures to enhance market transformation
|
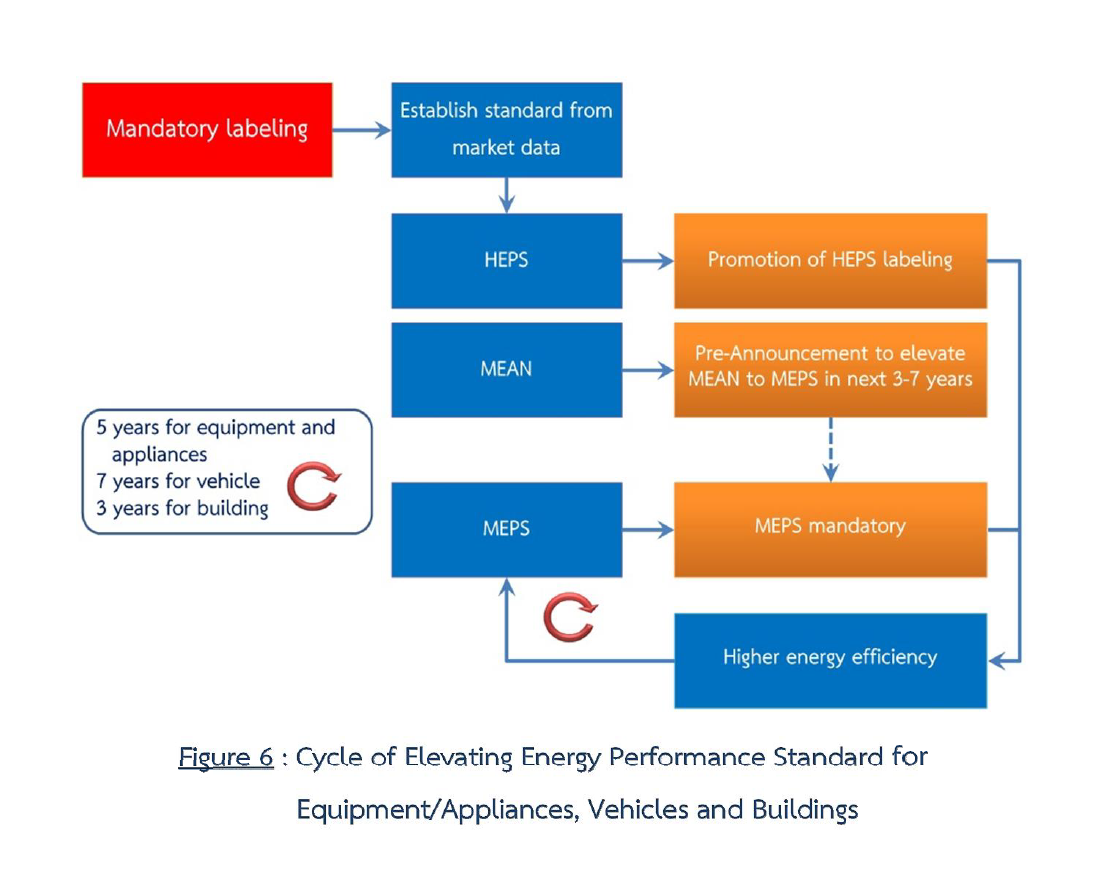
Equipment/Appliances,Vehiclesand Buildings |
|
Support and Promotion of energy efficiency activities |
|
Return on investment of energy efficiency projects is relatively unattractive in comparison with other investments, due to uncertainty in technology, market size and human behaviors. Accordingly, investment in energy efficiency projects has been less priority. These have impeded achievement of energy efficiency. To overcome such hindrances, EEAP has offered financial and fiscal incentive measures and international proven practices. EEAP offers financial and fiscal incentive measures, internationally proven practices, to overcome such hindrances.
Energy Conservation Fund
(1) Subsidy
Partial or full subsidy for eligible parties hosted by government agencies.
(2) Soft loan
Long term or low interest rate or deferred capital payment during initial years, via financial institutions.
(3) Partial guarantee
Provide partial guarantee to collateral lacking borrowers, in acquiring loan via designated financial institutions.
(4) Energy Service Companies (ESCO) Fund
Provide funding, namely, leasing, venture capital, mezzanine financing, energy performance contract, to energy service companies to carry out energy efficiency projects.
• Other Sources
Due to limitation of the Energy Conservation Fund, Energy Trust Fund, being raised under the public private participation approach, is to ensure an adequate funding for huge investment on industrial restructuring during medium and long terms.
Fiscal measures apply through two main instruments
(1) Energy performance tax reduction for building and industry
(2) Tax exemption under Investment Promotion Act for energy efficient equipment and appliances manufactures.
Sector | Measures / Programs |
Cross cutting | - Voluntary agreement
- Promotion of voluntary labeling
- Financial support for energy performance achievement
- Support ESCO implementation
|
Industry | 5. Support R&D in process improvement |
Large commercial building | 6. (1) Support and promote energy labeling for large commercial building |
Small commercial and residential building | - (2) Support and promote energy labeling
for residential building - Financing and fiscal measures to drive energy efficiency performance
- Support high energy efficiency equipment and appliances
|
Transportation | - Support energy labeling on vehicle parts
- Support mass transport system and energy efficient logistics
|
Building public awareness and enhancement of behavioralchange |
|
Besides knowledge, funding and technology, consumer behavior is a vital factor in achieving the success of energy saving, as it is the ending mechanism to yield utmost energy efficiency. The individual’s familiarity of the conveniences consuming energy and low energy price influence on the inefficient use of energy because of the attitude that energy saving affects level of comfort and that it is affordable. Building widespread awareness and discipline will help to achieve the goal.
Measures under this strategy will enhance effective impact on awareness of consumers, perception of entrepreneurs in decision-making, and transformation of the market, together with innovative campaigns and public relation activities relevant with energy efficiency, environment issues, and climate change. State agencies are assigned to take a leading role in this strategy.
1)
Build awareness and perception, that energy efficiency is profitable in the long run, through public relation activities, aiming at elevating investment in energy efficiency as top priority at managerial level. Additionally, implanting awareness, discipline, and devotion on energy efficiency would rather do at youth level.
2) Confer honors and awards to organizations and persons for outstanding performances through events and publicity such as Thailand Energy Awards, green building labeling and innovations.
3) Enhance users’ insight of energy efficient appliances with clear and precise information, technological data, and economic matters for their conclusion and decision-making.
4) Use high energy efficient equipment and appliances instead of the existing low ones.
5) Reward benefactors and fairly punish malefactors.
6) Establish network for sharing experience and innovation to foster co- operation and avoid free riding.
7) Minimize free riders.
Sector | Measures / Programs |
Cross cutting | - Publicity and dissemination of knowledge and information on energy efficiency
- Push concept and practices in low - carbon economy and low-carbon society development
- Fiscal and financial measures to enhance behavior change and awareness in energy conservation and abating greenhouse effect
|
Transportation | - Publicity and dissemination of knowledge on eco-driving
- Push concept and support on sustainable transport systems and improve air quality in urban areas
|
Promotion of Technology Development and Innovation |
|
This strategic approach aims at promotion of domestic technology development and innovation to reduce dependency on foreign sources, by targeting domestic cost portion of Best Available Technology (BAT) at 20 percent of imported technology in the year 2030. The strategy is concerned with research and development of BAT in industrial, commercial, residential and transportation sector, high efficiency and low-carbon equipment and appliances which are generally used.
Under this approach, the updated policy and cutting-edge research will be continuously carried out to keep pace with the direction and target of energy
Figure7 : Energy Efficiency Technology Development Road Map |
|
efficiency implementation. Considering public attitudes and public acceptability, products of R&D have to be successfully passed through strictly verified and standardized testing for a considerable time before moving towards the commercialization stage. The imported technologies, which being researched and demonstrated, need to be critically scrutinized for being suitable for the locals before launching. Additionally, provision of systematic and adequate fund to support the implementation will engage with monitoring and evaluation.
Sector | Measures and Programs |
Cross cutting | - R&D Promotion
- Promotion on high energy performance technology demonstration
|
Large commercial building | 3. Promotion on development of high performance building prototype |
Small commercial and residential building | 4. Promotion on development high performance residential building prototype |
Transportation | - R&D Promotion
- Promotion on high efficiency equipment demonstration
|
Human and Institutional Development and strengthening |
|
Strategic approach in human development targets at the development of Energy Efficiency Professionals in all disciplines, namely Responsible Person under the Energy Efficiency Act, auditor, monitor and inspector, consultant, planner, regulator and promoter.
IEA identified 12 areas of expertise required for effective efficiency implementation (Ref: IEA’s Energy Efficiency Governance, 2010)
- Technical expertise
- Finance expertise
- Private sector practices
- Regulatory expertise
- Statistics analysis capability
- Economic analysis capability
- Marketing
- Behavioral analysis capability
- Training and education
- R&D capability
- Carbon market expertise
- Rural energy expertise
Human development in the past emphasized on technical expertise, due to criteria of promotion and career path of personnel in the industry, which gave more weight to technology. Under this program, human development will cover all disciplines and levels by providing proper education on energy efficiency knowledge, enhancing and accumulating experience to undergraduates, in parallel with implanting energy efficiency knowledge and awareness at school level.
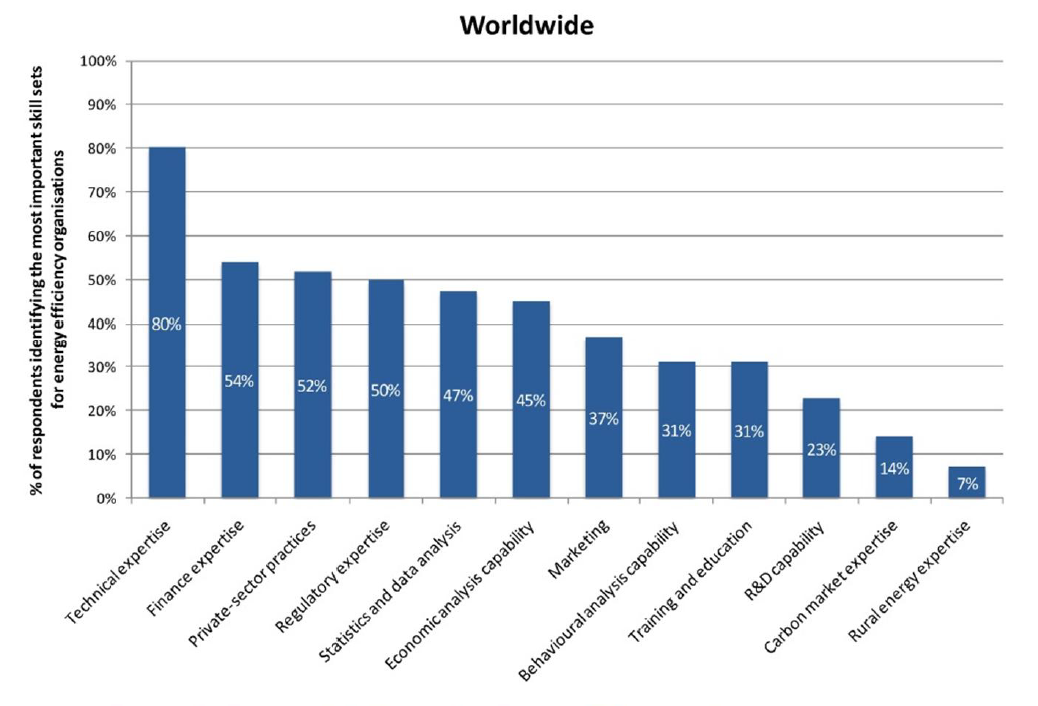
Figure 8 : Essential Skill Sets for Energy Efficiency Organizations |
|
- Institutional Strengthening |
|
Taken into consideration of the IEA suggestion on 12 successful factors for achieving good energy efficiency governance (Ref: IEA’s Energy Efficiency Governance, 2010), the ideal organization should possess
- High leadership
- High skill professional
- Incentive for all levels of management
- Good external relationship and support, particularly high level management in private sector
- Public accepted Strategies Plan and Target
- Good co-operation in implementation of private sector
- Financial Independence (Long and stable source of fund)
- Direct role in co-planning of energy plan
- In hand vast and ample information and data on energy use and energy efficiency potential in relevant economic sector
- Access to public agency co-operation
- International Co-operation
- Role in regulating and inspecting
In practice, it is unlikely that a single government agency can achieve all qualifications due to legal and regulatory implication and constraints. Even those obstacles are eliminated, the effectiveness of single centralized agency with gigantic responsibility is doubtful. As such, this strategy calls for a cluster of the implementing agencies, each dedicated to its own specialization and responsibility enacted by law and work integrally under the guidance and monitoring of the National Committee.
Taken into consideration of the IEA suggestion on 12 successful factors for achieving good energy efficiency governance (Ref: IEA’s Energy Efficiency Governance, 2010), the ideal organization should possess.
Private sector cooperation (7) Monitoring and inspecting (
Responsible Agen
Energy Policy and Planning Office (EPP
Sector | Measures and Programs |
Cross cutting | - Professional development promotion
- Strengthen government and private personnel capability
|
Large commercial building | 3. Promotion of Energy Efficiency Professional in building |
Measure # 1 Enforcement of the Energy Conservation Act |
|
Regulate, promote, and support designated buildings and factories to carry out energy efficiency tasks as stipulated in the Law, intensified enforcement is as much a matter of importance. It is to ensure their compliance with the law. To a greater extent, periodical amendment of the law to keep pace with social and economic evolution has to be done. The projects under this measure include:
- Monitor and regulate energy efficiency implementation of designated buildings and factories under the Law;
- Develop and register energy efficiency management auditors and certifiers;
- Study, revise and amend Act and Decrees, propose an extension of Law jurisdiction to cover all targets, for instance, SME and transportation.
Measure # 2 Mandatory Labeling |
|
Enlist energy efficient equipment and appliances to be mandatory labeled, enforce mandatory labeling and penalize ignorant people, publicize information and organize campaigns to gain acceptance in purchasing high energy performance equipment and appliances.
[...]
Measure # 3 Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) |
|
Measure # 4 Energy Efficiency Resource Standards (EERS) for Large |
|
Establish and enforce MEPS for energy equipment and appliances to be manufactured and sold in Thailand.
Establish standards for electricity utilities to assist consumers in the implementation of energy efficiency to reduce consumption but not supply, enforce implementation of EERS and monitor achievement and raise a standard consistent with the situation.
Measure # 5 Voluntary Agreement |
|
Measure# 6 Promotion and Motivation to encourage Voluntary |
|
Enlarge network of voluntary agreement with definite built-in energy saving target, under government sponsorship, by providing information, fund and publicity to enhance widespread of the network, embracing all groups in commercial and industrial sectors.
Support manufacturing and use of high energy performance equipment and appliances by voluntary labeling and High Energy Performance Standards (HEPS). Establish a target standard of HEPS for each product, time frame,
Measure # 7 Incentives for achieved Energy-Saving Projects |
|
testing and certification, improve standard to match development, disseminate and publicize data and information on efficiency and economy to create awareness and acceptance. Assessment and evaluation amount of labeled products sold annually, as input for considering future public financial support in listing and labeling.
Subsidy, soft loan, partial guarantee, ESCO Fund from the Energy Conservation Fund, and Public-Private Participation raising Energy Trust Fund DSM Bidding for large business, Standard Offer Program (SOP) for small Business.
Tax reduction, based on energy saving performance, for building, industrial, estate developer and investment incentives for equipment and appliance manufactures.
Measure # 8 Support for ESCO Activities |
|
Measures to strengthen ESCO capacity in finance and personnel aspects include:
- Enlarge ESCO fund by encouraging more participation from public and financial institutions to form a dedicated fund for energy efficiency purpose;
- Develop ESCO’s personnel to be high skill professionals, quality and quantity wise, to meet market demand. Provide training courses and curriculum, in cooperation with ESCO businesses.
Measure # 9 Publicity and Dissemination of Knowledge |
|
Publicize and disseminate information on successful cases aiming at behavior change and widespread achievement.
- Publicize high energy performance label
- Compile and select high potential energy efficiency technologies and disseminate knowledge.
- Develop regional technology demonstration centres to become high energy performance equipment and appliances demonstration outlets.
- Disseminate energy efficiency successful cases achieved by building and factory.
Measure # 10 Push Concept and Support for Low Carbon Society / Low |
|
Continue Thailand Energy Awards contest.
Carbon Economy and Environmental Conservation |
|
Measure # 11 Pricing and Taxation to Push Behavioral Change and |
|
Provide financial support to towns and communities that propose city planning and implementation under a low-carbon society concept, emphasizing on energy efficiency such as using mass transit as the main core of transportation and reducing environment effect, en-masse publicity on achievement to target groups and publics, coordinate with relevant parties to enforce implementation.
Implant Awareness on Energy Efficiency & Abating |
|
Energy pricing reflecting the true cost and tax imposition measures will be employed to render effective behavior change and implant deep awareness of energy consumers on energy efficient and abating greenhouse effect, in parallel with alleviation measures for effected consumers. A study on the measures will be carried out not only to establish a proper mechanism, but also to minimize regulatory burden. In other words, the public will not be much burdened with the measure, but it will yield effectiveness of signification behavioral change.
Measure # 12 R&D Promotion |
|
Measure # 13 Promotion of High Performance Energy Efficiency Technology |
|
Provide financial support to energy efficiency policy and technology R&D, which will create high impact, increase self-dependency, and meet industrial commercial residential and transportation sectors, market behavior and environment needs.
Promote and support demonstration of high performance energy efficiency technology by:
- Establish Administration Centre and Co-ordination Working Groups, to foster policy co-operation, research data and information sharing among various agencies and institution;
- Compile and select technologies to be demonstrated, formulate Demonstration Plan on technology which will elevate measure country’s competitiveness;
- Develop infrastructure to serve public-private participated R&D;
- Establish R&D Network;
- Transfer technologies and monitor outcomes.
Measure # 14 Promotion of Energy Efficiency Professionals |
|
Build up capacity of energy efficiency personnel to support implementation of new technologies by:
- Update curriculum of Person Responsible for Energy Efficiency (PRE), as well as technical and practical courses, to keep pace with technology change, and incorporate success cases in other countries as case studies;
- Promote professional energy auditor;
- Develop personnel for each specific industry category.
Measure # 15 Strengthening Institutional Capability |
|
Measure # 16 Benchmarking and Specific Energy Consumption (SEC) |
|
Strengthen the public institutions capability in planning, policy formulation, technology development, implementation (regulate, promote, support) monitoring and evaluation. Build up public personnel capability in modern knowledge and new experiences to improve operation.
Measure # 17 Promotion of R&D on Energy Efficiency Improvement in |
|
Support industries to investigate energy efficient process improvement as the key for industrial restructuring towards lower energy intensity-high value added industry. Benchmarking and SEC will be introduced as the tools to achieve such goal after completion of detailed study.
Promote study on energy efficiency improvement in the industrial process of energy intensive industries. Support replacement of high energy efficiency equipment in industry, study and plan for industrial infrastructure change, based on energy and economy balanced concept, and being suitable for
Thailand in the long run, to maintain country’s competitiveness and economic growth.
Measure # 18 Enforcement of Building Energy Code (BEC) |
|
Measure # 19 Mandatory Energy Labeling in New Large Buildings to be |
|
Accelerate effective enforcement of New Building Code, enacted under Ministerial Regulation, by amending law, regulation and practice to eliminate implementation obstacles. Enhance readiness for enforces, push and promote public and private pilot buildings which are willing to adopt the Code. Provide technical assistance, check and approve construction permit on energy efficiency aspect, study new criteria to improve Code every 3 years and amend the Code every 5 years. DEDE is the implementing agency of this measure.
Measure # 20 Promotion of Energy Labeling in Small Buildings and |
|
Study and establish regulation on building energy efficiency labeling, regulate implementation, evaluate achievement and label high energy efficient buildings. Disseminate knowledge aimed at behavior change in design and construct energy efficient buildings, starting with new government buildings to be constructed, as the evident showcase of public sector’s serious determination in energy conservation.
Promote energy auditing in existing and new, small buildings and houses, particularly, in estate development, label high energy efficiency buildings and houses, organize energy efficient buildings and houses contest, update evaluation criteria and raise standards, continuously.
Measure # 21 Support for Development of High Energy Efficiency |
|
Measure # 22 Promotion of Development of Energy Conservation in |
|
Support the construction of high energy efficiency demonstration building towards Net Zero Energy Building, disseminate knowledge and publicize for widespread implementation.
Measure # 23 Pricing and Taxation to drive Energy Conservation in Small |
|
Promote professional development in designing and checking new large buildings to be constructed or modified, under the Building Code by improving curriculum and arranging learning course for architectures, engineers and relating personnel for insight designing energy efficient buildings, checking and approving construction permits on energy efficiency aspect compliance. Develop and improve helping tools, for instance, a computer program to facilitate fast designing energy efficient buildings in compliance with the law. Drive this subject to be incorporated in educational and professional institutions’ curriculum for widespread effect.
Buildings and Residential |
|
Provide financial and tax incentive measures for small buildings, residential and condominium buyers and developers who use high energy performance appliances in those premises.
Measure # 24 Support for Usage of High Energy Performance Materials, |
|
Establish voluntary network of manufacturers and sales in large department store, providing training in technical and economic knowledge of high energy performance materials, equipment and appliances, provide assisting tool for instance, audio presentation, to facilitate fast deal conclusion and reward top seller;
Measure # 25 Support for Development of Energy Efficient House |
|
Support planning and use of energy efficient lighting system in streets and public areas and advertisement boards.
Measure # 26 Automotive Mandatory Labeling, Energy Efficient Labeling on |
|
Support design and build prototype houses to be demonstrated as models of energy efficient house, disseminate knowledge and publicize aimed at widespread construction, jointly funded by financial institution and public.
Automobile and Parts as information on purchasedecision |
|
Support research on energy efficiency technology to render highest benefit to consumers and country, by:
- Establish working group to study and determine measures, regulations processes and practices in labeling automobile and parts;
- Publicize pilot and demonstration automotive labeling to buyers, with the cooperation of automotive industry for testing car provision;
- Enforce mandatory label and revise the measures to keep pace with technology development.
Measure # 27 Mandatory Minimum Energy Performance Standards |
|
Study regulation, scope, standard, detail and testing procedure of automotive parts, eligible for minimum energy performance standard. Establish testing laboratory for energy efficiency performance automotive parts complying with standard, and impose measures for prohibited sale of poor performance parts.
Measure # 28 Taxation to Create Market Change |
|
Measure # 29 Promotion of High Energy Performance Labeling of |
|
Tax will be used as a tool to create behavior change and awareness on energy efficiency and greenhouse emission reduction gearing toward averting direction in manufacturing and sale of high energy efficient automobile, for instance, registration tax based on automobile fuel consumption.
Measure # 30 Support for Mass Transit and Energy Efficient Freight |
|
Support the development of high energy performance for every automotive parts to enhance overall high performance in automotive, for instance, labeling high energy performance tyre.
Support freight operations to widely employ well planned logistics. Support development of infrastructure to serve energy efficient logistics system in travel and freight business. Support use of mass transit and other energy efficient mode of transportation, including inland waterway, and electric motorcycle.
Measure # 31 Education and Publicity on Eco-driving |
|
Measure # 32 Push Concept and Promote Development of Sustainable |
|
Transport System and Improve urban air quality |
|
Support publicity and campaign on building awareness, training course in eco- driving, and push eco-driving to be a subject in driving license examination.
Measure # 33 Promoting of R&D |
|
Measure # 34 Promoting demonstration of high energy performance |
|
Support R&D on energy efficient automotive parts and accessories as well as energy efficient use of vehicles. Support human resource development in automotive industry through technology transfer of advanced production process and designing experience. Support R&D on energy efficient automotive technology.
Promote demonstration and dissemination of proven high energy performance automotive parts and technology for widespread applications, for instance, GPS, SAT NAV, aerodynamic kits.
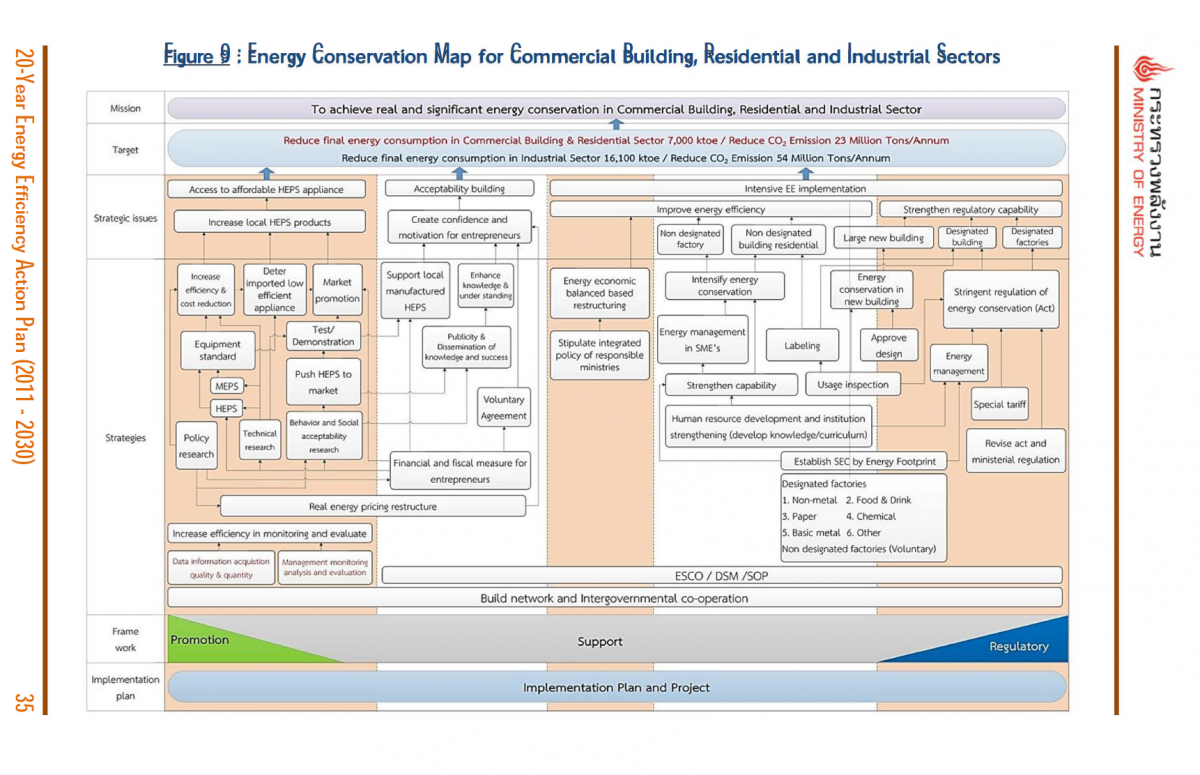
Figure 9 : Energy Conservation Map for Commercial Building, Residential and Industrial Sectors
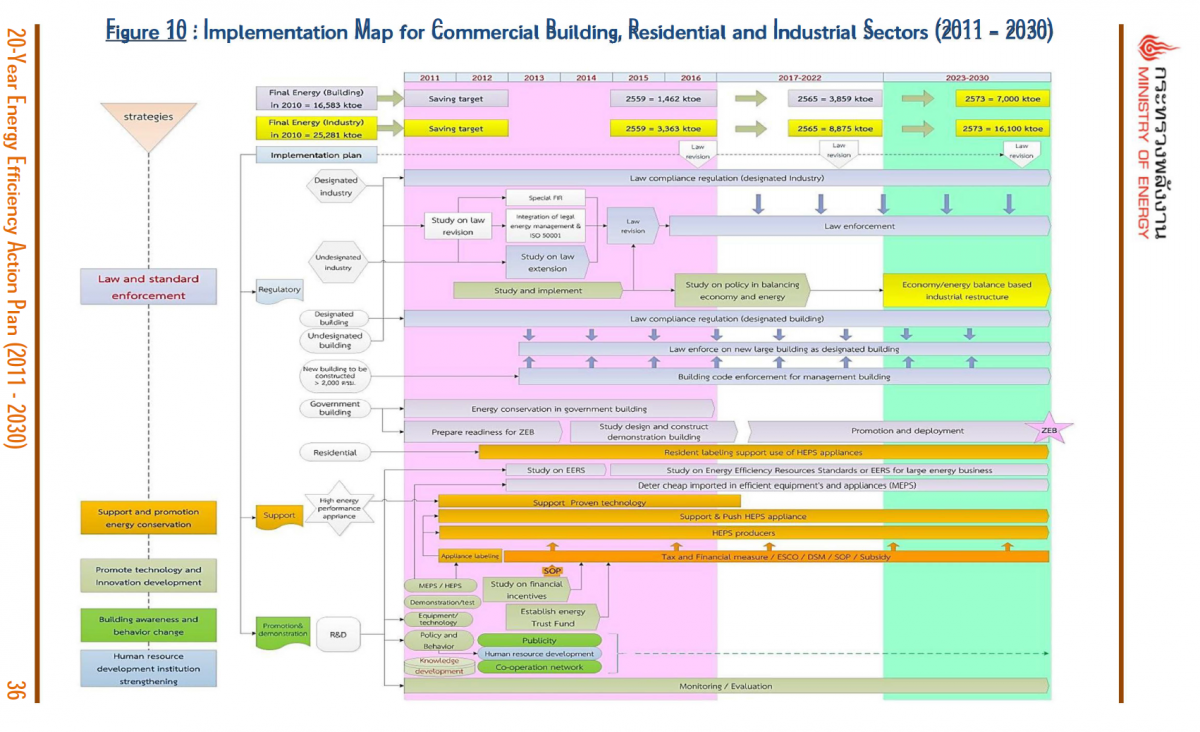
Figure 10 : Implementation Map for Commercial Building, Residential and Industrial Sectors (2011 – 2030)
Figure 11 : Energy Conservation Map for Transportation Sector
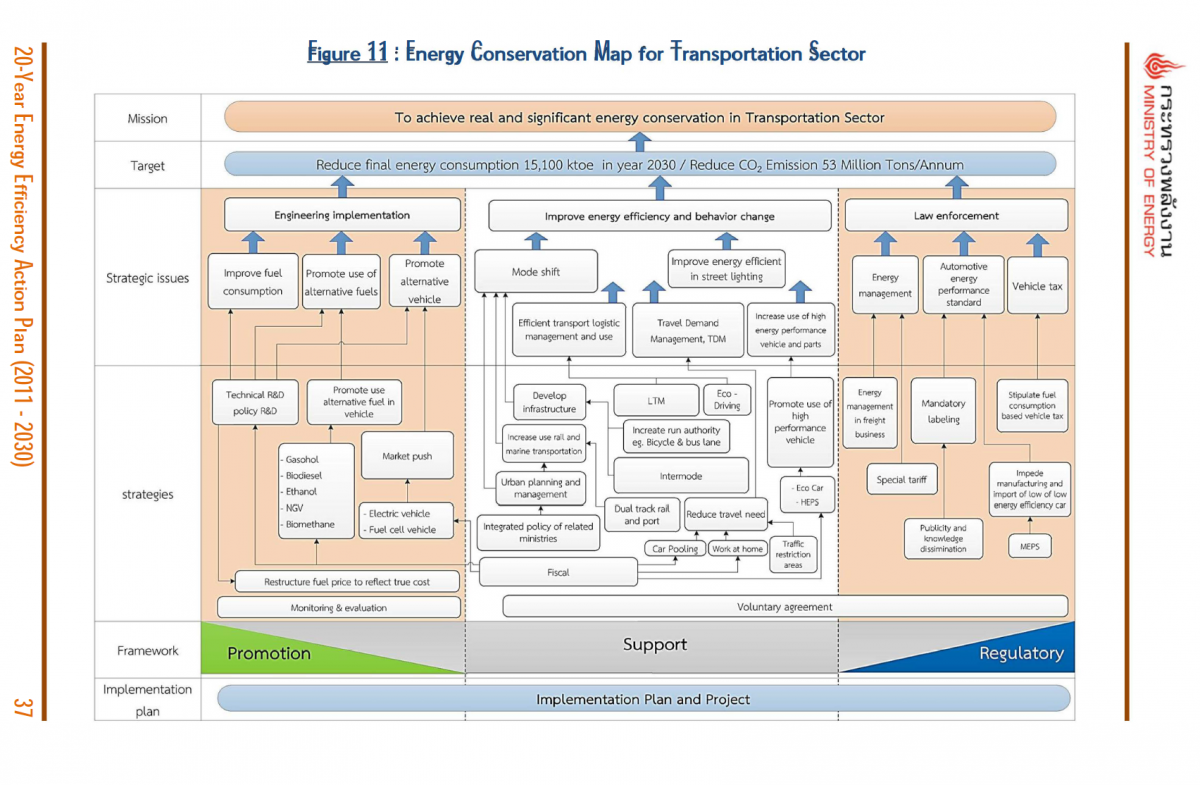
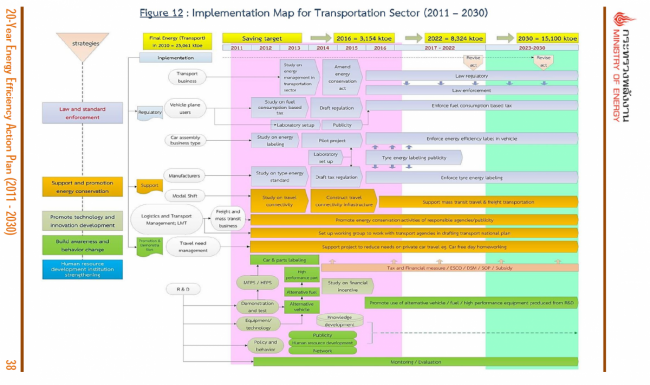
Figure 12 : Implementation Map for Transportation Sector (2011 – 2030)
Estimated Saving under 20-Year EEAP (Demand Side) |
|
Total energy saving implemented under EEAP was estimated at 38,845 ktoe. The industrial sector is the highest saver (41.9%), followed by transportation (39.4%), small commercial and residential building (9.4%), large commercial building (9.3%), respectively. Total financial saving, based on current energy price amounted to 1.11 trillion baht. The transportation sector is the highest saving (52.8%), followed by industrial (26.9%), large commercial building (10.6%), and lastly small and residential building (9.7%) The saving will be higher if energy price increases in the future.
Sector | Saving | Supporting Budget |
(ktoe) | (Trillion Baht) | (Million Baht) | (%) |
Transportation | 15,323 | 0.58 | 13,010* | 10.1 |
Industrial | 16,257 | 0.30 | 69,066 | 53.6 |
Large commercial building | 3,630 | 0.12 | 19,640 | 15.3 |
Small commercial and residential building | 3,635 | 0.11 | 27,024 | 21.0 |
Total | 38,845 | 1.11 | 128,740 | 100.0 |
* Exclude investment in the infrastructure construction of transportation sector such as mass transit, double track railway
[...]
Electricity generation and distribution systems in Thailand have been in usage for a considerable time period. Some of the system becomes aged and efficiency deteriorated. The current generation efficiency is around 39 percent, due to high share of thermal power plant which accounted for over 80 percent of the total. In the year 2011, transformation loss was recorded at 20,996 ktoe or 61 percent of the total consumption. Transmission and distribution loss amounted to 9,749 GWh or 6.3 percent of total generation.
Measure # 1 Energy Efficiency Improvement of Electrical Equipment in |
|
As electricity supply and distribution sector are dominated by public-owned utilities, EEAP on generation and distribution under responsibility of these utilities, are included under this 20-Year EEAP as follows:
Transmission and Distribution System |
|
Transmission and distribution in some areas are aged and need improvement to curb loss and failure risk. Study and the replacement of the existing equipment by high energy performance ones, for instance, high efficiency transformer, larger size cable as well as the investment required and viability will be carried out. EGAT will be responsible for transmission line and substations improvement. MEA plans to acquire Distribution Management System (DMS) while PEA has a plan to improve distribution system and improve islands distribution system using submarine cable to replace diesel fueled standalone sets.
Saving under this measure in year 2030 is estimated to be 172 ktoe and avoids 0.67 million tons of CO2 emission.
Measure # 2 Development of Smart Grid System |
|
Smart grid is the high efficiency transmission and distribution system that can reduce the loss by managing load in different area to match with power generation from various supply sources using a communication system to monitor and manage the enhancement of higher efficiency and reliability of the system. As its implementation scope is quite vast covering supply and load management including energy storage, advanced communication technology and standard, its implementation becomes national issue and requires good coordination and cooperation of various concerning agencies in study and planning.
The Ministry of Energy has already established a committee with members from various utilities to oversee the study on the development of suitable smart grid to fit requirement of all concerning agencies.
Saving under this measure is estimated at 129 ktoe in 2030 (excluding saving from EGAT’s Smart Grid) and avoids 0.83 million tons of CO2 emission.
Measure # 3 Power Generation Improvement |
|
Many power stations have been in operation for a long time, hence their performances deteriorated. Moreover, their technologies are outdated. Refurbishment and overhaul will improve their efficiencies and extend their service life. The cost of such implementation will be cheaper than new plants and causes less social impacts. Saving of this program is estimated at 551 ktoe in the year 2030 with the avoided CO2 emission of 1.73 million tons.
To sum up, total energy saving in a public-owned electricity sector under the 20- Year EEAP amounts to 852 ktoe in the year 2030 with the avoided CO2 emission of 3.23 million tons. The required investment is estimated at 421.74 billion baht, excluding investment of new power plants to replace retired plants under the 2012 - 2030 Power Development Plan.
EPILOGUE : ROAD TO SUCCESS
To achieve energy saving target set forth by the government, the EEAP formulates strategies in three stages, for short term, activities are focused on infrastructure laying and readiness preparation, based on previous proven technologies and implementation programs/projects success. In addition, an amendment of law and regulation will be carried out to eliminate obstacles which impeded achievement in the past, as well as study to raise long and stable dedicated Fund (Energy Trust Fund) under public-private participation approach to support huge investment required for industrial restructure during medium term and long term phases. Implemented plans and projects under medium and long term stage will be the continuity of the successful implementations of the short term stage as well as new potentials derived from the study in the short term phase with emphasis on investment promotion schemes to be completely implemented by all stakeholders.
The success of the 20-year EEAP depends largely on the full integration of strategies, issues, strategies programs and projects as one package. Some particular projects, by themselves may not yield energy saving directly but they will provide infrastructure mechanism to support other programs and projects which will produce significant outcomes to achieve the government’s goal in energy conservation and fulfill international commitments under ASIA PACIFIC economic co-operation in reducing energy intensity and in line with the 11th National Economic and Social Development Plan on moving towards low carbon society.
Energy Policy and Planning Office (EPPO) Ministry of Energy
121/1-2 Phetchaburi Road, Ratchathewi, Bangkok 10400, Thailand Tel 0 2612 1555, Fax 0 2612 1364
Fromoutside Thailand : Tel +66 2612 1555, Fax +66 2612 1364 Official Website : www.eppo.go.th