Executive Summary Water Resources Strategy
Nepal
His Majesty's Government of Nepal Water and Energy Commission Secretariat Singha Durbar, Kathmandu, Nepal
January 2002
Executive Summary
1. Purpose of the Water Resources Strategy
Every Nepali citizen should have access to water sufficient to meet basic needs, including drinking, cooking and sanitation. Every citizen should also benefit from Nepal’s abundant water supply through the production of food and energy at reasonable cost. For decades, Nepal’s economic development efforts have focused on its water resources. Despite these efforts, progress towards meeting the population’s basic water needs and promoting economic growth related to water resources development has been slow. As Nepal’s population grows, demands on existing water increase. These demands, combined with more frequent incidence and risk of pollution and other factors that limit the availability of potable water, increase the potential for future water resource conflicts.
Water Resources Strategy Formulation (WRSF) involves the reconciliation of a range of problems and constraints to sustainable water resource development, including those related to government policies, financial and human resources, institutions and actions. A key objective of WRSF is to identify effective, scientific, sustainable and consensus-based mechanisms to facilitate the implementation of action-oriented initiatives and programs and in doing so, successfully bring about this reconciliation.
With the goal of meeting its water supply needs and achieving long-term sustainability, The Water Resources Strategy will meet this need by providing a systematic framework for water resources development and identifying action plans to avoid and resolve conflicts, and achieve Nepal’s water-related development objectives.
His Majesty's Government through Water and Energy Commission Secretariat (WECS) formulated the first comprehensive Water Resources Strategy of the country under the financial assistance of the World Bank/IDA and CIDA
2. Strategy Formulation Process
WECS used a participatory log-frame approach with a clearly defined hierarchy of objectives, based on an existing policy framework, to formulate water sector strategies. This approach involved development of an overall strategic goal, identification of short-, medium- and long-term purposes to contribute to that goal, and the definition of ten strategic outputs to accomplish these purposes. In the short term (i.e., five years), the Strategy implementation is expected to provide tangible benefits to all Nepalese by improving their access to water sufficient to meet basic needs. The extent of these benefits will gradually increase over the medium term (i.e., 15 years) as sustainable water use and other aspects of the Strategy are realized. In the long term, the Strategy’s goal is to maximize benefits from water resources in a sustainable manner and in doing so, significantly improve Nepalese living conditions.
Several pre-conditions and assumptions relating to Strategy formulation and implementation, external to water sector participants and agencies, must be fulfilled before the targeted outputs can be achieved. Foremost among these pre-conditions and assumptions are:
- The water resources sector and the Water Resources Strategy will receive continued high priority and support from HMG;
- All stakeholders, including political parties, will support the Strategy and its implementation.
To provide the momentum necessary to achieve the Strateg y’s long-term objectives, some output- related activities will need to occur within a relatively short timeframe. Similarly, certain breakthroughs, such as achievement in fulfilling of ‘basic needs’ in all concerned sub-sectors, will need to occur relatively quickly, in order to maintain stakeholder support for the overall process. Socio- economic progress must be such that employment opportunities are created for most of that segment of the population that is of working age and that is actively seeking employment. If such breakthroughs cannot be achieved, serious socio-economic and political crises or flash points could arise that could jeopardize the very existence of the nation-state. A "business as usual" approach is not sustainable.
The next step in the Water Strategy Formulation Process (see Fig. 1) is the preparation of a National Water Plan to guide the implementation of the Water Resources Strategy. This work will be undertaken by WECS in close collaboration with relevant government agencies, institutions and stakeholders, and will involve continued public input. In parallel with the National Water Plan preparation, HMG will formulate a comprehensive Water Resources Policy and other related legislation.
3. Water Sector Needs and Issues
Water is one of the principal natural resources supporting the economy of Nepal. For example, at present, approximately 33% of Nepal’s agricultural production is based on irrigation. The expansion of Nepal’s irrigation systems represents one of the primary means of intensifying agricultural production and increasing food supplies to match future population growth. Similarly, 84% of Nepal’s electricity is currently available from hydroelectric generation. A large increase in hydropower generation capacity would allow Nepal to meet its domestic energy demands as well as increase its revenues by exporting surplus energy to India and other neighbouring countries.
Blessed with a rich but fragile environment, Nepal faces a number of physical and human challenges in recognizing benefits associated with water resources development. The country’s rugged topography, young geology and monsoon climate all combine to produce high rates of runoff, erosion and sedimentation. Human activities have resulted in impacts to Nepal’s forests, soils and terrestrial and aquatic species and habitats. Increasing population pressure and demand for agricultural land often conflict with plans for protection of the natural environment. In urban areas, wastewater, solid wastes and air pollution have seriously degraded living conditions. Poverty and environmental degradation are closely interrelated in Nepal.
The present situation with regard to Nepal’s water resources can be summarized as follows:
- 66% of the population has access to safe water;
- 41% of irrigated land has 'year round irrigation' 1 ;
- less than 400 MW of hydropower capacity is available; and
- Little consideration is being given to environmental requirements.
A summary of consensus- based issues identified by stakeholders during WRSF is shown in Table 1.
1 “Year-round Irrigation” denotes the availability of water when and as required (i.e., demanded) for the optimal use of the land for agricultural production. At present, if the land is subject to over 155% cropping intensity on average, it is said to have year-round irrigation.
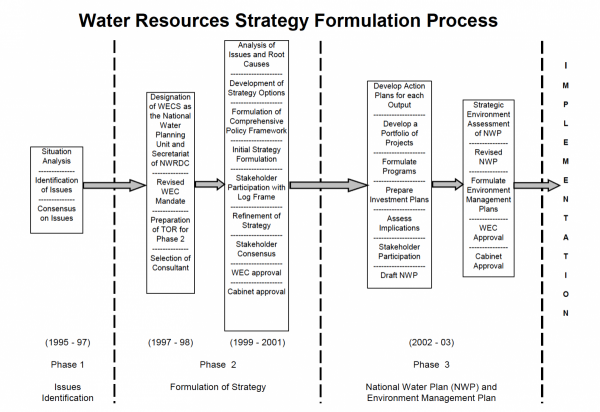
Table 1
Consensus-based Water Sector Issues
Summary of Water Sector Issues |
General Issues - Need for comprehensive water resources policy
- Lack of integrated river basi n planning and management
- Water pricing and cost recovery
- Potential of water transportation – navigation
- Macro- economic implications
| Social Issues - Poverty and malnutrition
- Balanced gender participation
- Appropriate technology for primary target (social) groups
- Hill to Terai and rural to urban migration
- Project impact and resettlement
|
Water Supply and Sanitation Issues - Lack of adequate planning, design and construction of water supply and sanitation projects
- Lack of appropriate approach towards rural water supply system
- Improper management of water supply systems of Kathmandu Valley and other urban centres
- Lack of water quality standards for drinking water
| Irrigation Issues - Reorientation of supply-driven approach
- Poor performance of irrigation systems
- Lack of effective implementation of Agriculture Perspective Plan (APP)
- Farmers' dependency syndromes and sustainability
- Problems of river management
- Weak institutional capability
- Symbiotic relationship between agriculture and irrigation (weak linkages)
- Strengthening of Water User Associations (WUAs)
|
Hydropower Issues - Improving power system planning
- Increasing access to electrification in rural areas
- Encouraging private investment in hydropower
- Reducing cost of development
| Legal Issues - Non-specificity of water rights and ownership
- Lack of sub-ordinate enabling legislation
- Lack of harmony among related legislation
- Lack of adequate legal provisions to encourage private sector participation in multipurpose projects
|
Summary of Water Sector Issues |
Database Issues - Inadequate hydro-m eteorological network
- Inadequate funding and management of existing network
- Inadequate flood forecasting and warning systems
- Lack of regulatory mechanism in hydrogeology and geo- seismology sectors
- Inadequate geo-seismic data and information
| International Issues - Compliance with the provisions stipulated in Kosi and Gandak agreements
- Implementation of the provisions of the Mahakali Treaty
- Formulation of general legal framework for development of trans- boundary rivers
- Absence of mechanism for institutionalized cooperation between riparian countries
|
Environmental Issues - Environmental database and mapping
- Integration of environmental considerations into planning of water resources developments
- Effective implementation and enforcement of environmental impact assessment (EIA) and strategic environmental assessment (SEA) norms and recommendations
- Bio-diversity conservation
- Surface and groundwater pollution
- Lowering of groundwater tables
- Lack of environmental awareness
- Landslides, erosion, sedimentation, glacial lake outburst flood (GLOF), flooding.
- Watershed conservation
| Institutional Issues - Absence of an effective central planning organization
- Blurred responsibilities between policy, implementation, operational and regulatory institutions
- Absence of an institutional framework for coordinated and integrated development
- Jurisdictional overlaps and the challenge of maintaining coordination between public and local bodies
|
- Policy Framework Adopted for Water Resources StrategyFormulation
With key stakeholder input, WECS developed and adopted a set of objectives and policy principles that provide the framework for WRSF. The proposed policy framework, which has been endorsed by HMG as an integral part of the Strategy, consists of a set of water sector objectives, policy principles and development objectives. The goal of water resources development, like that of other types of resource development, should be to improve, or contribute to the improvement of, quality of life for the Nepalese people.
Specific objectives adopted for WRSF include:
- Help reduce the incidence of poverty, unemployment and under-employment.
- Provide access to safe and adequate drinking water and sanitation for ensuring health security.
- Increase agricultural production, ensuring the nation’s food security.
- Generate hydropower to satisfy national energy requirements and to allow for export of surplus energy.
- Supply the needs of the industrial sector and other sectors of the economy.
- Facilitate water transport, particularly connection to a seaport.
- Protect the environment and sustain the biodiversity of natural habitat.
- Prevent and mitigate water- induced disasters.
Policy principles that have guided Nepal’s water sector during WRSF include:
- Development and management of water resources shall be undertaken in a holistic, systematic manner, relying on integrated water resources management.
- Water utilization shall be sustainable to ensure conservation of the resource and protection of the environment. Each river basin system shall be managed holistically.
- Delivery of water services shall be decentralized in a manner that involves autonomous and accountable agencies (e.g., public, private, community and user-based agencies).
- Economic efficiency and social equity shall guide water resource development and management.
- Participation of and consultation with all the stakeholders shall constitute the basis of water sector development.
- Sharing of water resource benefits among the co-riparian countries shall be on an equitable basis for mutual benefit.
- Institutional and legal frameworks for coordination and transparency shall be an essential feature of water sector management.
- Wider adoption of the best existing technologies and practices, and rapid innovation and adaptation of both institutional arrangements and new technologies, shall be ensured.
It is recognized that water resources development needs to be more closely integrated with sustainable social and economic development. Therefore, in addition to the above policy principles, some general guiding principles (i.e., evaluation guidelines) have been established to contribute to the national objectives of social and economic development, and environmental sustainability. These principles are essential to WRSF because each is an inherent component of the Strategy’s ultimate goal.
Social Development Principles
- People who are affected by a project should be encouraged to participate or take ownership, as appropriate.
- Water sector development should directly contribute to improved health and living conditions.
- Water sector development should ensure long-term food security for Nepal.
- Socially and economically disadvantaged/vulnerable groups (e.g., poor, disabled) should be considered for targeted assistance to ensure they benefit sig nificantly from projects.
- There should be more balanced participation of men and women.
- Appropriate technology should be emphasized that is affordable, manageable and cost- effective and that generates local employment opportunities.
- Water resource projects should be integrated with social development, wherever possible.
- Water resources development should strive for more equal balance between rural and urban areas (i.e., rural areas should provide better opportunities for employment and improved living conditions).
- The common property resource system should be maintained and enhanced, or if affected, adequately restored.
- People should be informed and made responsible for managing water efficiently, conserving water, preserving/protecting water sources from degradation and maintaining water quality.
- All people who are adversely affected by a water resource project should be made better off after project implementation.
- Project-induced resettlement should be avoided or minimized; if resettlement is required, adequate and timely compensation and rehabilitation measures should be provided to fully offset social and economic losses and to enable affected people to share in overall project benefits.
Economic Development Principles
- Water resources development should contribute significantly to national economic output.
- Water resources development should be targeted to address poverty alleviation & unemployment.
- Hydropower development should satisfy domestic needs for electricity and an increasing share of national energy requirements, as well as generate export earnings for Nepal.
- Irrigation development should be one of the main inputs in increasing food production.
- The cost of drinking water supply and sanitation should eventually be recovered from the users.
- The economic benefits of water resources development should be shared equitably by region and income groups.
- The cost of water pollution should be borne by the polluters.
- Private sector investment and/or participation should be promoted to provide an increasing share of the required capital and operational capacity in the water sector.
Environmental Sustainability Principles
- Environmental and ecological considerations should be integrated at every level of the development process from policy setting and strategy formulation through project planning, design, implementation and operation.
- Increased environmental awareness, local knowledge and public participation in environmental protection, conservation and management should be essential for the sustainable development of water resources.
- Conservation of biodiversity, endemic, rare and endangered species, and habitats such as forests and wetlands, should be given priority in planning, developing and managing water resources.
- Adequate water quantity and quality is fundamental to human and ecosystem health. Water resource projects should ensure that water quantity and quality meet appropriate standards for human consumption, recreation and irrigation as well as aquatic ecosystems, species and habitats.
- Sustainable development of watersheds and water resources should result in reduced incidence of natural and manmade environmental impacts and disasters such as GLOF, landslides, siltation, flooding, pollution and global warming.
- An ecosystem approach to watershed management that includes consideration of direct and indirect biophysical and social effects and compliance with participatory, comprehensive and rigorous environmental assessment and management should be adopted for sustainable water resources development.
- Water resources development should be optimized through comprehensive identification and evaluation of options and alternatives with the goal of avoiding, rather than finding means of reducing and/or mitigating, environmental impacts to watersheds and aquatic ecosystems.
- As a condition of approval, all water resources development projects should include a fully funded environmental protection or enhancement component to compensate for the project’s environmental impacts.
- Environmentally acceptable water resources development should justify and minimize destruction of productive ecosystems, including forests and wetlands.
- The Siwalik Range and Babar Zone should be protected and managed to improve forest cover, soil conservation and groundwater recharge.
5. Water Resources Strategy
Nepal’s national goal has been defined as “living conditions of Nepali people are significantly improved in a sustainable manner”. The Water Resources Strategy outputs will contribute to this goal through the achievement of short-, medium- and long- term purposes, defined as follows:
Short- term (5-year) Purpose: Implementation of the comprehensive Water Resources Strategy provides tangible benefits to people in line with basic needs fulfillment, supported and managed by capable institutions involving all stakeholders.
Medium-term (15-year) Purpose: The Water Resources Strategy is operationalized to provide substantial benefits to people for basic needs fulfillment as well as other increased benefits related to sustainable water use.
Long-term (25-year) Purpose: Benefits from water resources are maximized in Nepal in a sustainable manner.
The ten strategic outputs required to achieve these purposes are described below. In addition to the key activities associated with each of the outputs, indicators that may be used to evaluate the success of Strategy implementation are identified for 5-, 15- and 25-year timeframes. These targets and dates were derived based on stakeholder consultation and, in some cases, will need to be verified or refined during development of the National Water Plan (Phase 3).
Each output is categorized with reference to a particular aspect of water resources development:
- Security (Outputs 1 and 2) – security from water- induced impacts and secu rity of water supply;
- Uses (Outputs 3 to 6) – types of water use (e.g., domestic water supply and sanitation; irrigation; hydropower; and other economic uses of water such as for industry, tourism, fisheries and navigation); and
- Mechanisms (Outputs 7 to 10) – mechanisms (i.e., regional cooperation, development of water-related information systems and appropriate regulatory frameworks, provision of appropriate institutional support) that enable the benefits of sustainable water use to be realized, enhanced or maximized.
Summary of the strategy output is presented in Table 5.1
Output 1: Effective Measures to Manage and Mitigate Water -Induced Disasters are functional.
Catastrophic events that cannot be controlled can, to some degree, be rendered less dangerous by advance planning and preparation. In addition to preparations for emergency response, rescue and relief, the Water Resources Strategy identifies a number of actions that will be taken to mitigate the effects of water-induced disasters.
Activities
- Prepare and implement a water- induced disaster management policy and plan.
- Conduct risk/vulnerability mapping and zoning.
- Strengthen the disaster networking and information system.
- Establish disaster relief and rehabilitation systems.
- Carry out community awareness/education on disaster management.
- Activate Inundation Committee(s) with respect to neighbouring countries.
- Prepare and implement floodplain action plans.
- Implement disaster reduction/mitigation measures.
- Strengthen institutional set-up and capacity.
Indicators
- by 2007, potential disaster zones identified by type and located on district maps;
- by 2007, emergency relief materials are available in all five regions;
- by 2017, infrastructure for mitigating predictable disasters put in place in 20 districts;
- by 2017, warning systems established and functioning, encompassing the country; and
- by 2027, social and economic losses reduced to levels experienced in developed countries.
The goal during the Strategy’s first five years is to enhance institutional capabilities for managing water- induced disasters. To that end, the Department of Water Induced Disaster Prevention (DWIDP) will be designated as lead agency and given a clear mandate to implement output activities, including the development of a disaster management policy and plan. DWIDP will also be responsible for coordinating efforts to reduce risks and mitigate damages. Other agencies involved in the prevention and management of water- induced disasters will include the Department of Hydrology and Meteor ology (DHM), the Department of Irrigation (DOI), and the Ministry of Home (MOH).
In the following ten years, effective measures will be adopted to better manage and mitigate the effects of water-induced disasters. High-risk areas will be identified and warning systems will be established in locations subject to flooding and landslides. A disaster relief plan will be developed for each priority area and DWIDP and other agencies will assist local authorities in carrying out community awareness and educatio n campaigns. Within 25 years, the Strategy’s goal is to make Nepal’s water disaster management system fully functional, effective and responsive to people’s needs.
Output 2: Sustainable Management of Watersheds and Aquatic Ecosystems Achieved.
Achieving the sustainable development of water resources is one of the most important challenges facing Nepal. Meeting the challenge requires emphasizing the development of the country’s water resources from a holistic perspective that brings environmental considerations into the mainstream of the Water Resources Strategy.
Activities
- Improve environmental database system.
- Map important, critical and priority watersheds and aquatic ecosystems.
- Develop water and wastewater quality standards and regulations.
- Implement a water conservation education programme.
- Utilize strategic environmental assessment in water resources management.
- Ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
- Promote community participation.
- Increase institutional capacity and co -ordination.
Table 5.1
Summary of Strategy Outputs
GOAL | LIVING CONDITIONS OF NEPALI PEOPLE SIGNIFICANTLY IMPROVED IN A SUSTAINABLE MANNER |
TIMEFRAME | 5-Year Strategy | 15-Year Strategy | 25-Year Strategy |
PURPOSE | The comprehensive Water Resources Strategy implementation providing tangible benefits to people in line with basic needs fulfillment, supported and managed by capable institutions of all stakeholders | Water Resources Strategy operationalized to provide substantial benefits to people for basic needs fulfillments as well as other benefits supported and managed by capable institutions of all stakeholders. | Sustainable benefits of water use to Nepal maximized |
OUTPUTS | SECURITY | 1. Disaster Management | Institutional capabilities enhanced to manage water- induced disasters | Effective measures adopted to manage water- related disasters and mitigate their adverse effects | Effective water induced disasters management systems are functional |
2. Environment | Institution strengthened for watershed and ecosystem protection / management | Full scale watershed/aquatic ecosystems activities implemented | Watersheds and Aquatic ecosystems managed sustainably |
USERS | 3. Water Supply | Access to water supply and sanitation expanded / enhanced | With increasing sanitation and drinking water coverage, service level and quality improved | Adequate supply of and access to quality potable water, sanitation and hygiene awareness provided for all people |
4. Irrigation | Irrigation systems planned, developed and continued for sustainable management. | Reliable irrigation service expanded on the basis of sustainability and wealth creation | Appropriate and efficient irrigation available for the optimal use of irrigable land in a sustainable manner |
5. Hydropower | Hydropower developed for domestic needs and viable exports | Hydropower development maximized for different uses (including energy intensive industries and export of power) providing substantial benefits | Hydropower optimally developed |
6. Other Economic Activities | Economic activities for fisheries, aquaculture, recreation, tourism, navigation, and industrial water uses implemented | Economic uses of water and water bodies by recreation, tourism, fisheries, aquaculture navigation and industries enhanced | Economic uses of water and water bodies by recreation, tourism, fisheries, aquaculture navigation and industries optimized |
MECHANISMS | 7. Information Systems | Functional water-related information & Dissemination system strengthened/ established | Water- related information/ dissemination system functioning | Water-related information systems enhanced |
8. Policy & Legal | Appropriate policy and legal framework including equitable water use rights established | Adequate legal framework functioning | Adequate legal framework functioning and adopting to changing circumstances |
9. International Cooperation | Regional/ bilateral cooperation framework/ norms operationalized | Effective mechanism for regional/ bilateral cooperation functioning | Regional/bilateral cooperation for substantial mutual benefits achieved |
10. Institutional Mechanisms | Appropriate institutions established / activated | Institutional mechanism for integrated water management functioning | All Institutions functioning efficiently in tune with changing circumstances |
Note: The long-term Water Resource Strategy envisions a continuous process with some thresholds in between. Broadly speaking, the 5-year strategy is oriented towards fulfillment of basic needs of people, the 15-year strategy is for consolidation of sub-sector programs for maximization of these benefits and the 25-year strategy is for their optimization.
Indicators
- by 2007, management plan for pilot watershed and aquatic system prepared and initiated;
- by 2007, water quality and wastewater quality standards developed and initiated;
- by 2017, full scale environmental protection and management projects implemented in all priority watershed and aquatic ecosystems;
- by 2017, stakeholders participating in environmental protection and management;
- by 2027, quality of watersheds increased by 80% in all regions; and
- by 2027, adequate water quality for aquatic habitat including fish, human consumption and recreation, in all rivers and lakes.
In the next five years, emphasis will be placed on strengthening Nepal’s institutional capacity for watershed and aquatic ecosystem protection and management. WECS will be given a mandate to develop an integrated and centralized environmental database system for information related to water resources development and management. The Department of Soil Conservation and Watershed Management (DSCWM) and the Department of Wildlife and National Parks (DWNP) will be designated as lead agencies for the design and implementation of pilot scale programs in selected watersheds and aquatic ecosystems.
During the following ten years, based on the outcome of these programs, full- scale management activities will be implemented in all priority areas. An important component of this output will be the development of water and wastewater quality standards and regulations, to be carried out by the Ministry of Physical Planning and Works (MOPP&W) with the assistance of a new National Water Resources Quality and Tariff Regulatory Agency. MOPE will be responsible for the development, implementation and enforcement of effective environmental review and assessment mechanisms.
Within 25 years, sustainable management of major watersheds and aquatic ecosystems will be a reality and development projects in all sectors will be expected to fully comply with environmental protection measures identified in project- specific EIAs. In recognition of the importance of community involvement in environmentally sustainable development, the Ministry of Local Development (MOLD) will promote, facilitate and monitor community participation in watershed management and the protection of aquatic ecosystems.
Output 3: Adequate Supply of and Access to Potable Water, Sanitation and Hygiene Awareness provided.
HMG had initially targeted 2001/2002 as the date by which reasonable access to safe water would be provided to the entire population of Nepal. Unfortunately, this goal could not be achieved so quickly. At present, only two-thirds of Nepalese people have access to a basic water supply service. National coverage with respect to sanitation is also very low. The output of the Water Resources Strategy is to provide every Nepali with reasonable access to quality potable water and sanitation facilities, as well as to promote and support hygiene awareness.
Activities
- Enhance institutional capacity for coordination, planning, implementation and monitoring.
- Enact and enforce standards and regulatory mechanisms for water quality and effluent discharge.
- Implement and enforce equitable mechanisms for cost- sharing.
- Strengthen implementation capacity for new rural water supply and sanitation schemes.
- Improve management of urban water supply and sewerage systems.
- Adopt effective conservation and protection measures.
Indicators
- by 2007, 85% of the population will have access to water supply;
- by 2007, 60% of the population will have safe sanitation facilities;
- by 2012, 10 0% coverage of water supply;
- by 2012, 80% of the population safe sanitation services;
- by 2017, 85% of the population will have improved quality water and good service level;
- by 2017, 100% of population will have safe sanitation facilities;
- by 2027, 100% of the population will have good quality water supply; and
- by 2027, all will have safe sanitation facilities.
The HMG has placed priority on increasing water supply coverage throughout Nepal, even at basic levels, over the next five years. Before this can be accomplished, it will be necessary to strengthen the institutional capacity for coordination, planning, implementation and monitoring. As a first step in this process, MOPPW will clearly redefine the respective roles of agencies and stakeholders, includ ing Water Users and Sanitation Committees (WUSCs), involved in the water supply sub -sector. The Department of Water Supply and Sewerage (DWSS) will take on the role of facilitator in support of local institutions responsible for the implementation and management of water supply and sanitation services at the district level. A National Drinking Water Quality Regulatory Board, under the National Water Resources Quality and Tariff Regulatory Agency, will formulate National Drinking Water Quality Standards and regulations. DWSS and the Nepal Water Supply Corporation (NWSC) will assume responsibility for monitoring water quality to ensure that these standards are being met.
In the following ten years, full coverage of drinking water supply and sanitation will be provided at the same time as improvements are being made to existing services. Equitable cost-sharing mechanisms will be developed and implemented to maintain existing water supply schemes and ensure financing for the expansion, rehabilitation and improvement of these schemes. The Strategy describes proposed mechanisms for rural water supply, urban water supply, rural sanitation, urban sewerage and wastewater treatment, and point source polluters.
Over time, NWSC will be restructured and then gradually phased out as ownership of urban water and sewerage schemes is transferred to the municipalities. In addition to adopting effective conservation and protection measures, new sources of potable water will be identified and protected through zoning and the extension of rainwater harvesting for consumptive uses will be promoted. By the end of 25 years, all Nepal ese will be benefiting from the provision of adequate water supply and sanitation, with related health improvements.
Output 4: Appropriate and Efficient Irrigation available to Support Optimal, Sustainable Use of Irrigable Land
Access to irrigation is a critical factor in the maintenance of food security and is key to increasing agricultural intensity and food production on Nepal’s cultivable lands. Its national importance is reflected in the scale of investments devoted to the country’s irrigation projects. In the Ninth Five Year Plan, approximately 13.4% of the national development budget for infrastructure was earmarked for irrigation. Despite government efforts to promote irrigation and agriculture, however, the overall extent of irrigation is limited and agricultural production on much of Nepal’s cultivated lands remains at subsistence levels. At present, only 42% of the country’s cultivated land is irrigated and only 41% of this land is irrigated year-round. In addition to problems associated with obtaining adequate cost contributions and cooperation from the beneficiaries of irrigation projects, agricultural production typically suffers due to low market price for crops such as rice, poor market accessibility, difficulties associated with fertilizer procurement and distribution, and the declining trend in farming as an occupation. The Water Resources Strategy sets out a number of activities that will improve the sustainability of irrigation services and promote agricultural production.
Activities
- Integrate irrigation planning and management with agricultural development.
- Improve management of existing irrigation systems.
- Improve planning and implementation of new irrigation systems.
- Develop year-round irrigation in support of intensification and diversification of agriculture.
- Strengthen local capacity for planning, implementation and management of irrigation.
- Encourage consolidation of land to promote irrigation/agricultural efficiency.
- Improve groundwater development and management.
Indicators
- by 2007, year-round irrigation increased to 50% of irrigated land;
- by 2007, all agency-managed irrigation systems managed jointly with Water User Associations;
- by 2017, year-round irrigation increased to 66% of irrigated land;
- by 2017, 80% of all irrigable land served by irrigation schemes;
- by 2017, APP target regarding irrigation achieved;
- by 2027, 90% of all irrigable land provided with year-round irrigation;
- by 2027, irrigation system efficiency increased to 60% and;
- Nepal’s food security maintained throughout the 25-year strategy period.
For the first five years, the Strategy will emphasize the implementation and promotion of sustainable, efficient irrigation systems, focusing on those projects that will enhance food security and rural employment, and improve the prosperity of individual farmers and rural economies. These projects will be selected and developed based an overall plan for sustainable agricultural development, taking into consideration issues such as the potential for cost- sharing, access to markets, market competition, and risk. A partnership involving the Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives (MOAC), DOI and individual WUAs will be established to develop this plan, support farmers in their cropping decisions, and cooperate in transfer of information regarding soil and water management techniques, respect for other water uses, and facility maintenance. Districts or groups of districts will be assigned responsibility for sponsoring irrigation developments and for jointly coordinating water allocation and management. Strengthening local capacity for planning, implementation and management will assure stronger local ownership and enhance the productivity and sustainability of selected irrigation projects.
In the following ten years, activities will be focused on achieving reliable irrigation services and expansion of these services based on sustainability and the creation of wealth. To improve the planning and efficiency of its new irrigation schemes, potentially viable projects will be assessed and ranked to identify those that are most sustainable, cost- effective and equitable. Where possible, irrigation development will be integrated with multipurpose storage projects and inter-basin transfers. By the end of 25 years, appropriate and efficient irrigation will be available for the optimal use of irrigable land in a sustainable manner.
Output 5: Cost -Effective Hydropower Developed in a Sustainable Manner.
Despite a wealth of water resources and a total potential hydroelectric capacity of 43,000 MW, Nepal’s installed capacity is currently just over 370 MW. Power generation projects currently under construction will increase this capacity by about 240 MW. This poor level of hydropower utilization is due primarily to financial resource constraints and inherent delays in project implementation. Nepal’s electricity tariff rate is considered to be one of the highest in the region and the domestic electricity charge is one of the major cost items in household expenditures. To remedy this situation, the Strategy seeks to develop sufficient capacity to meet domestic needs at affordable prices and to allow for export of electricity to neighbouring countries.
Activities
- Develop cost-effective small (including micro- and mini-) and medium hydropower projects to meet domestic demand at an affordable price.
- Encourage private investment in hydropower development and power distribution.
- Provide increased government support to accelerate rural electrification.
- Integrate improved social and environmental mechanisms into hydropower development.
- Encourage Nepal’s power-based industries and transportation system to create markets for large hyd ropower generation plants.
- Facilitate the flow of funds from the domestic financial sector to the hydropower sub-sector.
- Strengthen institutional and physical infrastructure for power export.
- Promote hydropower research and development.
- Restructure the power utility company.
Indicators
- by 2007, 820 MW hydropower capacity developed to meet projected demand, including 70 MW for export;
- by 2007, laws making national contractors/consultants participation mandatory in all types of projects promulgated;
- by 2007, 25% of households supplied with electricity;
- by 2017, 2230 MW hydropower developed to meet projected demand of 2230 MW, including 400 MW for export;
- by 2017, 38% of household supplied with electricity;
- by 2027, 60% of households have access to electricity; and
- by 2027, Nepal is exporting substantial amounts of electricity to earn national revenue.
In the Strategy’s first five years, emphasis will be placed on identifying and developing cost- effective small and medium hydropower projects that are capable of meeting domestic needs at affordable prices. In the following ten years, substantial benefits will be realized by maximizing hydropower development for different markets, including energy-intensive industries and power exports.
In cooperation with related agencies and project stakeholders, the Department of Electricity Development (DOED) will undertake feasibility assessments and environmental impact assessments, and develop cost estimates to help reduce project uncertainties and improve power system planning. The Nepal Electrical Authority (NEA) will be made more commercially viable through corporatization, management improvements, and the establishment of a separate entity to oversee rural electrification. Policies and mechanisms will be developed to encourage private sector investment and an effective regulatory body with a mandate to address issues such as price-fixing and investment security will be established. The use of Nepali contractors and consultants in hydropower planning, design, manufacturing and construction will be strongly encouraged.
Power-intensive industries such as fertilizer plants, magnesite mines, cement factories and calcium carbide plants will be encouraged to develop generation facilities capable of producing surplus power that could be sold to NEA. To boost the national economy, impediments to hydropower investments by the domestic financial sector will be reviewed and removed. Initiatives involving the use of local, isolated generation as the basis of village and rural electrification will be identified and supported to avoid excessive transmission costs in remote areas. Nepal will continually improve the quality and quantity of its hydropower developments so that it may keep expanding its power exchange capacity with India.
By the end of 25 years, the hydropower potential of the country will be optimally developed. The country will have a total hydropower capacity of 22,000 MW, including 15,000 MW for export, and more than 60% of all households will be provided with electricity.
Output 6: Economic Uses of Water by Industries and Water Bodies by Tourism, Fisheries and Navigation optimized.
In addition to guiding water use for domestic water supply and sanitation, irrigation and hydropower, the Water Resources Strategy will promote and enhance other uses of water (e.g., cultural, tourism, recreation, fisheries and aquaculture, navigation) that can provide business and employment benefits and/or improve the quality of life. Such uses should be compatible with existing water uses and future demands, and should be sustainable and environmentally friendly.
Activities
- Promote water-based cultural, recreational and eco- tourism activities.
- Support bottling of spring water for export and domestic uses.
- Develop productive uses of floodplains.
- Investigate navigation opportunities.
- Enhance fisheries and aquaculture.
- Improve industrial use of water.
Indicators
- by 2007, action plan for fisheries, tourism, industrial and navigational use of water resources prepared and approved, and implementation initiated;
- by 2017, private sector investment substantially improved ;
- by 2027, contribution to Gross Domestic Product (GDP) from these uses has becomes significant and increased overtime; and
- by 2027, opportunities for developing further uses identified.
In the Strategy’s first five years, efforts will be made to identify opportunities for providing long- term benefits to Nepal without compromising other types of water use, and to establish mechanisms to support and control future water resources development. In the subsequent ten years, investments in alternative water use projects are expected to come primarily from the private sector, subject to planning controls over zoning and development designed to protect Nepal’s interests. The Ministry of Water Resources (MOWR) will work with the Ministry of Culture, Tourism and Civil Aviation (MOCT&CA) to develop integrated river basin management plans that will, in turn, improve the confidence level of private sector investors. To safeguard the religious and cultural ethos of the country from being marginalized by materialistic goals, projects that threaten cultural heritage sites will not be pursued without broad -based consensus. Temples and other cultural sites located next to water that possess significant religious value will be protected and maintained in good condition.
Action plans will be prepared and implemented based on feasibility studies regarding water- based cultural, recreational, eco -tourism and other economic opportunities. There will be a thorough review of navigation potential and a decision will be made regarding whether to pursue navigation investments as an aspect of multipurpose water resource projects. MOCT&CA will be responsible for identifying and promoting projects of potential benefit to Nepal. The Ministry of Industry will promote the bottling of Himalayan spring water as an economic opportunity to generate employment and domestic and foreign earnings.
DWIDP will be responsible for assessing the viability of projects propo sed in floodplain areas. Such assessments will be undertaken in the context of the overall river basin and with reference to the local economic development plans. Developments will not be permitted where flood damage risks are too great. MOPPW will explore the potential for navigation projects, including opportunities to link up with navigable rivers in India. In rivers, lakes and ponds that offer good potential, the Department of Fishery will promote fisheries and aquaculture development through the provision of facilities (e.g., cages, hatcheries) and will support the processing and marketing of fish. MOPPW will be responsible for monitoring and regulating industrial water uses to ensure that a reliable supply of water is made available at a reasonable cost, while protecting the sustainability and quality of the resource.
In the long term, other economic uses of water should be enhanced to the point where they are significantly contributing to the national economy, based on Nepalese priorities.
Output 7: Regional Cooperation for Substantial Mutual Benefits achieved.
The cooperation of regional partners is essential to the successful development of Nepal’s large- scale water resource potential and projects capable of supporting multipurpose benefits. Previous experience with regional/bilateral cooperation in water sharing indicates the need for a more confident approach to eliminate anomalies and inequity in benefit sharing. Despite the obvious potential benefits, little progress will be achieved until the countries involved develop a better framework for cooperation. To be successful, all countries must accept that a nation’s right to an equitable share of its own water resources is fundamental. Throughout the Strategy implementation period, Nepal will continue to foster good cooperation with its partners through government and non-government channels.
Activities
- Appraise and understand the water- related needs of neighbouring countries.
- Pursue confidence-building measures with neighbouring countries.
- Implement mutually beneficial development programs.
Indicators
- by 2007, approximately 150 MW of hydropower exchanged with India;
- by 2007, some multipurpose projects agreed to and undergoing implementation;
- by 2007, power trade agreement with India ratified or amended;
- by 2017, expected benefits from treaties and multipurpose projects achieved;
- by 2017, riparian issues between neighbouring nations resolved;
- by 2027, several joint/multilateral water resource development projects implemented and functioning satisfactorily; and
- by 2027, international cooperation agreements and mechanisms for water- sharing available and mutually beneficial.
In its first five years, the Strategy emphasizes the need to develop and implement an improved framework for regional cooperation. Existing water- sharing treaties will be monitored in conjunction with an effective mechanism for ensuring compliance. Nepal will evaluate regional water use demands and the potential for hydropower trade with its neighbours and will continue to explore appropriate treaty mechanisms for equitable sharing of water. The power trade agreement with India will be ratified or amended, as necessary.
In the following ten years, the Strategy anticipates that an effective mechanism will be found to facilitate regional and bilateral cooperation. Expected benefits from multipurpose projects such as the Pancheshwar will be realized, riparian issues between neighbouring countries will be resolved, and effective bilateral agreements for equitable water sharing will be in place. By the end of 25 years, various bilateral and multilateral projects for irrigation, hydropower, transmission grid and navigation will be completed and substantial mutual benefits will be achieved.
Output 8: Enhanced Water -Related Information Systems are functional.
Effective planning and water sector-related management depend on access to up-to-date and reliable data and a method of ensuring that this information is made available to users and institutions in an appropriate form and a timely manner. Nepal’s present information systems, including its hydro-meteorological station network, are unable to support users in their efforts to accurately assess water demands, available supplies and risks. The data that are available have been criticized for providing inconsistent results. To ameliorate this situation, the Water Resources Strategy will establish functional information collection and dissemination systems and upgrade data quality by strengthening the DHM and other relevant institutions.
Activities
- Improve information collection and dissemination mechanisms.
- Extend and upgrade the hydro-meteorological network.
- Develop a snow/glacier hydrology information system.
- Establish basin-wide water accounting systems.
- Integrate water resource databa se with environmental databases.
Indicators
- By 2007, all 120 DHM hydro-meteorological stations are well equipped & operationalized;
- by 2007, Himalaya n Climate Change Study Centre established;
- by 2007, satisfactory dissemination of water quality data achieved;
- by 2017, DHM stations meet World Meteorology Organization (WMO) standards in coverage, and quality data acquisition and dissemination;
- by 2027, high level of satisfaction by public and users of information system achieved; and
- by 2027, number of well-equipped hydro-meteorological stations increased to meet Nepal’s requirement in WMO standards.
With the guidance of DHM, existing data acquisition, collation and dissemination systems will be reviewed and upgraded, as necessary, to improve data accuracy, consistency and reliability. Data and data products will be made available to users in a timely manner. Greater access to reliable, up- to-date information will assist in ensuring the cost-effective and efficient use of water, while the provision of reliable weather forecasts and disaster warnings will enhance public support. Over time, the number of river and stream gauging and meteorological stations will be increased to meet the minimum requirements of accepted international standards. International cooperation will be sought for the development of a Himalayan Climate Change Study Center, to be established under the Department of Hydrology and Meteorology, Ministry of Science and Technology (MOS&T) to foster understanding of global climate change and its effects on freshwater supply. Water balance data will be computed for each of Nepal’s river basins, utilizing appropriate data and modeling techniques. WECS will be given a mandate to develop and maintain an integrated and centralized database for the compilation, storage and retrieval of information related to water resources development throughout Nepal.
Output 9: Appropriate Legal Frameworks are functional.
The legal framework for water use in Nepal must address emerging issues such as water use rights, user conflicts, compensation for reductions in water quality and/or quantity, and the need for improvement in the enforcement of statutory laws and regulations.
Activities:
- Prepare an Integrated Water Resources Policy and amend the Water Resources Act.
- Harmonize and amend conflicting laws and regulations.
- Incorporate legislative provisions for groundwater use and management.
- Improve the enforcement of acts and regulations.
- Establish equitable and functional water use rights.
Indicators
- by 2007, integrated national water policy approved;
- by 2007, conflicting water-related laws amended.
- by 2007, all water-related acts, regulations and policies reviewed and amended;
- by 2017, conflict resolution mechanisms are functional;
- by 2017, 90% of water-related conflicts will be resolved;
- by 2027, full compliance with acts and regulations maintained; and
- by 2027, water- related conflicts decreased and those remaining resolved quickly.
Within the first five years, existing sub- sectoral policies, enabling laws and regula tions will be reviewed and equitable water use rights will be developed to allow the effective implementation of water-related developments. An Integrated National Water Resources Policy will be developed and approved by HMG, and conflicting laws related to water resources development will be harmonized and amended, as necessary. Communication with the general public regarding their water rights and obligations will be improved. In the following ten years, regular monitoring and updating of enabling laws will be carried out to ensure that the legal framework continues to function satisfactorily. Conflict resolution mechanisms will be developed so that the majority of conflicts can be resolved quickly. All individual and community water use rights will be registered and documented and regulatory compliance will be strictly enforced. By the end of 25 years, mechanisms will be in place to ensure that legal frameworks are functioning and able to adapt to changing circumstances. Water-related conflicts will have decreased substantially and those remaining will be quickly resolved.
Output 10: Appropriate Institutional Mechanisms for Water Sector Management are functional.
Traditionally, Nepal’s centralized system of governance sought primarily to satisfy the intere sts of ruling elites, rather than those of the country’s producers, traders and consumers. More recently, with the advent of democratically elected governments, there has been a shift towards community participation and private sector involvement in decision-making. In response, there has been a change in the way government institutions operate, as well as the role played by non-government institutions. Although these changes are viewed as positive, overlapping authority and the lack of coordination among institutions, coupled with the conflicts in relevant legislation, have led to confusion regarding responsibility and accountability. The Strategy identifies five activities intended to address this issue.
Activities
- Enhance planning and implementation capacities of all stakeholder institutions.
- Strengthen WECS as a central planning/coordination agency.
- Re-organize and strengthen concerned government institutions.
- Promote and strengthen water management bodies at the community level.
- Promote private sector participation.
Indicators
- by 2007, WECS designated and empowered to coordinate national level planning for the entire water sector;
- by 2007, rights and duties of all relevant institution at all levels clearly defined and available, and their accountability demonstrated;
- by 2007, 25% of local level projects planned, implemented and managed at the local level;
- by 2007, river basin planning concept agreed to and approved by HMG;
- by 2017, WECS is fulfilling its new mandate and has adequate resources;
- by 2017, 75% of local level projects are planned, implemented and managed by local level agencies with competent staff;
- by 2017, three major river basin planning units established and addressing river basin water issues;
- by 2027, 100% of local level projects satisfactorily planned, implemented and managed by local level agencies; and
- by 2027, all major and medium river basin planning units functioning well by addressing water issues.
During the next five years, existing institutions will be assessed to determine their capabilities and to identify the mechanisms that would allow them to function more effectively. Lead government agencies, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), academic institutions, community organizations and private entities will be promoted and strengthened so that they can take on greater responsibilities in water resources management and development. In particular, WECS will be re-designated as the central water planning and coordinating agency. WECS, in turn, will establish an Information Directorate that will collect, collate, manage and disseminate information, and conduct liaison with other organizations on issues relating to water resources and water use. Planning and implementation processes will be streamlined so that a greater percentage of sector funds reach the beneficiary institutions. In the subsequent ten years, there will be increased emphasis on integrated water resources management, at both the central and local government level. Within 25 years, all institutions will be functioning efficiently with the goal of maximizing the benefits associated with sustainable water resources development.
A complete set of strategic outputs and related activities to be carried out in the short-, medium - and long- term are provided in log-frame format in the Water Resources Strategy, Annex B.
6. Resources Required for Strategy Implementation
Effective implementation of the Water Resources Strategy will require strengthening of Nepal’s human resources capacity at all levels of government, in the private sector and academic research institutions, in user groups and community-based organizations, and in NGOs. The Strategy summarizes human resource development needs in each of these areas with reference to planning, implementation, operation, data collection, research and regulation activities.
Table 6.2 Recommended Institutional Changes
Institution (Relevant Mandate) | Proposed Changes | Actions to Strengthen |
WEC/WECS (integrated water resources management – policy, strategy, coordination and monitoring) | Elevate status and mandate it as central planning / coordinating agency for water resources | - Advice/approval from WEC should be a mandatory requirement for water sector component of the Five Year Plan - Establish a permanent WEC Board |
NWRDC (policy and international water treaties) | None | - None |
National Planning Commission (Member Water) | None | - WECS to liaise closely with NPC |
Kathmandu Valley Water Authority (integrated water resources management – planning, coordination and regulation of water use) | Newly established under the MOPP&W | - Transfer of staff to KVWA - Mandate approved to coordinate water related planning and management |
DWSS (rural water supply and sanitation – planning and implementation of projects) | None. It remains lead agency to coord ination rural water supply and sanitation programmes | - Continue to reorient staff to facilitate community participation and ownership of schemes - Improved coordination of implementation programmes |
National Drinking Water Quality Regulatory Board (water supply and sewerage – licensing and regulation) | Restructur e existing Tariff Commission into a full regulatory body for domestic water supply | - Strengthen mandate to regulate domestic water use, quality, effluents, tariffs, and private operators - Increased staffing and facilities (laboratory) |
NWSC (urban water supply and sewerage – planning, implementation and operation). | Declining role as urban water supply schemes are transferred to municipalities and/or private operators | - None |
Institution (Relevant Mandate) | Proposed Changes | Actions to Strengthen |
DOI (irrigation – planning, implementation and operation) | Re-orientate and transfer of flood control mandate to other departments | - Continue to reorient staff to facilitate community participation and ownership of schemes - Focus on multipurpose project planning and implementation. - Focus on conjunctive use of surface and groundwater resources to achieve year round irrigation status |
Groundwater Regulation Authority (groundwater – investigation, monitoring and regulation) | Convert the existing Groundwater Development Board to a regulating Authority to monitor, regulate and investigate groundwater potential | - Increase capability of staff to license and monitor groundwater use, including water quality - Increase capability of staff to investigate and maintain a scientific database of groundwater aquifers |
NEA (hydropower and electricity – planning, implementation and operation) | Restructure NEA to operate more efficiently and in a compatible manner with private operators | - Corporatization of NEA’s operating units |
Rural Electrification Office/Board (electricity development for rural areas) | Separate unit from NEA | - Improve management capabilities |
Electricity Regulatory Board (electricity regulation and tariff regulation) MOPE (environment policy, approvals and regulation) | Restructuring existing Tariff Commission into a full regulatory body for power sector No institutional changes | - Strengthen mandate to license and regulate generation, transmission, distribution and tariffs - Increased staffing and skills - Adoption of sectoral guidelines proposed by sub- sector agencies - Increased capacity to appraise EIAs, SEAs, Environmental Management Plans (EMPs), Rehabilitation Action Plans (RAPs) , and compliance reports |
Institution (Relevant Mandate) | Proposed Changes | Actions to Strengthen |
DSCWM (watershed management) | No changes but designate as lead agency to protect and enhance watersheds | - Strengthen mandate to control and protect watersheds - Increased funding of programmes to enhance watersheds |
DWNP | No changes but designate | - Strengthen mandate to control and protect aquatic ecosystems - Increased funding of programmes to enhance wetlands and aquatic ecosystems - Strengthen mandate to coordinate disaster prevention and mitigation measures - Transfer flood control responsibilities and staff from DOI - Increased funding for development programmes |
(aquatic ecosystems | as lead agency to protect |
management) | aquatic ecosystems |
DWIDP | Expanded mandate as lead |
(water-induced disasters | agency for all water- related |
investigation, research and | disasters |
planning) | |
DHM (information and warning systems) | Himalayan Climate Change Study Center will also be established. | - Strengthen mandate to provide information and warning systems - Increased staffing, facilities and budget |
DWRCs (licensing of water use and conflict resolution) | Provide mandate for local planning and approvals | - Strengthen mandate to license and resolve water use disputes - Increased staffing and budget |
DOED (promotion and licensing of private sector hydropower) | Restructure to focus on licensing, promotion and studies | - Ongoing capacity building for private sector hydropower promotion |
In addition to improvements in human resources capacity, successful Strategy implementation will involve the provision of adequate funding. Total required investments for Nepal’s water sector over 25 years are estimated to be in the order of Rs. 1000 billion, excluding investments needed to develop sufficient hydropower capacity for export and large multipurpose projects such as Pancheshwar. Approximately 25% of the total required investments are expected to come from the private sector, primarily for hydropower. The remainder will need to be provided by government, with significant donor support.
Priorities for specific projects and investment plans will be set out in the National Water Plan. The Water Resources Strategy identifies the general level of financial commitment that will be required from HMG to realize targeted outputs:
- Increased budget is required to provide and sustain basic levels of water and sanitation. This appears to be an area where government and donor commitments need to significantly increase.
- The budget for the irrigation sub- sector will remain at recent levels but needs to be targeted at projects that provide better economic returns. The emphasis will be on relatively low-cost groundwater development, rather than surface irrigation schemes.
- The investment in hydropower will increasingly come from commercial loans and private sector developers. Hydropower development costs will continue to be borne largely by consumers. Any significant increase in rural electrification coverage will require subsidies and therefore an essential increase in donor financial support.
- Increased funding will be required for other activities, including environmental protection, water-induced disaster prevention and data collection.
- The budget for institutions should remain constant in real terms. Although the Strategy proposes some reduction in the role of traditional line agencies, which will in turn reduce cost burdens over time, additional institutional strengthening is required to support decentralization and improve the regulatory mechanisms critical to the long- term success of water resource objectives.
The technical sustainability of the Strategy’s water resource schemes will depend upon full cost recovery or the provision of significantly higher budgets for subsidizing recurring costs and rehabilitation costs in the water sector.
Water Supply Sub-sector
Users currently only pay tariffs based on the operation and maintenance (O&M) costs of water supply and sanitation schemes. In urban water supply, these tariffs barely cover O&M costs. To improve the sustainability of urban water supply schemes, tariffs will have to be increased to cover capital costs and depreciation. In rural water supply, communities currently manage many schemes so far as operating costs are concerned but they continue to rely on capital investments from central agencies to pay for major repairs and rehabilitation.
Irrigation Sub-sector
HMG has already moved in the direction of full cost recovery for groundwater irrigation with the removal of capital subsidies for tubewells. A concern remains regarding whether this policy will enable sufficient new investments to meet planning targets. Nonetheless, HMG emphasis on groundwater development is certain to improve cost recovery. For surface irrigation, operating costs are low but maintenance costs can be high due to annual infilling of canals by sediment. WUAs have been formed to help recover these costs but no effort has been made to recover the capital costs of these schemes. If HMG is going to continue supporting large surface water schemes, it will have to recover more revenues from project beneficiaries and continue allocating a significant amount of central tax revenues to re-pay loans for these projects. The extent to which HMG can do this will depend upon other sectoral needs and priorities.
Table 7.1 Summary of Capital Investment Requirements (Actual and Required Expenditures - Rs. billion
(excluding large multipurpose projects)
| Existing Capital Expenditures | Planned Capital Ependitures (2000 prices) | Private Sector Share |
Plan Period Investment Category Water Supply & Sanitation - Melamchi water supply - Other Urban water supply - Urban sewerage - Rural water supply - Rural sanitation (latrines) - Other investment Irrigation - Surface schemes - new - rehabilitation - Groundwater schemes - new - rehabilitation - Management Transfer - Other investment Electricity (ex. Exports) Additional Capacity Installed (MW) - Large hydro schemes - Medium hydro schemes - public sector - private sector - Small & micro hydro schemes - Transmission - Distribution (ex. RE) - Rural electrification - Other investment Disaster Prevention - Engineering solutions - Monitoring & warning systems - Studies & investigations Water Transportation - Studies & investigation - Infrastructure Other Water Uses - Tourism and recreation - Fisheries - Other Environmental Programs - Watershed management - Water pollution abatement - Monitoring & enforcement Data Collection & Information - Data collection network - Data analysis - Information dissemination Institutional Strengthening - Central planning agency - Central regulatory agencies - Central line agencies - Public corporations - District level agencies - River basin authorities - WUAs & WMAs - International Commission | 8th Plan | 9th Plan1 | 9th Plan2 | 10th Plan | 11th Plan | 12th Plan | 13th Plan | 14th Plan | TOTAL |
1993-1997 | 1998-2002 | 1998-2002 | 2003-2007 | 2008-2012 | 2013-2017 | 2018-2022 | 2024-2027 | 2003-2027 |
8.6 | 26.5 | 21.2 | 48.0 | 32.0 | 34.0 | 38.0 | 32.0 | 184.0 | 21.0 |
0.0 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 25.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 10.0 | 5.0 | 50.0 | 5.0 |
1.5 | 5.7 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 40.0 | 4.0 |
1.5 | 9.2 | 7.0 | 10.0 | 12.0 | 10.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 50.0 | 0.0 |
4.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 22.0 | 5.5 |
1.0 | 2.7 | 1.4 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 13.0 | 6.5 |
0.6 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 9.0 | 0.0 |
17.4 | 24.8 | 14.7 | 24.0 | 32.7 | 22.0 | 26.5 | 40.7 | 145.9 | 20.8 |
13.6 | 21.1 | 9.5 | 16.5 | 24.8 | 14.0 | 20.4 | 34.6 | 110.4 | 7.1 |
(8.6) | (10.4) | (3.4) | (7.6) | (15.9) | (5.1) | (17.9) | (32.1) | (78.5) | (3.9) |
(5.0) | (10.7) | (6.0) | (8.9) | (8.9) | (8.9) | (2.5) | (2.5) | (31.8) | (3.2) |
2.3 | 2.7 | 3.8 | 6.1 | 6.1 | 6.1 | 3.9 | 3.9 | 26.0 | 13.7 |
(2.3) | (2.7) | (3.8) | (5.7) | (5.7) | (5.7) | (1.0) | (1.0) | (19.1) | (9.6) |
(0.0) | (0.0) | (0.0) | (0.4) | (0.4) | (0.4) | (2.9) | (2.9) | (6.9) | (4.1) |
1.0 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 5.0 | 0.0 |
0.5 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 4.5 | 0.0 |
20.7 | 122.7 | 69.0 | 72.0 | 63.0 | 111.0 | 118.0 | 132.0 | 496.0 | 206.7 |
13 | 293 | 285 | 230 | 400 | 500 | 500 | 600 | 2230 | 59% |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
7.4 | 100.5 | 49.0 | 45.0 | 29.0 | 70.0 | 70.0 | 84.0 | 298.0 | 175.0 |
(3.2) | (38.4) | (33.0) | (26.0) | (13.0) | (28.0) | (28.0) | (28.0) | (123.0) | (0.0) |
(4.2) | (62.1) | (16.0) | (19.0) | (16.0) | (42.0) | (42.0) | (56.0) | (175.0) | (175.0) |
0.5 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 13.0 | 6.5 |
0.6 | 4.7 | 5.0 | 8.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 48.0 | 16.0 |
3.3 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 17.0 | 4.3 |
2.0 | 7.8 | 6.0 | 10.0 | 15.0 | 20.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 95.0 | 0.0 |
7.0 | 7.4 | 7.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 25.0 | 5.0 |
1.5 | 0.0 | 3.5 | 6.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 56.0 | 0.0 |
1.0 | | 2.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 33.0 | 0.0 |
0.0 | | 1.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 14.0 | 0.0 |
0.5 | | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 9.0 | 0.0 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 6.0 | 5.0 | 13.5 | 0.0 |
0.0 | | 0.0 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 3.5 | 0.0 |
0.0 | | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 10.0 | 0.0 |
0.3 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.7 | 2.8 | 4.0 | 10.0 | 9.6 |
0.2 | | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 6.8 | 6.8 |
0.1 | | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 1.7 | 1.3 |
0.0 | | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
2.0 | 0.0 | 2.0 | 8.0 | 11.0 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 55.0 | 2.1 |
2.0 | | 2.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 24.0 | 0.0 |
0.0 | | 0.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 21.0 | 2.1 |
0.0 | | 0.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 10.0 | 0.0 |
0.6 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 2.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 17.5 | 3.9 |
0.3 | | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 9.0 | 1.8 |
0.2 | | 0.2 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 5.0 | 1.3 |
0.1 | | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 3.5 | 0.9 |
5.6 | 1.1 | 6.1 | 10.8 | 10.4 | 6.2 | 5.1 | 3.2 | 35.7 | 0.0 |
0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 2.3 | 0.0 |
0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 4.3 | 0.0 |
2.0 | | 2.0 | 2.0 | 1.5 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 5.5 | 0.0 |
2.0 | | 2.0 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 5.0 | |
0.2 | | 0.5 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 10.0 | 0.0 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 3.5 | 0.0 |
0.3 | | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 4.0 | 0.0 |
0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 1.1 | 0.0 |
Total Capital Investment | 56.7 | 175.1 | 117.6 | 172.3 | 164.6 | 201.4 | 227.4 | 247.9 | 1013.6 | 264.1 26% |
Notes: 1. Target 2. Estimated Expenditures ( ) Signifies a sub-total
Sources: - "Economic Survey 1999/2000", Ministry of Finance, May 2000 (figures are adjusted to 1998/99 value).
- "The Ninth Plan (1997 - 2002)", National Planning Commission, July 1998.
- "Corporate Development Plan - FY 2000/01 to FY 2004/05", Nepal Electricity Authority, December 2000.
- WRSF Consortium Report, Annex 5: Irrigation, December 2000.
- WRSF Consortium Report, Annex 6: Water Supply and Sanitation, December 2000.
- WECS estimates.
Figure 7.1 Nepal's Water Sector Investment Requirements
Hydropower/ Electricity Sub-sector
During the past five years the hydropower sub- sector has been moving closer to full cost recovery and as a result, tariffs have risen significantly. Nonetheless, the need for higher tariffs is consistent with the large amounts of investment required in generation, transmission and distribution to meet domestic demands and increase access to electricity. The introduction of private sector investment will reduce the burden on government but in the short term, consumers will continue to pay higher tariffs for electricity. In the longer term, there will be benefits from older plants and economies of scale that will make electricity more affordable and competitive with other forms of energy. As for rural electrification, it will have to be subsidized by all consumers because the costs are going to remain higher than expected revenues from rural customers for many years.
Other Water Sub-sectors
Annual costs for environmental protection, water-induced disaster prevention, data collection and institutional requirements will continue to be managed through the central government’s recurring budgets. In the case of commercial fisheries, water-related tourism and other industrial water uses, it is anticipated that full cost recovery will be achieved by the private sector.