NOTE: Some content may not display correctly, including tables and figures. See PDF for full details.
Ministry of Power & Energy
Sri Lanka Energy Sector Development Plan
For a Knowledge-based Economy 2015-2025
‘Guide the nation in all its efforts to become an energy self-sufficient nation by developing full potential of renewable and other indigenous energy resources while achieving maximum energy conservation through exploration, facilitation, research & development and knowledge management’
Message of the
Minister of Power & Energy
Hon. Patali Champika Ranawaka, M.P.
Sri Lanka has now embarked on a challenging task of entering into a new energy era. This will be a long journey with full of challenges. With the resolution, steadfastness and dedication we should overcome the obstacles on the way.
A long journey has just begun. We cannot expect success at every corner but strive hard to achieve set targets. Our entrepreneurs now must invest and look for more opportunities in this equitable and transparent environment.
We have set an ambitious goal of 100% energy self-sufficiency by 2030. As a developing economy the challenge ahead of us is enormous and I am convinced that we can reach this goal if we set our priorities right and adjust our actions along the way. I hope this “Sri Lanka Energy Sector Development Plan for a Knowledge-based Economy, 2015-2025” will help us to re-structure the energy sector of Sri Lanka.
Message of the
State Minister of Power and Energy
Hon. Palitha Range Bandara, M.P.
The Ministry has embarked on an ambitious action plan to provide reliable and quality electricity access to every citizen in Sri Lanka within this year.
Sri Lanka Energy Sector Development Plan for Knowledge – based Economy, 2015-2025 places a strong emphasis on energy security from both national and individual perspectives. The Plan envisions a situation wherein reliable, affordable, and clean energy will be made available to all citizens at all times. This requires multi – billion investments both from the public and private sectors. Many actions in diverse areas need follow-up and I hope that the business community in Sri Lanka will actively participate in the process of Implementation of this plan.
Our Vision
Energy Security of the Nation is assured…
Our Mission
Provide quality, reliable, sustainable and affordable energy for economic prosperity of the Nation
Introduction
Sri Lanka is on the path towards becoming an internationally competitive middle-income country. This power and energy sector development plan is aligned to the country’s development drive, and has been prepared to provide affordable, high quality and reliable energy for all citizens, rich or poor, equally by conserving country’s precious natural environment, giving priority to the indigenous energy sources, and minimizing regional disparities in energy service delivery. The power and energy sector vision is to capture the full potential of all renewable and other indigenous resources in order for Sri Lanka to become a nation self-sufficient in energy.
The total energy requirement of the country was around 11,125 ktoe in 2013, and the primary energy supply mainly consisted of 4,814 ktoe of biomass , 4,582 ktoe of fossil fuels, and 1,442 ktoe of hydro. Accordingly, 56% of total energy consumption is from indigenous (biomass + hydro), and Sri Lanka has to import fossil fuels to meet the balance. This requires importing 02 MMT of crude oil, 04 MMT of refined petroleum products and 2.25 MMT of coal to the country annually, costing approximately USD 5 billion in foreign exchange. The average annual total bill of imported fossil fuel is therefore 25% of our import expenditure, and nearly 50% of total export income. Therefore the power and energy sector has a huge bearing on the country’s balance of trade and exchange rates.
Sri Lanka has already achieved a grid connectivity of 98%, which is commendable by South Asian standards. Current total installed power generation capacity of the country is approximately 4,050 MW, consisting of 900 MW of coal power, 1,335 MW of oil burning thermal power, 1,375 MW of hydro power and 442 MW of non-conventional renewable energy sources such as wind, mini hydro, biomass and solar power plants.
The annual total electricity demand is about 10,500 GWh, comprising of 38% from domestic consumers, 39% from industries and 20% from commercial enterprises, with the balance coming from other sectors such as religious organizations and street lighting. The overall annual demand for electricity is expected to increase by around 4-6 %, a number constrained by high prices.
The annual total electricity demand is about 10,500 GWh, comprising of 38% from domestic consumers, 39% from industries and 20% from commercial enterprises, with the balance coming from other sectors such as religious organizations and street lighting.
The transport sector is also an important pillar of the economy. A sustainable transportation system contributes towards better socio-economic development by increasing rural connectivity and sustaining an efficient and clean urban environment. As shown by studies conducted in the recent past, the transport sector is the highest contributor to
GHG emissions with a share of about 48% of all CO2 emitted from fossil fuel combustion. In 2013, out of a 5.2 million total vehicle fleet, the number of two wheeled and three wheeled vehicles was 3.6 million, which is expected to increase with higher economic development, posing both financial and environmental challenges in the future.
In this context, it is clear that a strategic balance between the national energy demand and supply has to be maintained with a long term perspective, in order to support a steady economic growth in Sri Lanka. With one of Sri Lanka’s primary resources being her human capital, this sector development plan for a knowledge based economy has primarily developed to meet energy demand through renewable and other indigenous energy resources, and their potentials towards a “green” economy, energy conservation measures for its sustainability, measures for energy security, financially and economically justifiable pricing policies for electricity and petroleum products, research and development
initiatives, and importantly management and good governance practices for the sector. These initiatives will ensure that consumers and businesses are not unduly vulnerable to external market factors, and that the economy can benefit from a secure and affordable energy supply. Sri Lanka will be elevated to a regional hub by increasing its refinery capacity and utilizing the gas and condensate discoveries in the Mannar basin to create and meet domestic demand as well as to supply international oil and gas markets. Development of a natural gas processing plant in Norochcholai and an oil storage and trading centre using the Trincomalee tank farm are part of this strategy. Large scale deployment of renewable energy will further increase the resilience of Sri Lanka’s energy supply, with a large scale wind farm in Mannar and a wide spread network of fuel wood exchanges being some planned Green initiatives.
The power and energy sector of Sri Lanka is looking forward to an energy self-sufficient nation by 2030.



Energy Sector Targets:
i) To make Sri Lanka an energy self-sufficient nation by 2030
ii) Increase the share of electricity generation from renewable energy sources from 50% in 2014 to 60% by 2020 and finally to meet the total demand from renewable and other indigenous energy resources by 2030.
iii) Increase the electricity generation capacity of the system from 4,050 MW to 6,400 MW by 2025.
iv) Generate a minimum 1,000 MW of discovered in Mannar basin by 2020electricity using indigenous gas resources.
v) Increase generation capacity of low cost thermal power plants fired by natural gas and biomass to 2,000 MW to reduce the generation costs and to diversify generation mix by 2020.
vi) Provide affordable electricity coverage to100% of the people of the country on a continuous basis before end 2015.
vii) Reduce the technical and commercial losses of the electricity transmission and distribution network from 11% to 8% by 2020.
viii) Reduce annual energy demand growth by 2% through conservation and efficient use.
ix) Reduce annual energy demand growth by 2% through conservation and efficient use.
x) Produce the total petroleum product demand of the country through our own refinery by 2025.
xi) Upgrade quality of Gasoline and Diesel to EURO IV and EURO III respectively by 2018.
xii) Further enhance the quality and reliability of electricity and fuel supply.
xiii) Broadening energy sector investment windows to include bonds, debentures, public private partnerships and other such novel financial instruments.
xiv) Reduce the carbon footprint of the energy sector by 5% by 2025.

Thrust Area | 01
Integrated National Energy Policy Formulation
A conscious effort will be made towards the economic consolidation of the energy supply of the country by exploiting all opportunities available. Domestic natural gas will be mainstreamed as the fourth fuel in the electricity generation and transport energy diversity will be pursued through electrification of both rail and road transport. Further economic opportunities in cross-border energy trading will be explored and gainfully utilized. Conversion of oil burning power plants to operate on natural gas, repowering of hydropower plants and revamping the petroleum refining and distribution sectors will be approached to further consolidate the energy security and resilience of the supply. Internationally competitive pricing policies to commercialize oil and gas discoveries, as well as a cost-based domestic pricing structure will also be introduced.
Strategies:
- Ensure optimum fuel diversity in electricity generation.
- Develop indigenous energy resources to the optimum level.
- Develop indigenous energy resources to the optimum level.
- Promote shifting the preferred fuel choice in the transport sector from Liquid Petroleum to Electricity & Gas with the intention of reducing dependence on imported petroleum products.
- Encourage viable cross-border energy transfer and cooperation with neighbouring countries.
- Provision of a basic electricity connection to 50, 000 customers who are in remote Locations through renewable energy solutions.
- Provision of electricity to remaining 126, 000 rural homes without electricity through grid connected Rural Electrification schemes.
- Implement a transparent pricing methodology and periodic revision mechanism.
- Rationalization of Net Metering tariff.
- Special off-peak tariff for irrigation of agricultural land.
- Special off-peak tariff for charging electric vehicles for domestic customers.
Thrust Area | 02 A Cleaner Future through green energy
The vast renewable energy resource base of Sri Lanka will be developed to increase the dominance of indigenous energy in both electricity and thermal energy supplies. This initiative will cover the whole value chain of the electricity sector from electrification of remote locations through off-grid solutions to large scale infrastructure development to absorb wind, solar, remaining hydro and other renewable energy resources based power generation to the national grid. Investment climate will be improved to encourage and develop the markets for small scale green energy systems for SMEs and state sector and also to ensure a stable market for fuel wood through a guaranteed price.
Strategies:
- Develop the renewable energy portfolio in the generation mix to an optimum level.
- Establish a competitive bidding process for large scale wind and solar power generation projects.
- Promote grid connected small renewable based power generation through net-metering.
- Promote use of biomass by elevating its use as a modern, convenient energy source.
- Promote off-grid renewable energy applications for small/medium scale applications.
- Integrate the environmental protection and climate change issues with the energy sector development plans.
- Reduce the carbon footprint of energy sector to address global warming and climate change impacts
Key Programs
- Establishment of a fuel wood exchange
- Rehabilitation/ refurbishment old hydro power plants
- Establishment of a natural gas processing facility in Norochcholei
- Development of grid connected large scale wind and solar power
Thrust Area | 03 Conservation and efficient use of energy- a national priority
Efficiency of the energy supply and use will be improved across the many value chains of the country, starting from the petroleum refinery and power plants through the transmission and distribution and at final end user levels. The whole nation will be engaged in this effort through a nationwide awareness campaign. Energy conservation and efficiency improvement opportunities in electricity transport and thermal energy systems will be exploited using newer technologies ranging from Time of Use meters to combined heat and Power and tri-generation and bus rapid transit systems to advanced intermodal transport solutions. Through these efforts, a 10% reduction in total energy demand will be realized by 2020.
Strategies:
- Enhance the efficiency of power generation and petroleum refinery facilities
- Reduce electricity network losses and petroleum distribution losses to acceptable norms.
- Promote energy efficient modes of transport
- A conscious effort to reduce the energy sector carbon footprint.
- Improve end-user efficiency of electricity and petroleum products
- Promote sustainable and environmentally friendly building concepts in urban development.
Key Programs
- Energy Conservation in transport, industrial and commercial sectors
- Standardization/Automation of street lighting
- Introduction of Time of Use meters and Tariffs
- Smart cities and green buildings
- Sustainable energy zone programs
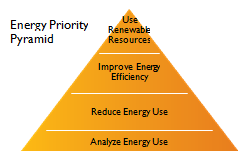
Thrust Area | 04 Customer Satisfaction in service and quality
A complete overhaul of customer interfaces in all energy delivery points will be made to change the customer perception of the energy sector. Quality of supply will be ensured by adhering to a scheme of stated quality standards, whilst developing the sector professionals to meet the new level of service quality. Novel ICT solutions will be used to enhance the customer service and to diversify the payment options available in electricity and petroleum distribution.
Strategies:
- Introduce service quality standards
- Maintain supply quality standards
- Establish/update equipment standards to quality and reliability of energy services
- Capacity building of energy sector professionals to meet challenges in the emerging competitive environment.
Key Programs:
- Smart Meters and advance payment mechanism
- Pre-paid card facilities for electricity bill payment and fuel payment
- Loyalty card for bulk fuel purchases
- Use of mobile telephone base applications
- Introduction of a supply service code for power sector
- Declaration of Rights and Obligations of Electricity Consumers
- One day service for new electricity connections
- A responsive breakdown service
- Establishment of an ombudsman service for customers
Thrust Area | 05 Timely development of infrastructure
In view of the all role played by the energy systems in long term economic development of the country, early action will be taken to secure central locations and corridors for energy infrastructure facilities. Petroleum transfer facilities and power transmission facilities will be enhanced and new infrastructure for natural gas will be established on a timely basis.
Strategies:
- Strengthening of the electricity transmission network to meet additional generation capacity
- Rehabilitation of the petroleum transfer network
- Centrally locate major utilities and secure backbone corridors for future utility infrastructure.
- Enhancing and construction of new electricity transmission lines as the transmission expansion plan of CEB.
- Develop a natural gas transmission and distribution network.
Strategies:
- Strengthening of the electricity transmission network to meet additional generational capacity
- Rehabilitation of the petroleum transfer network
- Centrally locate major utilities and secure backbone corridors for future utility infrastructure
- Enhancing and construction of new electricity transmission lines as the transmission expansion plan of CEB
- Develop a natural gas transmission and distribution network.

Thrust Area | 06 Efficient energy sector institutions and good governance
The sector utility governing structure will be revamped through an enhanced regulatory framework, where customer rights, satisfaction and service quality will be the hallmarks. Transparency, efficiency and competence will be the pillars of support in the new sector governance strategy.
Strategies:
- Introduce effective regulation in both upstream and downstream energy sectors
- Create an open, transparent investment climate with protection to all stakeholders
- Encourage diversity in all areas of energy supply and delivery for maximum economic benefit through competitive maker mechanisms for the benefit of the consumer
- Monitor service and supply quality
- Implementing a transparent pricing methodology and periodic revision mechanism
- Eliminate legal hindrances to sectoral development activities (e.g. way leave clearances)
- Empower energy sector institutions by removing inefficient rules and practices.
Key Programs:
- Introduction of e-procurement system
- Enhancement employee performance through Balanced Scorecard system
- Implementation of 5S and ISO systems for productivity enhancement
- Introduction of e-governance for all energy sector institutions
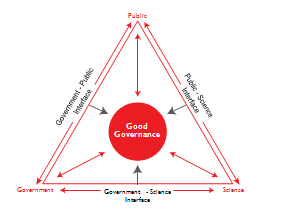
Thrust Area | 07 Innovative financing for a diverse energy sector
The financial health of the energy sector will be improved through efficient treasury operations by restructuring debt portfolios of the sector entities using innovative mechanisms and tools ranging from trade debtors and public private partnerships in investments.
Strategies:
- Explore and adopt Innovative means of energy infrastructure financing
- Introduction of efficient treasury operations
- Reducing the cost of finance by introduction of new financing tools such as issuance of Bonds/Debentures/shares etc.
- Reviewing existing credit policy
- Restructuring CEB/CPC loan portfolio
- Competitive financing markets
- Implementation of Asset Management policy effectively.
Key Programs:
- Issuance of debentures and institutional bonds (CPC bonds-USD 2 billion and CEB debentures –USD 500 million) for restructuring of debt portfolios
- Financial restructuring of CEB and CPC
- Introduce concessionary loan schemes for low income electricity customers
- Introduce concessionary financing for small renewable energy systems
- Introduce loan schemes for large and medium scale renewable power development
Thrust Area | 08 Investment in R&D for cutting-edge product development
Available opportunities in product development and service delivery will be exploited to develop home grown technologies in energy conversion, storage, and delivery, metering and billing to enhance the stake of renewable energy, carbon emissions avoidance and efficiency in the energy systems.
Strategies:
- Establishment of a consultancy arm for energy sector projects
- Encourage to develop standard high-tech instruments
Key Programs:
- Peaceful applications in Nuclear Energy for Agriculture, Human health, Environment and Industry
- Electricity charging stations
- Smart Meters and ICT solutions for energy sector transactions
- Develop local capacity in renewable energy technologies and energy efficiency improvement technologies.
Our Investment Program
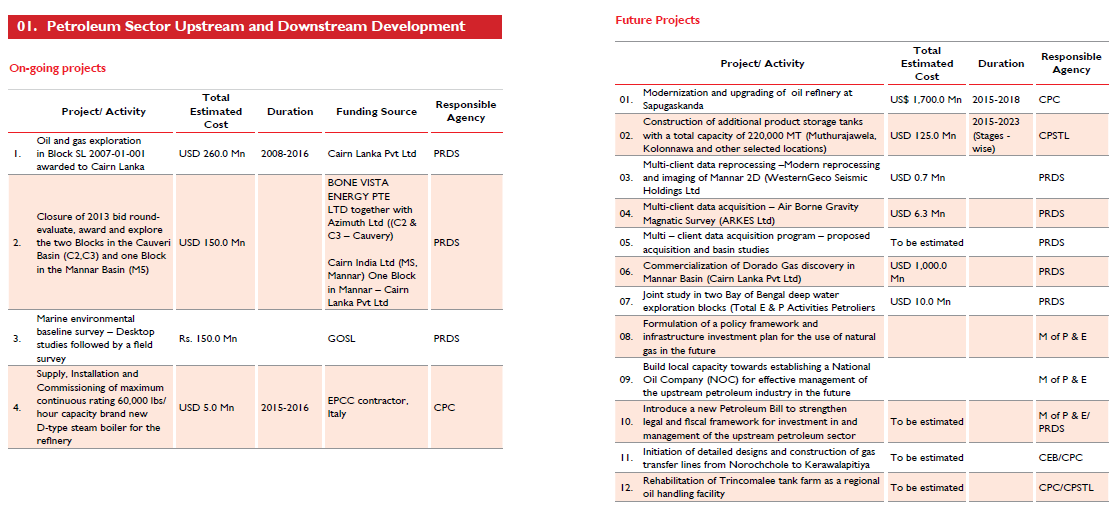
Petroleum Sector Upstream and Downstream Development |
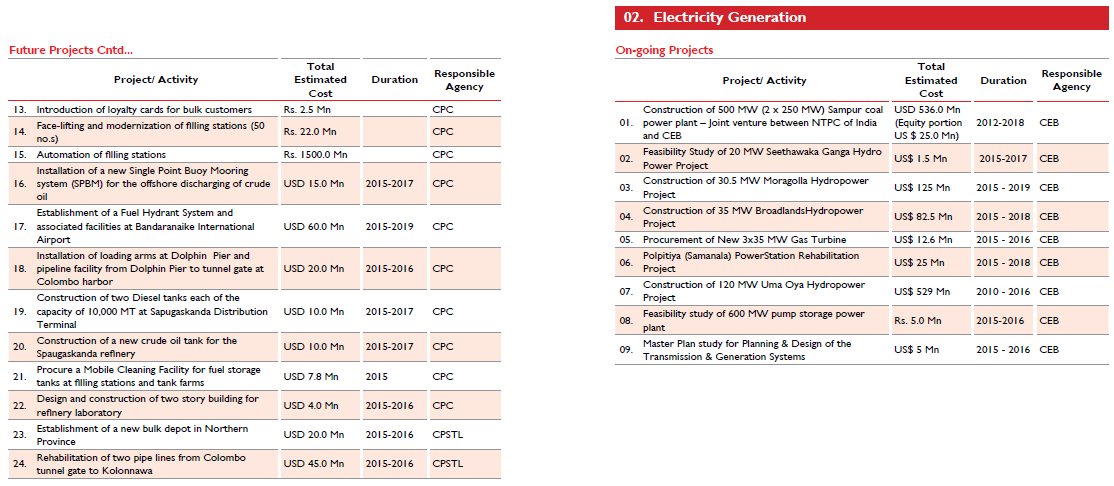
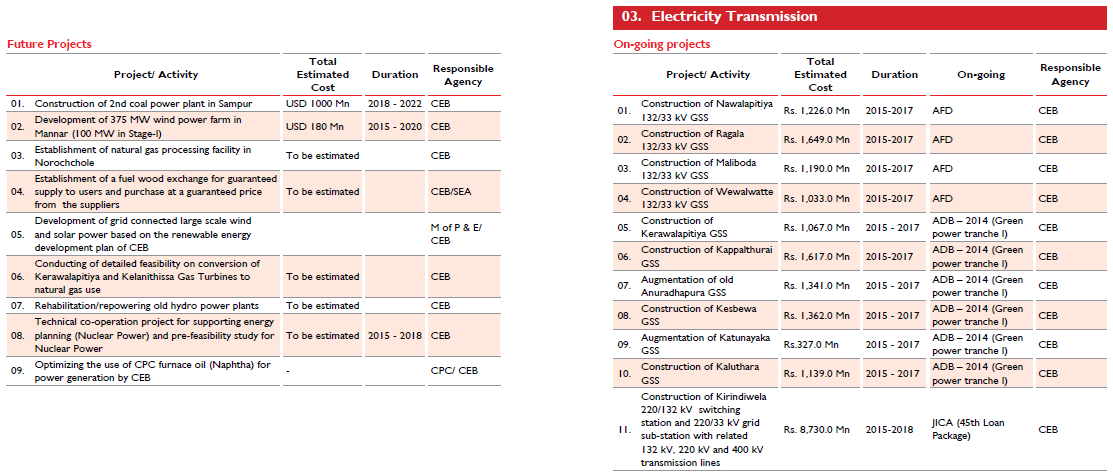
Electricity Generation |
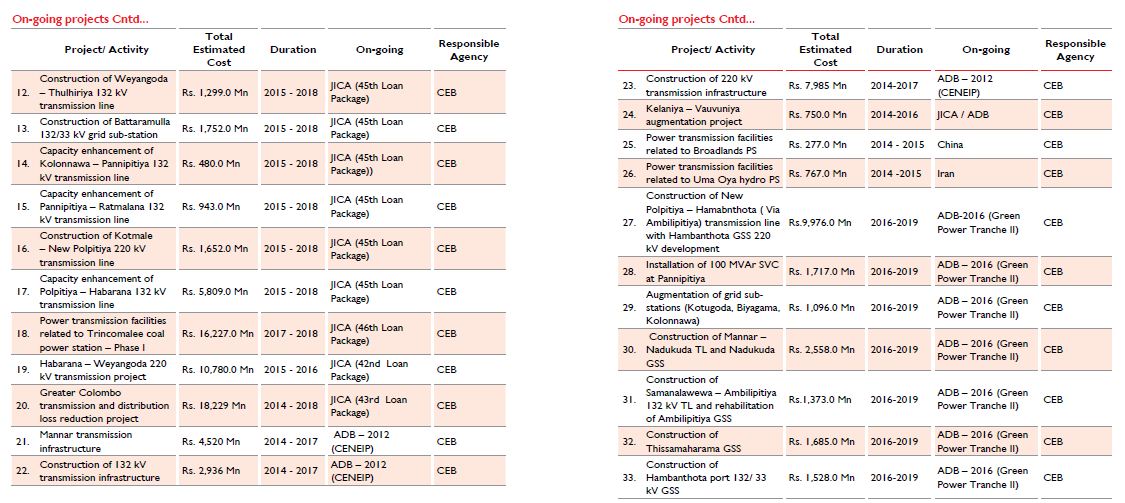
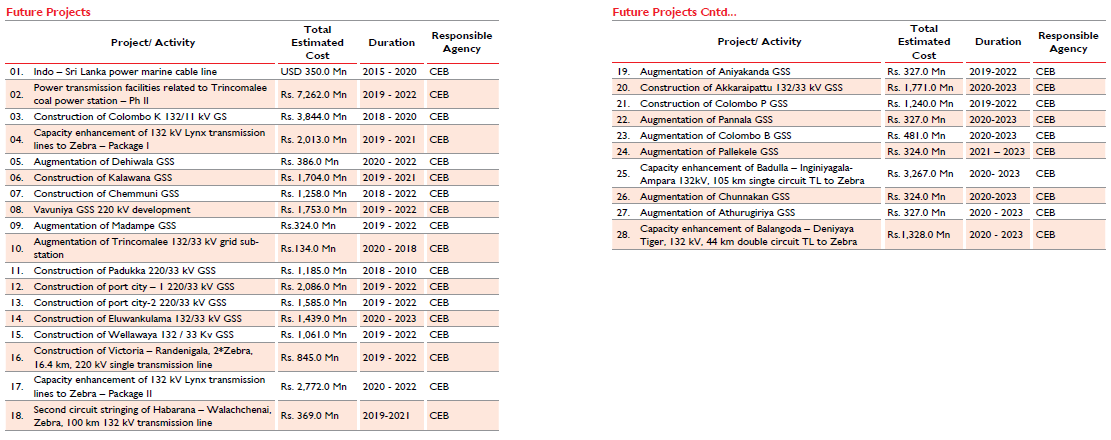
Electricity Transmission |
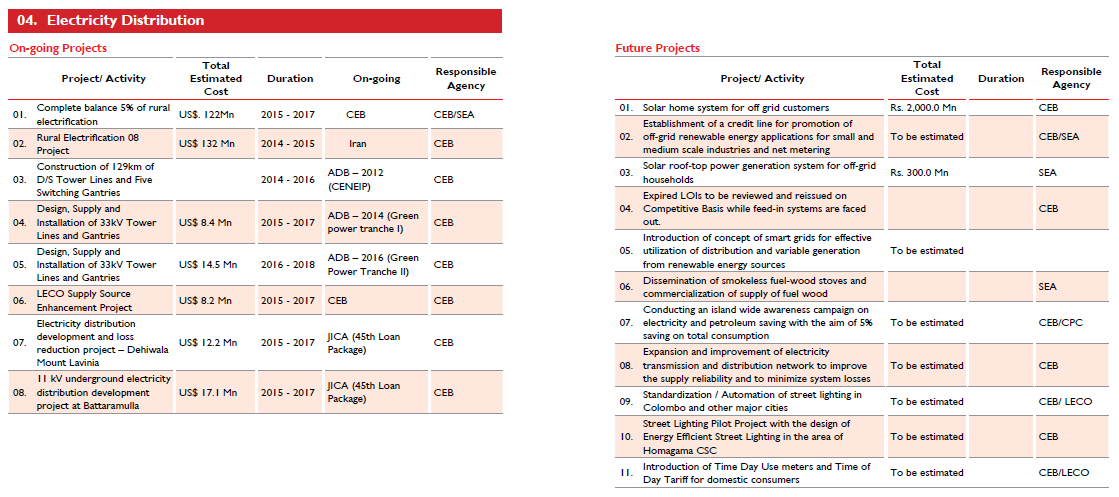
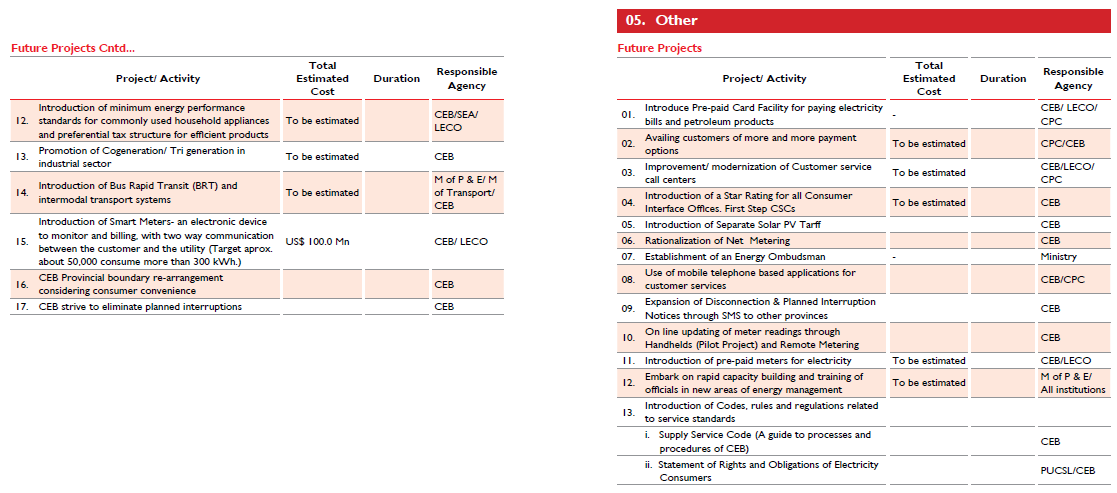
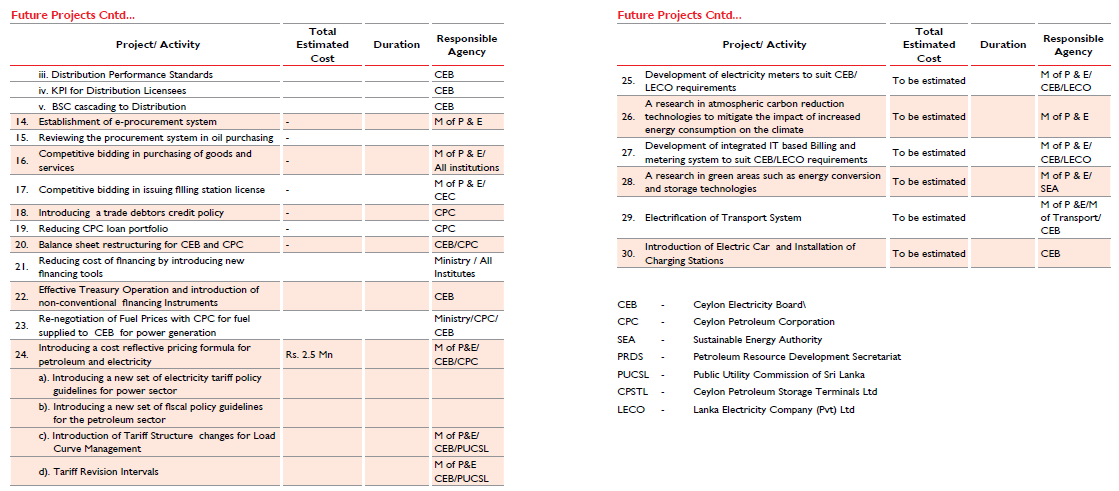
Electricity Distribution |