NOTE: Some content may not display correctly, including tables and figures. See PDF for full details.
Energy Efficiency and Conservation
Master Plan up to 2030
Sustainable and Renewable Energy Development Authority (SREDA)
and
Power Division
Ministry of Power, Energy and Mineral Resources Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh
March 2015
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Executive Summary
- Background ii
- Energy Demand ii
- Master Plan v
- Objective of Energy Efficiency and Conservation Master Plan v
- Overview of Energy Consumption vi
- EE&C Potential viii
- Toward “Self-Reliant EE&C Society”: Target and Implementation Roadmap ix
- Action Plan x
- Overview x
- Roles and Responsibilities x
- EE&C Programs xi
- Monitoring and Review of the EE&C Programs xii
- Economic Analysis xiii
- Capacity Development and Awareness Raising xv
Chapter 1 Introduction 1
- Background 1
- Objective of the Energy Efficiency and Conservation Master Plan 6
- Overview of Energy and Electricity 7
- Existing policies on energy supply and energy use including acts, rules, regulations, standards, guidelines and projects 13
- Stakeholder’s Participation in EE&C Planning and Policy Making 15
Chapter 2 Master Plan 16
2.1 Master Plan 16
2.2 Roadmap (from 2015 up to 2030, every 5years)...................................................................
2.3 Monitoring and Review of the Plan 24
Chapter 3 Action Plan 27
- EE&C Programs (Overview) 35
- Energy Management Program 35
- EE (Energy Efficiency) Labeling Program 46
- EE Building Program 53
- EE&C Financial Incentive Programs 61
- Government Own Initiative on EE&C Implementation 71
- Country’s Energy Consumption Data Collection Mechanism 73
- Global Warming Countermeasure 75
- Cooperation with International Donor Agencies 77
Chapter 4 Economic Analysis of the EE&C Programs 78
- Background and Objectives 78
- Economic Impact of EE&C Implementation 78
- Cost-Benefit Analysis 79
- Cost Effectiveness Analysis 83
Chapter 5 Capacity Development and EE&C Awareness Raising 86
- Overview 86
- Roles of the Government on Capacity Development and Awareness Raising 86
- Capacity Development for the Government 86
- Capacity Development for Energy Experts 87
- Capacity Development and Awareness Raising for Private Sectors 87
- Awareness raising for Residential Sectors 88
- Roadmap 88
Energy Efficiency and Conservation Master Plan
Foreword
Energy has become one of the most important factors for better economic growth and people’s life in Bangladesh. After decades of dependency on domestic natural gas, we find ourselves not equipped with sufficient energy resources in our land, and will gradually rely on imported fuels. Also, we are well aware that the use of fossil energy increases Greenhouse Gas emission, which accelerates global warming and causes climate change, and suffers our country by natural calamities.
Energy efficiency and conservation is a cross-cutting issue for all the people. We hereby issue the Energy Efficiency and Conservation Master Plan, and declare our unyielding commitment of its implementation.
ABBREVIATION
Terms and Definition
Outline of EE&C Master Plan
Executive Summary
- Background
- Energy Demand
Bangladesh is a densely populated country with about 161 million people living in 147,570 square kilometers of land. In order to maintain a sustainable GDP growth of 7% and above up to 2020 and beyond, the Government of Bangladesh (GOB) needs to meet the essential energy needs of the people and industries. For this purpose, demand-side energy management is just as important as supply-side infrastructure development. The Sustainable & Renewable Energy Development Authority (SREDA) was thus established by Bangladesh Parliament in May 2012 as a national nodal organization for promoting demand-side energy efficiency and conservation in the country.
A rapidly growing country like Bangladesh needs a huge amount of energy to feed its large growth appetite. There is no room for wasting energy.
Energy Efficiency (EE) means high competitiveness; it means producing more with less energy. Thus earned “energy savings” can be wisely reinvested. Business establishments can reinvest them to expand their businesses. The households can reinvest them for their children’s’ education and health cares. The Government can invest less in energy subsidies and more in industrial development.
EE is about national energy security; the Government can reduce import of expensive fuels, which is expected to increase in early 2020’s, and improve the international balance of payments.
The Government aims to improve energy intensity (national primary energy consumption per gross domestic product/GDP) in 2030 by 20% compared to the 2013 level: A total of 95 million toe (113 billion m3 of gas equivalent) is expected to be saved in the period. Energy savings will amount to BDT 768 billion in total, or an annual average BDT 51 billion at the current weighted average natural gas price. This goal will not be attained without the Government’s strong leadership, peoples’ consciousness and actions to realize it.
In 2030, the total primary energy consumption of Bangladesh, excluding transportation and biomass, is estimated to reach over 72 Mtoe, triple the size of 2013. (See Figure 1-1) It is now the high time for stakeholders to start Energy Efficiency & Conservation (EE&C). Before the country’s natural gas reserves start to decrease in 2018, before the imports of coal and LNG starts to increase in 2021-22, and before the country’s industrial structure change from labor intensive to energy intensive ones, the Government must strive ahead with the promotion of EE&C, to urge the general public to lead energy efficient, non-energy wasting and most productive lives.
- Energy Supply
Bangladesh has been able to exploit its abundant natural gas reserves. As shown in Figure 1-2, around one fourth of its energy supply depends on natural gas. It is anticipated, however, that the gas supply will reach its peak in 2018 and gradually decrease thereafter. Therefore, the country cannot build another gas fired power plants, but instead resort to other natural resources for power generation, such as oil, LNG and coal, as shown in Figure 1-3. The Government plans to develop the Matarbari Island area to build ports and facilities which allow imports of coals and liquefied natural gas (LNG) for power generations from after 2021 and 2022, respectively. The development of other type of power generation (such as nuclear and hydro power generation) awaits negotiation with partner countries, and seems not able to start operation before 2030.
Figure 1-2 Trend of Source of Energy Supply
Source: IEA country statistics, excluding biomass
It is expected that by taking the EE&C scenario (i.e., 20% energy efficiency improvement by 2030 compared with the 2013 level), the electricity demand in 2030 will be reduced by 8GW compared with the BAU case. This will lead to the decrease in the amount of fuel imports for power generation, resulting in a cumulative savings of DBT 2.3trillion between 2015 and 2030 or an average annual savings of 135 billion taka, which is equivalent of 6% of national budget and 1% of GDP (2013).
- Energy Balance in Bangladesh
Figure 1-4 shows the energy balance of Bangladesh in 2012 with data mainly from International Energy Agency (IEA). Our primary energy supply is 33,172 ktoe, of which 55% is dependent on domestic natural gas, followed by 27% of biomass & waste in rural area and 15% of imported oil. On the demand side, out of 24,445 ktoe final consumption, the industrial sector uses 24% and residential sector (excluding biomass & waste) follows at 15%.
Source: Compiled by JICA EE&C Project Team based on IEA country statistics (2012 data)
Figure 1-4 Energy Balance in Bangladesh (2012)
- Bangladesh’s Vulnerability for Climate Change
Bangladesh is vulnerable for sea level rise, high tide wave and river flood by cyclone potentially caused by the climate change through global greenhouse gas (GHG) emission by fossil fuel consumption. Our EE&C implementation is not only for the economic benefit but also closely links to protecting Bangladesh from such disasters.
- Necessity of EE&C Policy and Implementation
There is lack of urgency among the public and industries to save energy under the current situation where GOB highly subsidizes energy and power sector to lower the costs of fuel and electricity prices for the household and industries. Nevertheless, people and entrepreneurs are wise enough to know the importance of energy saving once they find out the magnitude of economic benefits they can earn, even under the current low energy prices.
It is important for the Government, therefore, to facilitate the installment, execution and proliferation of EE&C Programs as well as to create the momentum to promote energy saving activities among all the general public through EE awareness-raising activities.
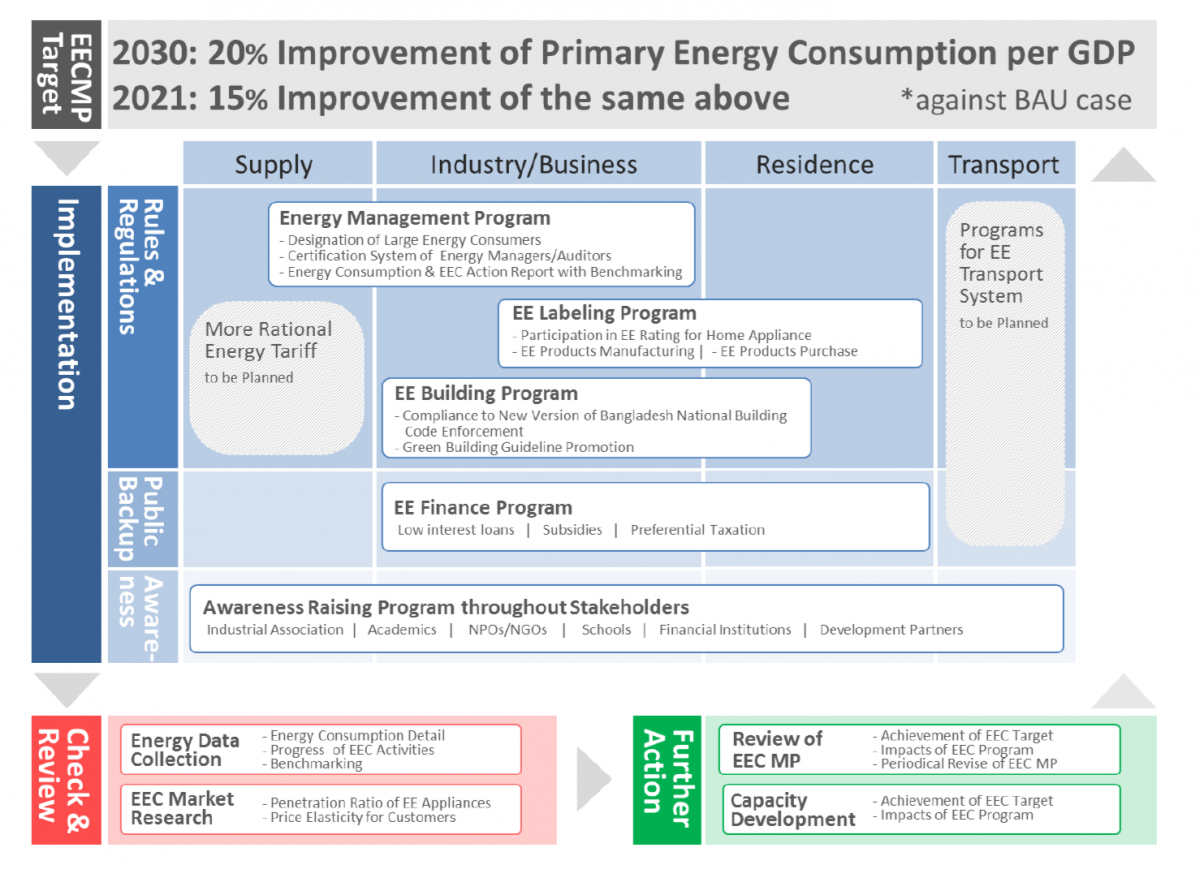
Under this EE&C Master Plan, three EE&C programs will be promoted, namely, Energy Management Program, EE Labeling Program and EE Buildings Program, which will be targeted at large energy consuming entities and equipment in the industrial, residential and commercial sectors. During the period between 2015 and 2030, a total of 5.3 Mtoe/ year or the energy savings of approx. BDT 100 billion/year can be achieved through the adoption and implementation of the three EE&C Programs.
In addition, the Government considers it important to provide EE Finance Program to raise EE awareness among the power end users and boost their investments in EE products. Financial incentives such as loan interest loans, subsides and preferential tax will be provided to lessen the financial burden (initial cots) of end users who will purchase high energy efficient electric appliances and industrial equipment.
- Master Plan
- Objective of Energy Efficiency and Conservation Master Plan
Structure of EE&C Planning and Implementation
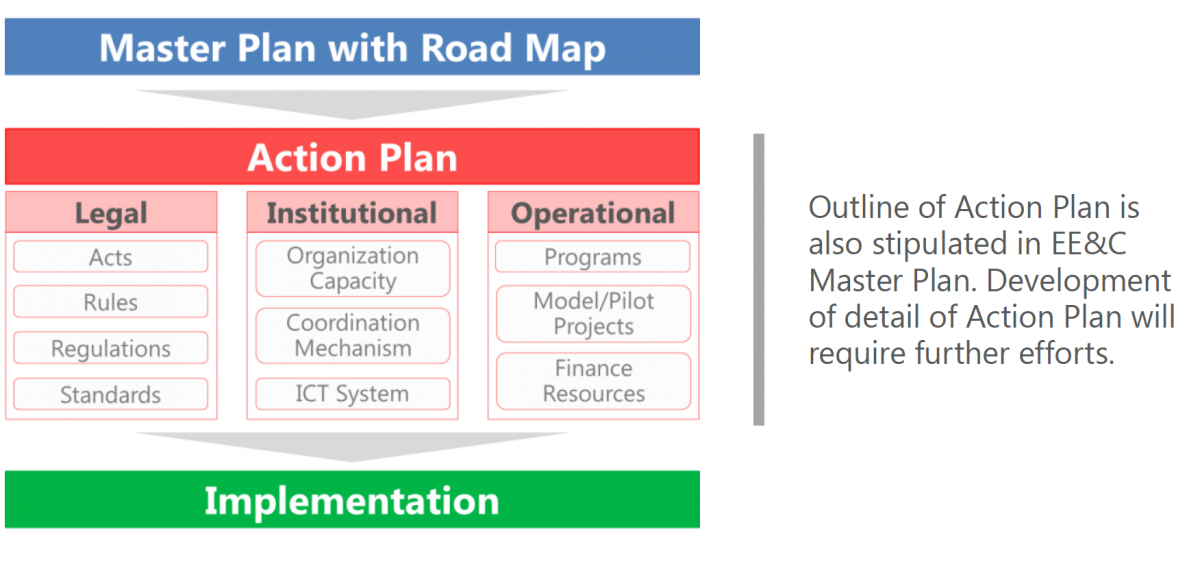
The EECMP is a supreme plan of Bangladesh’s initiative on energy efficiency and conservation, of which preparation requirement is stipulated in the Energy Efficiency and Conservation Rules (2014). The Plan declares Bagladesh’s unyielding commitment for EE&C implementation to our people and to the world. Under the EECMP, all the policies, programs, legal documents (Act, Rules, Regulations, Circulars or Standards etc.) and frameworks are to be established. Figure 2-1 shows the basic structure of EE&C planning and implementation. In the EECMP, we clearly indicate Roadmap up to 2030 with Action Plan, consisting of the outlines of legal, institutional and operational framework for implementation of EE&C initiative.
Figure 2-1 Structure of EE&C Planning and Implementation
- Cross-cutting EE&C Policies and Actions
EE&C actions are to be taken by all the people and establishments, including governmental organizations and private sectors. The Master Plan shows a systematic structure of EE&C policies/programs and actions carried out by ourselves. More elaborated plan is to be implemented through cross-cutting discussions among the related stakeholders.
- Overview of Energy Consumption
- Present Situation of Energy Consumption
Bangladesh is one of the lowest among the world in the primary energy consumption per capita. In 2012, the country’s per GDP annual energy consumption was 238 kgoe (excluding biomass1). Compared to those of surrounding counties, such as India and Thailand, it stands lower. In the last decade, the energy use per GDP (“energy intensity”) of Bangladesh has been on the downward trend (implying the improvement in energy efficiency) due to strong economic growth backed by the expansion of less-energy-intensive export industries, such as garments.
(See Figure 2-2)
Figure 2-2 Trends of Energy Use per GDP (kgOE / 1,000USD)
[...]
Source: Compiled by JICA Project Team based on the data from IEA country statistics and WB, as for 2013 and 2014; energy use data derived from Power Cell, Power Division, Ministry of Power, Energy and Mineral Resources | Gas: 2013-14, MIS of Petrobangla
Note: all sectors excluding biomass, Electricity: 2,867kcal/kWh (thermal efficiency 30% basis
From the macro point of view, however, the energy supply and demand balance of Bangladesh has been deteriorating, with the current amount of national energy production stands at 27,187 ktoe, while the amount of primary energy use is 33,550 ktoe including imported fuels3. As shown in Figure 2-3, this gap between national energy production and the amount of primary energy use is becoming very steep in the recent years. The risk of further deterioration is foreseeable as the country’s industrialization accelerates. Therefore, it is an utmost importance for the Government to take leadership in controlling the energy use by implementing appropriate
1 In this EECMP, we will focus on commercial energy and exclude non-commercial energy; i.e. biomass.
3 IEA country statistics EE&C plan, programs and measures and therewith promote energy efficiency in the entire economy.
Figure 2-3 Gap between National Energy Production and Primary Energy Use (ktoe)
- [...]
Sector-wise Energy Consumption
The latest sector-wise energy consumption (industrial, residential, transport, agriculture and commercial) is shown in Figure 2-4: industry has the biggest share at 47.8%, followed by residence and transport at 30.5% and 11.5%, respectively. While transport sector is out of this EECMP’s scope, by focusing on the industrial, residential and commercial sectors, we are able to cover more than 80% of the total energy use of this country.
Figure 2-4 Primary Energy Consumption by Sector (as of 2013-14)
2.2.2 Long-Term Energy Consumption Forecast
It is estimated that the primary energy consumption (excluding transportation and biomass) will increase approximately three-fold from 27,500 ktoe in 2015 to 71,600 ktoe in 2030 as shown in Figure 2-5. The composition of sector-wise share will not see a significant change; the consumption in industrial sector will remain nearly half.
Figure 2-5 Forecast of Primary Energy Consumption in 2030(BAU case, excluding transportation and biomass)
[...]
Source: Compiled by JICA Project Team, based on the present energy consumption data and forecast of future growth rate by sub-sector derived from UNFCCC Second National Communications, Oct. 2012
- EE&C Potential
When setting the EE&C target, it is imperative to grasp the EE&C potential or, in other words, how much we are currently wasting energy. The concept of energy intensity is an indicator to comprehensively capture energy efficiency of production in factories, buildings and nationwide economic activities, which can be described as the unit energy consumption per production, floor areas and GDP, respectively. EE&C potential can be calculated by comparing the actual energy intensity of a product/building/economy with the best-case energy intensity in the most advanced factory in Bangladesh or in other countries.
- Industrial Sector
Manufacturing industries in Bangladesh are not efficient in energy use because of continuous usage of old/ mal-maintained machines and poor energy management. We identify that, through energy intensity comparison and actual on-site energy audits, the accumulating EE&C potential in industrial sub-sectors is estimated at around 30% of the entire sector consumption. Considering that about 50% of national primary energy is consumed in industrial sector, the potential impact of EE&C measures is massive; almost 15% reduction.
- Residential Sector
If all the existing home appliances in residences are to be replaced by the highest efficiency products (as of today), huge scale of energy consumption reduction can be achieved. It is calculated that maximum potential is 36% reduction in energy consumption.
- Commercial Sector (Buildings)
Electricity is the main mode of energy in commercial buildings. In detail, nearly 50% of the total energy is consumed by ACs and 10-30% by lighting systems. It is expected that a simple replacement of ACs and lighting systems with energy efficiency ones alone can save about 50% of total electricity consumptions in the commercial sector. It should be noted, however, that luminance improvement and additional AC systems for better space condition are not included here.
- Toward “Self-Reliant EE&C Society”: Target and Implementation Roadmap
There are several indicators to evaluate the improvement of future national energy efficiency, such as energy consumption per capita, energy consumption per Growth Domestic Product (GDP) and the reduction amount of energy consumption, etc. Energy consumption per capita is not suitable for developing countries like Bangladesh. And in case of evaluating by the reduction amount, it is not easy to fix the national baseline in the future. Besides energy consumption per GDP can consider both the energy efficiency and increase of national economy. Therefore we will use “primary energy consumption per GDP” as an indicator to evaluate future national energy efficiency.
While identifying a huge potential, we should take practical approach to gradually realize it in phased manner since EE&C implementation requires huge investment and time. And it is estimated that with formulating suitable regulatory measures and incentive mechanisms, which are mentioned in the following pages, in accordance with nationwide actions for energy conservation, approx. 20% reduction of primary energy consumption per GDP can be achieved by 2030. And by 2021, when gas and power supply shortage is expected, 15% reduction of primary energy consumption per GDP is to be achieved. Here in the Master Plan, EE&C target and road map are set as Table 2 -1. The targets both for 2021 and 2030 are set with consideration of the EE&C potential and current energy consumption status; i.e. low electrification ratio, insufficient industry’s environmental protection measures, improvement of work condition and life style etc. Final goal of EE&C policies is to realize self-reliant cycles, rather than compulsory EE&C activities. We aim to accomplish the target, and realize a “self-reliant EE&C” society by 2030.
Table 2-1 EE&C Implementation Roadmap (2015-30)
- Action Plan
- Overview
The Action Plan containing the EE&C policies and programs frameworks and organization structure is prepared to show practical methodology to achieve and accomplish the targets set in the EECMP.
- Roles and Responsibilities
EE&C implementation is a multi-sectoral issue and should be done by the participation of all the parties including the people, private/public establishments and other organizations in the country. Our EE&C activities are related with each other. Some of organizations have roles and responsibilities of support and enforcement of rules, and/or EE&C awareness and dissemination. Table 3-1 shows major roles and responsibilities of the participating parties.
Table 3-1 Roles and Responsibilities of Participating Parties
Party Roles and Responsibilities
MPEMR
■ Responsible ministry for EE&C policy planning and implementation
- Overall planning and development of electricity, gas and energy sector
SREDA
■ Implementing body to promote EE&C nationwide
- Multi-sectoral / cross-cutting coordination of EE&C policies among all governmental organizations and non-governmental organizations
- Nationwide monitoring of energy consumption and EE&C implementation
Party Roles and Responsibilities
- Reporting energy consumption status to the people
Local Governments
- Administration of New version of Bangladesh National Building Code (BNBC [Revised]) and Green Building Guideline (GBG)
- Initiatives on EE&C activities in office, projects and own procurement
Utility Companies (energy supplier)
- Energy conservation improvement in plants
- Transmission efficiency increase in supply system
- Functional tariff system formulation/introduction for EE&C incentives
Business ies, People and Society
- Compliance of EE&C Rules and regulations
- Preparedness / acceptance for future energy/power price increase and risks
Energy Experts, Academics, Labos and Researchers
- Leading EE&C implementation initiative
- Network/community development among energy experts
- Educational Institutions
- Awareness raising for students
- EE&C Programs
Action Plans for the major EE&C programs are summarized in Table 3-2. Necessity of the programs, relating situation on energy consumption, program outline and implementation methodology, stakeholders’ roles and responsibilities, roadmap and expecting outcome are introduced. These programs have been introduced in advanced and neighboring countries. EE&C programs on transport sector, energy supply sector and energy tariff have not yet been included in the EECMP, and policies/programs on these remaining fields should be studied and issued in future.
Here, Energy Management Program is mainly focusing on promoting energy efficiency in industrial sector, EE Labeling Program in residential sector and EE Building Program in buildings. Besides the other programs are common for these three programs.
Table 3-2 Summary of EE&C Programs in Action Plan
Program Target Methodology
Energy Management Program
Large Industrial Energy Consumers
- Large energy consumer designation
- Energy Manager, Certified Energy Auditor and Accredited Energy Auditor certification with qualification and examination system
- Energy audit (mandatory/voluntary)
- Energy consumption reporting (mandatory)
- Benchmarking
Program Target Methodology
EE Labeling Program
Residential Consumers
- Label certification / Laboratory accreditation system
- Standardization of EE measurement method and Star Label Rating criteria
- Star Label Standardization (Unification)
- Participation of manufactures, importers and retail shops (mandatory/voluntary)
- MEPS (Minimum Energy Performance Standard)
EE Building Program
■ New version of BNBC [Revised] Implementation
- GBG development
- Manual and assessment system introduction
EE&C Finance Program
Private Companies
- Low-interest loan for EE&C investment
- Preferential taxation on high efficiency equipment/appliances and/or EE&C investment
- Monitoring and Review of the EE&C Programs
- Monitoring and Data Collection
Periodical monitoring and data collection of indicators on the energy consumption in various sectors are key factors of success in the EE&C implementation. The web-based information collecting mechanism proposed under this EECMP will ensure the smooth data accumulation for enabling the appropriate PDCA cycle of the entire EE&C policies.
- Review of EECMP
All the data are maintained by SREDA as a regulatory authority for the EE&C initiative. SREDA is mandated to analyze them and review the progress of the EECMP and subordinate programs. The annual reporting in this regard should be presented to the Joint Coordination Committee, chaired by SREDA Chairman with participation from all the relevant ministries/agencies, for the follow-up of the EECMP. Result of the review will be reflected in the details in Action Plan. The annual report will be uploaded on SREDA website for disclosure to the public.
- Revision of EECMP
The EECMP should be periodically revised along with the progress of initiative in accordance with the EE&C program development. We intend to make a next revision in five years: i.e. year 2020.
- Economic Analysis
- Overview
Economic viability of each EE&C measure has to be verified by the cost-benefit analysis; clarifying and comparing its costs and benefits. Although energy consumption reduction is the primary and direct benefit of EE&C measures, secondary and indirect benefit shall, in some cases, be taken into consideration in order to justify the costs involved. From the viewpoint of effective allocation of limited resources, the Government will compare candidate EE&C measures and projects according to their cost effectiveness (or costs per unit of energy saved), since the Government has responsibility in prioritizing allocation of limited resources to economically viable projects and to avoid implementation of projects with less economic values.
- Economic Impact of EE&C Programs as a Whole
As shown in Figures 4-1, in the EE&C scenario (20% energy efficiency improvement by 2030) compared to the BAU case, the demand in 2030 will be reduced by 8GW. This would lead to the decrease in the amount of fuel imports for power generation, resulting in a cumulative savings of DBT 2.3trillion (or an annual average of DBT 135billion) from 2015 to 2030. This annual savings are equivalent of 6% of national budget and 1% of GDP (2013).
Figure 4-1 Impact on Power Demand and Supply (MW)
Figure 4-2 Impact on Fuel Costs (BDT billion)
- Cost Effectiveness Analysis of Target EE&C Programs
Marginal Abatement Cost (MAC) curve can be drawn by plotting the data of costs (BDT) per unit of energy saved (toe) and absolute annual amount of energy saved. In the MAC curve, the project which require the lowest costs (BDT) per unit of energy saved (toe) is placed at the lower left of the diagram and the project with the highest cost will be placed at the upper right of the diagram, as shown in Figure 4-3. In other words, those projects that appear below the horizontal axis can be implemented at a net benefit, while those above the horizontal axis can be implemented at a net cost. For the effective allocation of limited resources, it is wise for the Government to prioritize the implementation of EE&C projects according to their cost effectiveness.
Source: Compiled by JICA EE&C MP Project Team based on independently collected data
With regard to the implementation of EE&C programs, namely, EE Building Program, EE Labeling Program and Energy Management Program, it is also recommended for the Government to prioritize their implementation according to their cost effectiveness.
- Capacity Development and Awareness Raising
For successful implementation of EE&C initiatives, all the stakeholders such as governmental organizations, private sectors and energy experts should accurately understand the urgency and necessity on the improvement of energy efficiency. Also, close cooperation/collaboration among them is imperative. Thus, the Government will promote awareness raising and information provision
The Government will initially lead and take a responsibility for the capacity development and awareness raising on the EE&C policies/programs for all the stakeholders. Considering the importance of EE&C for our country, however, such roles are to be also taken by relevant private sectors, NPO/NGO and individuals in the long run.
The final goal is that all the people and establishments take voluntary EE&C actions.
Chapter 1 Introduction
- Background
- Economic Growth and Increase of Energy Consumption
Bangladesh is one of the lowest among the world in the primary energy consumption per capita. In 2012, the country’s per GDP annual energy consumption was 238 kgoe (excluding biomass4). Compared to those of surrounding counties, such as India and Thailand, it stands lower. The trend of energy use per GDP in last decade as shown in Figure 1.1-2 has been on downward (i.e. energy efficiency improving) due to strong economic growth backed up by less-energy-intensity export industries, such as garments. However from the macro point of view, the amount of national energy production stands at 27,187 ktoe while the amount of primary energy use was 33,550 ktoe including imported fuel5. As shown in Figure 1.1-2, this gap between national energy production and the amount of primary energy use is becoming larger in recent few years. There risks awaited in line with further industrialization of economy that the energy efficiency would be deteriorated drastically if no plan/programs and measures are taken.
Figure 1.1-1 Trend of Energy Use per GDP (kgoe / 1,000USD)
Source: Compiled by JICA Project Team based on the data from IEA country statistics and WB, as for 2013 and 2014; energy use data derived from Power Cell, Power Division, Ministry of Power, Energy and Mineral Resources | Gas: 2013-14, MIS of Petrobangla
Note: all sectors excluding biomass, Electricity: 2,867kcal/kWh (thermal efficiency 30% basis
4 In this EECMP, we will focus on commercial energy and exclude non-commercial energy; i.e. biomass.
5 IEA country statistics
Source: Compiled by JICA Project Team, based on IEA country statistics Note: Grid electricity 1kWh-= 2,867kcal (efficiency 30%) basis
Figure 1.1-2 Gap between National Energy Production and Primary Energy Use (ktoe)
- Energy Security and Domestic Energy Resource
Bangladesh has been able to exploit its abundant natural gas reserves. As shown in Figure 1.1-3, around one fourth of its energy supply depends on natural gas. It is anticipated, however, that the gas supply will reach its peak in 2018 and gradually decrease thereafter. Therefore, the country cannot build another gas fired power plants, but instead resort to other natural resources for power generation, such as oil, LNG and coal, as shown in Figure 1.1-4. The Government plans to develop Matarbari Island area to build ports and facilities which allow imports of coals and liquefied natural gas (LNG) for power generations from after 2021 and 2022, respectively. The development of other type of power generation (such as nuclear and hydro power generation) awaits negotiation with partner countries, and seems not able to start operation before 2030.
Figure 1.1-3 Trend of Source of Energy Supply
Source: IEA country statistics, excluding biomass
Figure 1.1-4 Forecast of Transformation of Power Generation Resources
Source: Estimation of JICA expert revising the forecast in JICA Power Supply Master Plan, 2010
It is expected that in the EE&C scenario (20% energy efficiency improvement by 2030), the electricity demand in 2030 will be reduced by 8GW compared to the BAU case. This will lead to the decrease in the amount of fuel imports for power generation, resulting in a cumulative savings of DBT 2.3trillion (or an annual average of DBT 135billion) from 2015 to 2030. This average annual savings are equivalent of 6% of national budget and 1% of GDP (2013).
- Global Warming and Our Country’s Vulnerability for Climate Change
- Global warming issues
Release of CO2 to the atmosphere, mainly due to the burning of fossil fuels is the major driver of Global Warming. The consequence of such warming is being anticipated as a very serious global issue for several decades and has started to raise global awareness mainly after the United Nations Conference on the Human Environment, hold at Stockholm from 5 to 16 June 1972.
Since 1988, United Nations created a Technical Unit, called as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) to study, analyze and make recommendations on how to mitigate global warming, how to adapt human society to live in a warming world, and finally how to precisely understand all scientific aspects of climate.
Nowadays significant number of scientific work, dealing with Climate Change, has been produced and are available as free literature, five very complete assessments, covering Climate Change science, Climate Change adaptation and Climate Change mitigation had been officially produced by the UN designated body (IPCC), and several national and international policies are implemented, mostly to mitigate Climate Change. Unfortunately, as reported in the freshest IPCC report6, published in early 2014, the World is still following an unsustainable path, regarding the Global Warming issue. In the decade of 2001-2010, CO2eq emissions have grown faster than in all the previous decades where emission data are available. Keeping the present trend, by the year 2100, average global temperature shall be around 40C
6 The Fifth Assessment Report – Working Group III - Mitigation
above pre-industrial figure, which is by far above globally agreed pledges set at the Cancun Conference of the Parties, which requires global temperature should not increase by more than 2ºC, above the pre-industrial average, in any date in the future.
Some of the most relevant international action plans, like the Kyoto Protocol, which had its first committed period concluded by the end of 2012, achieved some partial success on GHG mitigation, but shall achieve more modest results under the second period, which are presently in effect. Future international and/or national agreements on a more ample action plan has been agreed, by all participants of the UNFCCC7 , to be set until the end of 2015, and become effective by 2020. Huge expectations exist that in the COP8 to be held in Paris, at the end of 2015, the new agreement will be finalized.
In the meantime, it is notorious the Government, the society, and the major establishments concern with the Climate Change issue, and a plan like this one, being elaborated for our country, should take into account such issue.
In reality, the Master Plan on EE&C, is naturally aligned with Climate Change mitigation, since one of the five mitigation options9, identified by IPCC, is energy efficiency either when using or producing it. What has to be considered in the EE&C Master Plan is how to manage potential conflicts due the higher cost of clean technologies when compared with traditional ones. Such costs include investment and operational expenses, as well as indirect costs due social and environment improvements, usually associated with the practice of clean technologies. When performing the full cost evaluation, it is necessary to add investment cost, which probably occurs immediately, with operational, social and environmental costs distributed during many years, during the full life of the project.
Furthermore, political and strategic consideration must be included, on top of cost evaluation, for the final decision when embracing a project. The political aspect includes items like the prestige of the country regarding its action on minimizing a global issue, as is the case for Global Warming, the reaction of its population to certain technology or policy and, the possibility of receiving financial reward, from the international community. Strategic decisions shall consider the relevance of a new technology regarding the economic contribution for the country development, through creation of new jobs and activities in the country.
In conclusion, it is transparent from the above discussion that all suggested actions must include Climate Change impact analysis, even for countries where the GHG emissions are small compared with the major emitter countries, and that are well recognized internationally as deserving further supply of energy to guarantee its development to reasonable pattern, as is our country’s case.
7 UNFCCC = United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
8 COP = Conference of the Parties is the supreme forum for decisions regarding actions between the more than 190 countries and parties signatories of the UNFCCC.
9 The other 4 are: Decarbonisation of fossil fuels, Biological carbon sequestration, More use of renewable energy resources, and
Reducing other greenhouse gases from industry, agriculture, waste management
- What is impact of the global warming?
Source: JCCCA (Japan Center for Climate Change Actions) http://www.jccca.org/english/
- GHG (CO2) emission in the world
70% of GHG in the world comes from energy consumption. Therefore, EE&C will mostly contribute global warming countermeasure.
Source: http://greenblog.typepad.com/d41e/global/
Figure 1.1-5 GHG (CO2) emission in the world
- Necessity of EE&C Implementation and Policy/program Establishment
There is lack of urgency among the public and industries to save energy under the current situation where GOB highly subsidizes energy and power sector to lower the costs of fuel and electricity prices for the household and industries. Nevertheless, people and entrepreneurs are wise enough to know the importance of energy saving once they find out the magnitude of economic benefits they can earn, even under the current low energy prices.
It is important for the Government, therefore, to facilitate the installment, execution and proliferation of EE&C Programs as well as to create the momentum to promote energy saving activities among all the general public through EE awareness-raising activities.
Under this EE&C Master Plan, three EE&C programs will be promoted, namely, Energy Management Program, EE Labeling Program and EE Buildings Program, which will be targeted at large energy consuming entities and equipment in the industrial, residential and commercial sectors. During the period between 2015 and 2030, a total of 5.3 Mtoe/ year or an energy saving of approx. BDT 100 billion/year can be achieved through the adoption and implementation of the three EE&C Programs.
In addition, the Government considers it important to provide EE Finance Program to raise EE awareness among the power end users and boost their investments in EE products. Financial incentives such as loan interest loans, subsides and preferential tax will be provided to lessen the financial burden (initial cots) of end users who will purchase high energy efficient electric appliances and industrial equipment.
- Objective of the Energy Efficiency and Conservation Master Plan
The Energy Efficiency and Conservation Master Plan (EECMP) is drafted to realize the following objectives:
- National plan under the EE&C Rules
The EECMP is a supreme plan of national policies on EE&C. Issue of the EECMP is indicated in EE&C Rules (2014).
- Our country’s commitment on EE&C implementation
The EECMP shows our country’s commitment for EE&C implementation declaring to the people and also to the world. Therefore, clear EE&C targets and roles and responsibility of all parties should be focused.
- EE&C awareness and dissemination tool
The EECMP should be read by not only government people, but also all the people and establishments in our country widely. For this purpose, the contents are written in easy terms with explanations. The EECMP can be used as a text book of EE&C.
- Sort of cross-cutting EE&C policies/programs and actions
EE&C actions are to be taken by all the people and establishments, including governmental organization, individuals, NPO/NGO and other establishments relating each other. The EECMP shows a systematic structure of EE&C policies/programs and actions sorting cross-cutting EE&C policies/programs and actions.
- Overview of Energy and Electricity
- Present Situation of Energy Consumption
- Overview
As mentioned before, Bangladesh is categorized as one of the lowest primary energy consumption per capita in the world. In 2014, the country’s annual grid electricity consumption per capita was about 270 kWh as shown in Table 1.3-1. However, only 60% of the population has now accessed to electricity grid. And it is expected that these values will surely increase rapidly with national economic growth.
Table 1.3-1 Grid Electricity Generation Amount per Capita
Source: System Planning Directorate, BPDB
Considering necessity and purpose of EE&C, it is clear and popular to focus on only commercial energy. Therefore here in the EECMP, “Energy” means “commercial energy”, thus biomass energy, such as fire wood for cooking is not included. We will focus on commercial energy and exclude non-commercial energy (biomass).
- Energy consumption by fuel type
At present, renewable and non- renewable sources contribute to total energy consumption. Currently about 80% of electricity is generated by natural gas. About 55% of the country's energy is provided by traditional biomass fuel (crop residues, animal dung and fire wood: non-commercial), 24% by natural gas, 19% by imported oil and coal and the remaining 2% by hydroelectricity.
The use of oil shows an increasing trend: In 2009, oil represented 11.1% of total energy supply, in 2010 18.3% and 23.8% in 2011.
- Consumption of gas and petroleum
Gas and petroleum are the main sources of primary energy to meet our energy demand. Considering gas consumption, electricity supply sector uses 31%, industrial sector uses 46% (incl. captive power). Residential sector occupies 12%. Considering the use of petroleum, transportation sector is the largest (45%); Agriculture is the next to it (19%). And 9% of petroleum product (in the form of kerosene oil) is used for domestic (residential) purpose. Petroleum oil in electricity sector is 25%.,as shown in Table1.3-2.
Table 1.3-2 Gas and Petroleum Use
Industry Transport Residence Commercial Agriculture
Gas 69.2% 8.2% 20.7% 1.8% 0.2%
Petroleum (Oil) 4.9% 59.8% 9.0% 0.5% 25.8%
Source: Gas MIS of Patrobangla, 2013-2014 , BPC ,2012-2013
- Energy conversion, primary energy and secondary energy
Table 1.3-3 shows energy conversion factors for grid electricity, crude oil and major units to measure heat quantity. The energy balance should be mainly checked and discussed in not a secondary but a primary energy10 basis. The conversion ratio from secondary to primary energy is calculated by considering the average conversion efficiency (In case of grid thermal electricity generation: about 35% 11 ) and transmission/distribution loss (In case of transmission and distribution loss 14% (35%*14%=5%)12). All energy should be discussed on primary energy basis in the same unit of TOE. Table 1.3-4 shows primary energy conversion factor. The table will be reviewed by SREDA time to time or as and when required.
10 Primary energy is a natural energy; such as fossil, hydro, solar and geo-thermal energy. Besides secondary energy is an artificially converted energy; such as electricity, gasoline etc.
11 Reported by MPEMR in the 2nd EM Committee
12 Reported by MPEMR in the 2nd EM Committee
Table 1.3-3 Heat Value Table (Primary Energy Basis) (Draft)
[...]
Heat value of various fuels can be converted by Table 1.3-3. Grid electricity heat value is based on end-users’ thermal efficiency: 36% (at plant) minus 6% (transmission and distribution loss) = 30%
Table 1.3-4 Primary Energy Conversion Factors
[...]
- Energy consumption by sector
Our country’s energy consumption by sector (industrial, transportation, commercial and residence) is shown in Figure 1.3-1. The largest energy consuming sector is industry, secondly residence and thirdly transportation.
Figure 1.3-1 Primary Energy Consumption by Sector
13 Confirmed in the 2nd EM Committee based on the data from MPEMR: 860/0.30=2,867
14 Tentatively derived from Japanese conversion factor, and to be revised to Bangladesh ones
15 Source: JICA Power Supply Master Plan 2010
[...]
(Note: primary energy basis, excluding biomass, Electricity: 2,867kcal/kWh (thermal efficiency 30% basis) Note: primary energy basis, excluding biomass, Electricity: 2,867kcal/kWh (thermal efficiency 30% basis)
[...]
(Source: Compiled by JICA Project Team based on the following data;
Electricity: 2013-14, Power Cell, Power Division, Ministry of Power, Energy and Mineral Resources | Gas: 2013-14, MIS of Patrobangla, Oil: 2012-13, BPC, | Coal:2012, IEA.
- Primary energy consumption by industrial sub-sector
Besides energy suppliers and industrial sector is the largest consuming sector. Energy consumption share of industrial sub-sectors is shown in Table 1.3-5.
Table 1.3-5 Primary energy consumption by industrial sub-sector
Natural Gas Electricity Oil & Coal Combined
Source: Compiled by JICA Project Team based on gas and electricity distribution companies’ data, as for oil and coal: breakdown data is estimated by JICA
- Natural gas production
Domestic gas supply will increase in the next few years, however it is estimated that it will soon reach the peak production and then decline and the demand will exceed the supply as shown in Figure 1.3-2. This means, we will have to import natural gas from abroad.
Figure 1.3-2 Domestic Natural Gas Production and Demand
Source: Compiled by JICA Project Team based on the data from Data collection survey on Bangladesh natural gas sector”, 2012, JICA
- Electricity Supply
- Electricity supply trend
Table 1.3-6 shows the amount of our country’s electricity generation and per capita generation. The amount is gradually increasing; however gap still exists between the demand and supply.
The peak load deficit resulted in regular load shedding during the peak hours and subsequent growth of electricity demand over 10% per year, owing to growth of population, industrialization, additional grid connection, and increasing trend in use of electrical appliances always making the present growing deficit even larger than in earlier decades. (Final Energy Efficiency Technical Report – Bangladesh (Revised), ADB RETA 8025, September 2012)
Table 1.3-6 Grid Electricity Generation per Capita
(Source: System Planning Directorate, BPDB)
- Electricity generation fuel mix
Table 1.3-7 shows the fuel mix used for electricity generation. As noted, electricity is strongly relaying on fossil fuels.
Table 1.3-7 Electricity Generation Fuel Mix (2013-14)
[...]
(Source: System Planning Directorate, MPEMR)
- Daily electricity load curve
Electricity daily load curve fluctuates by season and the day of a week. However throughout the year, the peak appears in the evening. Lighting, TV and other appliances in residential sector may cause the evening peak. Therefore, electricity saving in the evening is the most effective action to mitigate the limited electricity supply capacity as shown in Figure 1.3-3
Figure 1.3-3 Estimated Breakdown of Grid Electricity Daily Load Curve (31 May 2014)
Source: Compiled by JICA Project Team, based on BPDB’s data, hourly consumption pattern was estimated by the Team
- Electricity consumption by sectors
Electricity consumption by sector is shown in Table 1.3-8. Industrial sector and residential sectors occupy the largest shares.
Table 1.3-8 Grid Electricity Consumption by Sector
Source: Power Cell, Power Division, Ministry of Power, Energy and Mineral Resources,2013-14
- Electricity supply expansion plan
With the growth of economy, the demand for electricity increases rapidly. The Government has prepared Power System Master Plan 2010 (PSMP) to improve and expand electricity supply to support annual GDP growth of 7 percent. Given such a GDP growth scenario, the electricity demand including captive power is expected to increase, as shown in Table 1.3-9:
Table 1.3-9 Electricity Supply Expansion Plan
[...]
Gas supply shortage for generation
Although the situation of electricity generation has changed dramatically in last year, actual demand could not be met during the last few years, mainly due shortages of gas supply.
- Existing Policies and Legal Frameworks
- Overview of policies issued
MPEMR, which is the authority to deal with the issues on energy, has issued plans and regulations as shown in Table 1.4-1.
Table 1.4-1 Plans and Regulations Issued by MoPEMR
[...]
Other governmental organizations also have issued plans and regulations relating to energy and EE&C as shown in Table 1.4-2.
Table 1.4-2 Plans and Regulations Issued by Other Governmental Organizations[...]
- On-going EE&C Programs and Projects
In accordance with the EE&C plans and regulations mentioned above, several programs and projects are on-going as listed in Table 1.4-3:
Table 1.4-3 On-going Programs and Projects
National Building Code
Text Book Curriculum of schools, madrasas and colleges CFL, T- 5 tube light, electronic ballast
Free CFL Distribution program
Energy Star Labeling Program (fan, AC, refrigerator, CFL bulb, ballast and electric motors) Efficient Rice husk Parboiling Program
Improved Cook Stove Program
Improving Kiln Efficiency in the Brick Manufacturing Industry Electricity Week program
Energy audits by Energy Audit Cell under Electrical Advisor and Chief Electrical Inspector
1.5 Stakeholder’s Participation in EE&C Planning and Policy Making
Nobody can live without energy, and all of us have responsibility on energy use. In order to mobilize EE&C activities nationwide, EE&C policies and programs should be prepared getting as much as opinions and ideas from all concerned stakeholders and building a consensus among them; such as governmental organizations, individuals, establishments, residences, schools and industries,.
It is important to hold not only governmental officials meetings but also open discussion meetings inviting related stakeholders, including those from private sectors. Such manner will shorten the time for wider dissemination of the EE&C plans and regulations to the people and businesses.
For that purpose, the Joint Coordination Committee (JCC), committees and working groups (WGs) for specified EE&C programs, as shown in Figure 1.5-1, have been held with the presence of invited stakeholders’ representatives. These committees and WGs are expected to be held in the monitoring and reviewing stage, after the programs implementation. Moreover open seminars to discuss EE&C measures for wider participants are also effective to raise people’s awareness.
Figure 1.5-1 Structure of JCC, Committees and WGs
Chapter 2 Energy Efficiency and Conservation Master Plan
- Master Plan
- Overview
EE&C Master Plan is positioned at the summit of all national documents on EE&C plan, regulation and implementation. Figure 2.1-1 shows the basic structure and relation of the policy documents, organization and action plans. It should be noted that rules and acts are not placed at the summit, but supporting the Master Plan.
Figure 2.1-1 Structure of EE&C Planning and Implementation
In the Master Plan, roadmap up to 2030 and action plans should be described. Action plans consist of the basic methodology of EE&C policy implementation, frameworks of programs, outline of standards, rules and regulations, optimum organizational structures.
- Scope of the Plan
Originally, EE&C Master Plan should be formulated, covering all energy consuming sectors in the country. However, in this Master Plan, industry, commercial and residential sectors are focused and the transportation sector, utilities (energy supply sector) and energy tariff are not included. These remaining areas will be studied and properly addressed in the next version of the Master Plan.
Table 2.1-1 Remaining Areas in EE&C Master Plan
- Present Energy Consumption as the “Baseline”
Present energy consumption situation is summarized in Chapter1.3. A baseline which indicates nationwide energy consumption should be fixed in order to set EE&C target. The baseline should be set in energy intensity basis, which is calculated by primary energy consumption and GDP in 2013-14 as shown in Table 2.1-2.
Table 2.1-2 GDP and primary energy consumption in 2013-14
(Source: Compiled by JICA Project Team based on the following data sources: GDP from WB website, energy consumption from mainly distribution companies’ data (oil & coal: 2012-13 data))
- Energy Consumption in 2030, BAU Scenario
Figure 2.1-2 shows the forecast of primary energy consumption by sector up to 2030. Annual economic growth rate is assumed as 7.0%.
Figure 2.1-2 Primary Energy Consumption Forecast for 2030 (BAU case)
[...]
Source: Compiled by JICA Project Team, based on the present energy consumption data and forecast of the future growth rate by sub-sector, derived from UNFCCC Second National Communications, Oct. 2012
- EE&C Potential
- How to grasp EE&C potential?
Before start EE&C action and/or setting EE&C target, we must know how we are wasting energy or how much EE&C potential we have. Table 2.1-3 shows the comparison between no-EE&C and EE&C case in production, building and life style. The comparison can be evaluated through indicators, as shown.
Table 2.1-3 Comparison between No-EE&C and EE&C Case
[...]
“Energy intensity” is the indicator, which comprehensively represent energy efficiency of production in factory, building use, nationwide energy consumption per GDP and others. The energy intensity is given by calculating unit energy consumption per production, building floor area, GDP, etc.
Typical method to grasp EE&C potential is comparing the actual energy intensity of a production facility, to the best energy intensity which may be achieved in the most advanced factory in our country or foreign countries. The energy efficiency of appliances/equipment, such as AC, refrigerator, TV, motor and transformer can be compared to the “high efficiency type” in a similar way.
- EE&C potential in industrial sector
As already mentioned, our country’s manufacturing industries are not efficient in energy use, because of old and poorly-maintained machines and poor energy management. Table 2.1-4 shows examples for energy intensity comparison between our country and Japan, where almost all industrial production has the best energy intensity in the world.
Table 2.1-4 Comparison of Industrial Energy Intensities
[...]
Accumulating EE&C potential in industrial sub-sectors, through energy intensity comparison and actual on-site energy audits, we can find that our country has large potential on EE&C as shown in Table 2.1-5 and Figure 2.1-5. Total EE&C potential is estimated at around 30% of the entire sector consumption. Considering that about 50% of national primary energy is consumed in industrial sector, the potential impact of EE&C measures is massive; almost 15% reduction.
Table 2.1-5 EE&C Potential by Industrial Sub-sector
Source: JICA Project for EE&C Master Pan
A: Present energy consumption B: EE&C case energy consumption Source: Compiled by JICA Project Team based on the data from gas and electricity distribution companies’ data Figure 2.1-3 Industrial Sector’s EE&C Potential
- EE&C potential in residential sector
Efficient type products are available at the home appliance market, however the sales are minor at present. If all existing home appliances in residences are replaced by the highest efficiency type products, huge scale of energy consumption reduction can be achieved. This is the meaning of “EE&C Potential”. Table 2.1-6 shows rough estimation of energy consumption reduction rates (EE rate) by appliances introduced by the current EE technologies, and Figure 2.1-6 shows present electricity consumption by home appliance (A) and EE case electricity consumption (B) using the EE rates given in Table 2.1-6. EE&C potential is estimated at around 36%.
Table 2.1-6 EE Rate and EE&C Potential of Home Appliances
A: Present electricity consumption B: EE case electricity consumption
Source; Surveyed data by JICA Project Team, EE potential is estimated by the Team
Figure 2.1-4 EE&C Potential of Home Appliances
On the other hand, many people will become users of other home appliances, such as micro wave ovens, personal computers, audios and home-automation appliances, which consume additional electricity. And it is important to guide the people to choose energy efficient products, when we buy new ones.
- EE&C potential in commercial sector (buildings)
In buildings, electricity is the main energy consumed. Around 50% of the total energy is consumed in air conditioning and from 10 to 30% is consumed in lighting. And expected potentials for these 2 categories are as follows:
- Air conditioning: 50% by applying high efficient ACs with inverter technology
- Lighting: 50% by applying high efficient lighting system, such as LED lamp, T5 florescent lamp with electronic ballast or utilizing solar light
Thus total EE&C potential for commercial sector is supposed to be about 50 %.
- Target for 2030
There are several indicators to evaluate the improvement of future national energy efficiency, such as energy consumption per capita, energy consumption per Growth Domestic Product (GDP) and the reduction amount of energy consumption etc. Energy consumption per capita is not suitable for developing countries like Bangladesh. And in case of evaluating by the reduction amount, it is not easy to fix the national baseline in the future. Besides energy consumption per GDP can consider both the energy efficiency and increase of national economy. Therefore we will use “primary energy consumption per GDP” as an indicator to evaluate future national energy efficiency.
As mentioned in the last paragraph, theoretically EE&C potential for major energy consuming sectors ranges from 31% to 50%. However, there exist a quite large number of low efficient factories, buildings and home appliances. Changing these into higher efficient ones is not easy and takes time. And it is estimated that with formulating suitable regulatory measures and incentive mechanisms, which are mentioned in the following pages, in accordance with nationwide actions for energy conservation, 20% reduction of primary energy consumption per GDP can be achieved by 2030. And by 2021, when gas and power supply shortage is expected, 15% reduction of primary energy consumption per GDP is to be achieved. Here in the Master Plan, EE&C target and road map are set as Table 2.1-7. The targets both for 2021 and 2030 are set with consideration of the EE&C potential and current energy consumption status;
i.e. low electrification ratio, insufficient industry’s environmental protection measures, improvement of work condition and life style etc. Final goal of EE&C policies is to realize self-reliant cycles, rather than compulsory EE&C activities. We aim to accomplish the target, and realize a “self-reliant EE&C” society by 2030.
Table 2.1-7 EE&C Target & Implementation Roadmap (2015-30)
- Basic policy of the EE&C programs to meet the target
- Approaches to be considered
Since we are responsible for energy use, such policies and programs may represent heavy burden on some establishments and individuals. We have to take the following points into account:
- EE&C policies should be applied on large energy consumers and also small and medium sized enterprises (SMEs).
- The policies should start in a limited scope (narrow range) and expand to wide range, as administrative capacity buildings fostered.
- Starting with voluntary program and shift to mandatory program
- EE&C policies should not be prioritized and enforced, without providing basic regulations and measures for ensuring safety for, life, health and environment. For example, we recognize that pollution control in industrial sector has not yet been carried out at sufficient level, but environmental equipment consumes energy. Thus, before applying mandatory energy efficiency label on home appliances, regulation for assuring safety and minimum performance should be provided.
- Keyword is not “reduction of energy”, but “rational energy use”. Bangladesh people need more energy for better and convenient life
- Check all means to avoid fictitious achievement and ensure correct EE&C picture is highlighted at every level.
- EE&C policy/program mix
EE&C policy/program mix is needed for achieving the EE&C target shown in Table 2.1-8. These policies and programs have been introduced in advanced countries and neighboring countries.
Table 2.1-8 EE&C Policy Mix
[...]
Residential Consumers
- Large energy consumer designation
- Energy Manager, Certified Energy Auditor and Accredited Energy Auditor certification with qualification and examination system
- Energy audit (mandatory/voluntary)
- Energy consumption reporting (mandatory)
- Benchmarking
- Label certification / Laboratory accreditation system
- Standardization of EE measurement method and Star Label Rating criteria
- Star Label Standardization (Unification)
- Participation of manufactures, importers and retail shops (mandatory/voluntary)
- MEPS (Minimum Energy Performance Standard)
EE Building Program
Buildings ■ New version of BNBC [Revised] Implementation
- GBG development
- Manual and assessment system introduction
EE&C Finance Program
Private Companies
- Low-interest loan for EE&C investment
Preferential taxation on high efficiency equipment/appliances and/or EE&C investment
- Monitoring and Review of the Plan
- Follow up of Energy Consumption
We must establish energy consumption data collection mechanism, in order to monitor our country’s energy consumption accurately. Table 2.3-1 and Table 2.3-2 show the data and collection intervals.
Table 2.3-1 Collection of Energy Consumption Data (Primary energy)
[...]
Table 2.3-2 Collection of Energy Consumption Data (Secondary energy)
[...]Industry
- Primary energy consumption
- GDP
- Population
- Energy consumption and industrial production by:
- Chemical industries
- Fertilizer industries
- Cement Manufacturers
- Steel and Re-rolling Mills
- Brick Manufacturing
- Rice mills
- Cold Storage
- Frozen Foods
- Sugar Mills
- Paper Mills
- Jute Mills
- Textile Mills
- Garment Industry
[...]
- Monitoring of EE&C Programs Implementation
Besides energy consumption data, indicators which express EE&C programs implementation and achievement of the EE&C target will be collected as shown in Table 2.3-4.
Table 2.3-4 Monitoring for EE&C Programs Implementation
[...]
Program
- Report and Review of the EE&C Master Plan
The monitoring data will be reported by the Government (SREDA).The report will be uploaded on the Government website.
JCC (Joint Coordination Committee), whose members consist of the Governmental organizations and related stakeholders, will be held for the review of the EECMP. Result of review must be reported and uploaded on SREDA’s website.
Chapter 3 Action Plan
- Overview
EE&C action plan is prepared to describe practical methodology to achieve and accomplish the EE&C target fixed in the EECMP, which contains EE&C programs framework and organization structure. The following points are taken into account:
- Distinction between plans and rules: Provision of rules (regulations) is one of the measures to realize the plan, which gives administrative power to the Government and/or clarifies roles and responsibilities of each party (stakeholder).
- Distinction between standards and rules: Rules have administrative power, but standards have no such power. Standard should be provided solely for defining terms and methodologies relating to EE&C programs.
- Consideration of universality, adaptability for future changes in social and technical conditions, including EE&C technology development and improvement.
- Consideration of document issuance approval processes, authority and responsibility of the governmental organizations in charge, and/or importance of the concerned document
Roles and Responsibilities of Participating Parties
3.2.2 Organization Structure for EE&C Implementation
EE&C implementation is a multi-sectoral issue and should be done by the participation of all the people and establishments in the country. EE&C activities by the parties are related with several organizations which have roles and responsibilities for support and enforcement of rules, and/or EE&C awareness as shown in Figure 3.2-1.
Figure 3.2-1 Organization Structure for EE&C Implementation
- MPEMR
- Comprehensive Energy and EE&C policy implementation
Ministry of Power, Energy and Mineral Resources (MPEMR), has a responsibility for the overall planning and development of the energy and electricity sector. The ministry has two separate divisions namely: (i) Power Division and (ii) Energy and Mineral Resources Division and, each division is headed by a Secretary. The Power Division is responsible for the electricity sector including implementation of energy efficiency and renewable energy programs. The Energy and Mineral Resources Division is responsible for exploration and management of natural gas and mineral resources.
MPEMR also has a responsibility for EE&C on energy/electricity supply and energy tariff as the remaining part of the EE&C Master Plan.
- Multiple EE&C policies
MPEMR should formulate and implement multiple EE&C policies including voluntary program, mandatory program, financial program, informational program, environmental assessment and provision of infrastructure, in coordination with the necessary mandates.
- Consideration of EE&C on other policies
MPEMR should consider EE&C, when formulating and implementing their policies even when the subjects are not concerned with energy or EE&C.
- Government own initiative on EE&C implementation
MPEMR should lead government own initiatives of EE&C activities at its working places and in projects, in order to promote EE&C and lead all entities’ EE&C implementation.
- SREDA
- Establishment of SREDA
Based on the recognition that efficient energy use in demand side is essential, the Government established Sustainable and Renewable Energy Development Authority (SREDA) in 2012, which is the implementating agency for EE&C and renewable energy development under MPEMR.
- National representative on EE&C policies
SREDA’s status is a national EE&C policy representative. It has roles and responsibility on the following activities.
- National information center of energy and EE&C
- Cross cutting (multi-sectoral) coordination of EE&C policies among all governmental organizations and also non-governmental organizations, including EE&C requirement into other governmental organizations’ policies
- Formulation and implementation of its own EE&C policies, such as energy management program, EE labeling program etc.
- Nationwide monitoring of energy consumption and EE&C implementation and its reporting to the people
- Advocacy and awareness raising
- Relevant activities on EE&C implementation
Besides the above roles for the national representative, SREDA will have the following relevant actions:
- Conducting studies, research, development and pilot demonstrations for all stakeholders
- Provide training for capacity development at institutional levels
- Providing advisory services to the private sector corporate bodies, government and non-governmental organizations
- Promote local and international experience sharing in the field of RE, EE&C for capacity development
- Manage EE&C finances to promote innovative pilot projects in the country to enhance RE, EE&C coverage in the country
- Documentation and dissemination of results and information
- Strengthening consultancy services to establishments in the field of energy conservation.
- Establish close cooperation with the private sector by creating linkages with appropriate personnel in different establishments at root level and top level. Inter-ministerial focal points
- Development of expertise for successive implementation of EE&C throughout the country
- Other Governmental Organizations
- BERC
The Bangladesh Energy Regulatory Commission (BERC) was formulated under the Act of Parliament in March 2003, with the mandate to regulate the electricity, gas and petroleum sectors. Apart from the other activities, BERC is also empowered to ensure energy efficiency in generation, exploration, production, transmission and distribution levels of the related sectors.
BERC has a responsibility for formulating EE&C plan on electricity supply as the remaining part of the EECMP.
- BSTI
BSTI has provided BDSs (Bangladesh Standards) on energy efficiency (EE) measurement for the EE labeling program. It has the following roles and responsibility:
- Issue of BDSs relating with the EE labeling program
- Conduct of energy efficiency tests required for the EE labeling program
- MOI, BAB
MOI positions as the authority, administrating the industrial sectors, which should join in the energy management program and EE labeling program and other EE&C programs. MOI has the following roles and responsibility:
- Cooperation in the enforcement of energy management program with SREDA
- Cooperation in the enforcement of EE labeling program with SREDA, especially on encouraging appliance manufacturers participation on the program
- Coordination and monitoring of industrial associations on EE&C activities
BAB (Bangladesh Accreditation Board) belongs to MOI, and is an accreditation body for ISO9000, 14001 and 50001, which have a relation with EE&C. BAB is expected to have the following roles and responsibility:
- Accreditation of laboratories for energy efficiency measurement tests on the EE Labeling Program, based on ISO17025, etc.
- Roles on energy manager/auditor licensing system
- MOF and Governmental financial institutes
Ministry of Finance (MOF) is responsible for making budgets for EE&C policy promotion activities. MOF allocates budgets to relevant ministries and governmental organizations which request for financial support. For investments for both public and private establishments, MOF provides loans through government financial institutions, Bangladesh Bank (BB) and Infrastructure Development Corporation Ltd. (IDCOL), delegated by Subsidiary Loan Agreement (SLA) or Administrative Agreement (AA). For promoting EE&C through financial incentives, Sustainability and Renewable Energy Development Authority Fund (SREDA Fund) is another option. SREDA Fund is a fund for EE&C activities conducted by SREDA. SREDA Fund can be sourced through funds from grants or loans obtained from the Government, local authorities, international donor agencies, benefit obtained from business (consultancy, fees), etc.
BB and IDCOL are key financial institutions to support financial incentives for EE&C. They handle funds budgeted from MOF according to SLA and lend money to establishments or individuals who need money for investing in energy efficiency (EE) facilities and equipment. Both BB and IDCOL have already had experiences as a financial promoter of EE&C investment. BB is the central bank of Bangladesh; however, BB has the role of a development finance institution which supports business. Therefore, BB can take the role of supporting establishments by lending money via PFIs (Participating Financial Institutions).
- MOEF (Ministry of Environment and Forest)
MOEF is the responsible authority for global warming issues, which should be tightly dealt with energy and EE&C policies. MOEF has the following roles and responsibility:
- Countermeasures for global warming should be well coordinated with EE&C policies.
- Also, ozone layer destructive material emission relating to refrigerants used in AC, refrigerator and chilling machine should be coordinated with high energy efficiency products.
- Provision of regulations on pollution control and waste disposal, applicable to EE&C policies implementation (eccentric EE&C implementation without human life and health care should be avoided).
- MOC (Ministry of Commerce)
Activation of energy efficient product trade is expected for the promotion of EE&C in our country. For that purpose, MOC has the following roles and responsibility:
- Encouragement of trade of (high) energy efficiency products, including removal of NTB (Non-Tariff Barrier) collaborating with foreign countries
- Awareness and dissemination to the traders, retail shops and consumers
- MOHPW (Ministry of Housing and Public Works)
MOHPW has started New Version of Bangladesh National Building Code (BNBC [Revised]) and Green Building Guideline (GBG) which can promote EE&C at buildings. Therefore, MOHPW is expected to take following roles and responsibilities:
- To implement BNBC [Revised] steadily, including continuous up-dating the regulation
- To widely promote and spread GBGTo coordinate EE requirement in the building codes with SREDA
- Awareness and dissemination to the building owners, developers, designers and building users
- To support Ministry of Transportation for preparing EE&C plans on transportation
- Ministry of Transportation
The EE&C Master Plan has been made excluding plans for EE&C on transportation sector. This Ministry is expected to take the following roles and responsibilities:
- To prepare EE&C plans on transportation sector and add them to the EECMP
- To make coordination with SREDA especially on the level of EE&C requirement
- Ministry of Education
Awareness and dissemination of EE&C is the basic policy of self-reliant EE&C implementation. Ministry of Education is expected to be in charge of this field and have the following roles and responsibility:
- Introduction of EE&C, as one of themes for environmental education
- Initial instruction of EE&C to teachers
- EE&C improvement in schools
- Promotion of EE&C activities in households through students
- Promotion of self-reliant EE&C activities of the children
- Ministry of Agriculture
Modernization and mechanization in our country’s agriculture will accelerate growth in energy consumption. Ministry of Agriculture is expected to take the following roles and responsibility:
- Education of irrigation consumers including concerned organizations staffs
- Introduction of irrigation based on RE on massive scale
- Ministry of Information
Medias is influential on EE&C awareness and dissemination. Ministry of Information is expected to have roles and responsibility relating on media’s activities in EE&C.
- Local Governments
Local governments are expected to take the following roles and responsibilities considering their condition on environment and society respectively:
- To make efforts to plan, formulate and implement their own EE&C policies, considering their social and natural condition
- To conduct urban planning, namely “Low carbon city”, in which low energy consumption occurs by means of EE buildings and public transportation system
- To take initiatives and develop projects on EE&C activities on their own office, in order to lead the people and establishments in the area and motive them to take same EE&C actions are expected to occur in public hospitals, schools and other institutes under the local governments.
- It may be welcome to take more advanced (progressive) policy than the Government
- Administration of BNBC [Revised] and GBG
- Energy Supply Side
Energy supply companies are also large energy users. Therefore, they are expected to take the following roles and responsibilities:
- To improve energy conversion and transmission efficiency at their plants and delivery system
- To give instruction and advisory on EE&C to customers (energy consumers), using the direct connection with them.
- To collect/analyze energy consumption data, including its delivery to SREDA for monitoring nationwide energy consumption
- To prepare EE&C plan for energy supply sectors as the remaining part of the EECMP
- To formulate a functional tariff system, in order to foster EE&C and peak shifting incentives
- Establishments (Business Operators)
The establishments include both private and public sectors, which are expected to have the following roles and responsibilities:
- Compliance with EE&C rules and regulations
Business entities should keep and follow the EE&C rules and regulations, which will be introduced and scheduled to be officially issued by the Government, such as energy management program, EE Labeling Program and EE Building Program.
- EE&C as a social responsibility
Business entities should understand that energy is a social common resource, which should be used fairly and rationally. They should make plans for efficient energy use, monitor their energy use, and frequently review their EE&C implementation situation. They should instruct the employees about rational energy use, and jointly improve the activities with the other establishments, associations, unions and central/local governments, sharing information and technologies on EE&C.
- Culture and life-style of EE&C
Business entities are expected to create culture and life-style on EE&C and disseminate it to the people.
- Preparation for the coming energy price up
It will be impossible to keep the energy prices in future as cheap as at present which are mainly maintained by the governmental subsidy. Business entities should know this situation and should prepare the society for higher energy price in near future.
- Specific roles of the business entities
Relating to the EE&C programs introduced in this plan, the business entities should have the roles shown in Table 3.2-1.
Table 3.2-1 Specific Roles of the Business Entities
Organizations Expected roles[...]
- Preparation for the coming energy price increase
It will be impossible to keep the energy prices in future as cheap as the present levels, which are mainly maintained by the governmental subsidies. We have to recognize this situation and properly prepare consumers for higher energy price in near future. EE&C is the most effective countermeasure.
- NPOs, NGOs
Bangladesh is the country where relatively many NPOs and NGOs exist and have functional activities, influencing people’s life. Therefore, they are expected to take the following roles and responsibilities:
- To consider EE&C activities on their business, service and project
- To develop new business, service and project related with EE&C
- International Donor Agencies
International donor agencies (donors) provide grants, loans, and/or technical assistance for promoting EE&C dissemination for our country. Their roles are defined as follows:
- Long-term and continuous technical and financial support for proliferation of EE&C policy measures
- Capacity development for EE&C regulators and promoters: including ministry officials, staff members from public and private establishments, etc.
- Donor coordination to guarantee synergism on EE&C activities
Figure 3.2-1 shows a perspective of the projects which have been supported by the donors in our country, categorized by policy and financial supports (vertical axis) and demand-side and supply-side EE&C (horizontal axis). As shown at the bottom right of the figure, loans for the purpose of promoting demand-side EE&C seems not be implemented except for some small components. Possibility of mobilizing private funds for these untouched areas utilizing policy-based finance will also be needed.
[...]
Figure 3.2-1 Projects Supported by International Donor Agencies (Perspective)
At present, there are 6 donors, which are actively supporting EE&C in our country: ADB (Asia), GIZ/KfW (Germany), JICA (Japan), World Bank, UNDP, and USAID (USA) etc. It is important for all donors to know what each of them is doing for EE&C for this country. When they try to have interactive communication, their works will result in more synergism for all EE&C activities in our country.
- Energy Experts
Energy experts who have experiences to work at energy consuming industries and/or have knowledge about energy and EE&C are expected to take the following roles and responsibilities:
- To be a leader of EE&C implementation
- To watch and share the latest EE&C technologies and do their own capacity development
- Networking and information share among the energy experts
- Establishing the community of energy experts
- Academics, Laboratories and Researchers
Many professors and researchers are interested in the energy situation in our country and carrying out studies on energy issues. They are expected to take the following roles and responsibilities:
- To stimulate young generation people to become energy experts
- To participate in the committees and WGs for EE&C policy making, and to give advice and opinion from neutral view point position
- To carry out researches and development of the themes for rational energy supply and EE&C
- To take parts in energy efficiency measurement and test for appliances/equipment as 3rd party laboratory
- Committees and WGs
Several committees and working groups (WGs) should be formulated inviting relevant stakeholders, governmental organizations and academies to figure out an effective and feasible plan. Committees and WGs are expected to be continuously formulated focusing on the following roles and responsibilities:
- To periodically monitor and review implementation and achievement of the Master Plan
- To disseminate the Plan and programs through the industrial associations ,which take parts in the committees and/or WGs
- EE&C Programs (Overview)
Action plans for the major EE&C policies and programs shown in Table 2.1-1 are drafted in this clause. Necessity of policies and programs covering the relating situation on energy consumption, program outline and implementation methodology, stakeholders’ roles and responsibilities, roadmap and expected outcome are introduced hereinafter.
Action plan on transportation sector, energy supply sector and energy tariff have not yet been included in the Master Plan. Policies on these remaining fields should be studied and issued in future.
- Energy Management Program
- Overview
Energy supply companies (energy and power suppliers) and industrial sectors are the main consumers of energy and responsible for the increase of primary energy consumption as shown in Figure 3.4-1 and 4-2. Due to inefficient and old boilers, furnaces and motors used in the industries, a huge amount of energy is being wasted. The electricity consumption is increasing rapidly especially in the residential sector, recently. This sector is responsible for about 50% of the total electricity use while, the industrial sector share is 34%, and the commercial sector shares 9%.
Consumption of natural gas in industrial sector includes consumption for captive power. Also, gas consumption in industrial sector (incl. captive power) is increasing rapidly, recently.
The industrial sector is the largest energy consumer of natural gas and electricity. Therefore improvement of energy efficiency and conservation in the industrial sector is the highest priority issue. In this context, nationwide efficient energy management measures should be introduced to accelerate the energy efficiency and conservation of industrial sector.
Energy Management Program has been introduced in many countries aiming to promote EE&C implementation by large energy consumers. The program is composed of several parts as shown in Figure 3.4-3.
Figure 3.4-3 Energy Management Program
The Government is going to issue the regulations for the program. Large energy consumers in industrial sector and buildings will be named as “designated large energy consumers” (DCs) by the regulation. They are obliged to implement EE&C measures and report them to the Government, which is also described in the regulation. The regulation also stipulates the certification procedure for energy managers/auditors, who are directly engaged in EE&C implementation in the factories and buildings.
- Designation of Large Energy Consumers
50% of national primary energy consumption is consumed in industrial sector. And 30% of energy consumption in industry sector is consumed in about 100 large factories. And if these large factories can improve energy consumption by 20%, then national energy consumption will reduce by 3%. Designated large energy consumers (DCs) program aims to improve energy efficiency in large consumers in accordance with the leadership by SREDA. The numbers of DCs is estimated about 100 at first stage and will be increased to 1000 in 2030.
“Designated large energy consumers” (DCs) are defined by the regulation. Designation criteria of DCs by annual energy consumption are shown in Table 3.4-1 DCs, whose annual energy consumptions exceed the threshold value, should submit application sheets. DCs’ annual energy consumptions are calculated by using the heat value of fuels and primary energy conversion factor of the grid electricity as shown in Table 1.3-4.
Table 3.4-1 Designation Criteria and Number of DCs by Category
- Energy Management in DCs and Other Energy Consumers
DCs are obligated to conduct “energy management” in their factories and/or buildings, in order to implement EE&C measures. Energy consumers out of DCs are also expected to conduct energy management. The energy management consists of the following elements:
- Establishment of EMS (Energy Management System)
DCs must establish EMS which includes the following actions:
- Setting up EE&C target and establish energy management team (group)
- Appointing a full-time energy manager
- Implement EE&C activities according to EE&C promotion plan
■ Conduct energy audit of the facilities on annual base
- Follow the EE&C target and certain criteria including benchmark, minimum energy efficiency standards and specific technology requirement
- Conduct training of EE&C activities for management and employees
- Accreditation of ISO 50001 is welcome. It will be recognized as the establishment of EMS.
- Appointment of Energy Manager
Energy managers should be a cadre, who runs EMS and conducts EE&C actions in the factory and/or buildings including in-house energy audits. The energy manager in DCs must have national certificate of “energy manager”.
- Energy Audit
Energy consumers will implement energy audits for their facilities or buildings periodically. DCs must submit energy audit reports to the Government (SREDA). The energy audits will be done by certified energy auditors. In case of large DCs, the energy audits must be done by “accredited energy auditors”
- Annual Energy Report
DCs must prepare annual energy reports and submit them to the Government (SREDA). SREDA will check the trend of energy intensity for a continuous period of 5 years. The annual energy reports will contain the followings:
- Total energy consumption (by source of energy, i.e., fuel, heat, electricity)
- Name, outline, operating condition and modification of energy intensive equipment
- Energy efficiency and productivity levels (relative to output, measured through the production volume)
- Energy intensity trend for 5 years
- Identification of appointed energy manager
- Annual EE&C plan including measures and target as shown in Table 3.4-2
- Medium term EE&C plan including measures and target as shown in Table 3.4-2
Table 3.4-2 EE&C Improvement Plan
[...]
- Certification of Energy Manager, Certified Energy Auditor and Accredited Energy Auditor
- Certification system
The Government (SREDA) will establish national certification system of energy managers, certified energy auditors and accredited energy auditors defining the followings:
- Training program
- Examination
- Qualification criteria for applicants for the training program and examination of the energy managers, energy auditors and accredited energy auditors, knowledge and work experiences.
- Disclosure and maintenance of personnel list of energy managers, certified energy auditors and accredited energy auditors.
- Energy Managers, Energy Auditors and Accredited Energy Auditors
- Participation of many eligible candidates for the certification is expected.
- Industrial sector, academy and relevant entities should find and induce the candidates.
- Benchmarking
(1) What is the “Benchmark?”
Benchmark is the target values of energy efficiency, which will be defined for the nominated sub-sectors with specific process, such as steel-making, cement, paper& pulp and soda chemical. Benchmark is described in kgoe/ tonne of production or floor area (m2). Processes of these industries are same as that of the other countries in the world. Therefore the energy intensity of these industries is comparable to other countries without any compensation.
Benchmark data are reported in the annual energy report to SREDA. The factories attained the target level are awarded by SREDA and their name and award data are published on the SREDA website.
The candidate industries qualified for the benchmarking at 1st stage are shown in Table 3.4-3 with
benchmark index and target level. Target level figures in the table are referenced based on international data. Real target level is decided through discussion between manufacturers and SREDA.
Table 3.4-3 Benchmark Target Level by Industrial Sub-sector
[...]
(Source: Data provided by Prof. Ijaz, BUET)
(Note: Target level should be changed with the increase of EE technologies)
The role of benchmarking will be decided by SREDA, such as voluntary target or future mandatory target with penalty system.
- DCs’ Energy Consumption Data Collection System
- Objective
DCs are obligated to report their annual energy consumption and EE&C actions to SREDA.. SREDA is developing “Periodical Energy Consumption Reporting System (PRS)”. PRS has the following objectives;
- To provide DCs’ convenience on making the reports, grasping their own energy consumption and reviewing EE&C actions.
- To watch DCs’ EE&C actions and make administrative instruction, if necessary.
- To aggregate energy consumption data by sector, industrial sub-sector, calculate energy intensity and grasp nationwide energy consumption and EE’C implementation tendency.
- To utilized the data for the benchmarking program.
- To disclose accumulated data to use for awareness and dissemination.
- Energy Data Reporting
Energy data to be reported is shown in Table 3.4-4. Each datum listed in the table below is collected annually. Besides annual energy consumption, monthly consumption data are also reported optionally.
Table 3.4-4 Reporting Items
[...]
Figure 3.4-4 shows reporting scheme of the periodical energy report
Energy managers prepare annual energy report under President or CEO’s supervision. Energy manager can submit the report by the following two methods.
Method -1: Prepare paper report and send it to SREDA directly or by mail. Submission by e-mail will be permitted. The data is fed to computer by SREDA officers.
Method -2: Energy managers login the Energy Reporting page of SREDA website with LN (login name) and PW (password), and input the energy data in the decided format of each establishment.
Energy consumption data are sent to Data Base (DB) server and accumulated. The DB data are processed as statistical graphs and disclosed on the energy consumption statistics page in SREDA website. It is available for inspection by anyone with PC, tablet and smart phone.
Figure 3.4-4 Periodical Reporting System
- Roles and Responsibilities of Energy Management Program
Roles and responsibilities of each participating ies in the program are summarized in Table 3.4-5.
Table 3.4-5 Roles and Responsibilities of Energy Management Program
- [...]
Roadmap up to 2030
Roadmap up to 2030 for the energy management program implementation is shown in Table 3.4-6. Targeted implementation ratio (energy consumption basis), which is expected to be achieved by introducing the regulatory measures below, is shown in Table 3.4-7.
Table 3.4-6 Energy Management Program Implementation Roadmap
Table 3.4-7 Targeted Coverage Ratio of EM Program by Industrial Sub-sector (energy consumption basis)
To be discussed in 5th mission
- EE (Energy Efficiency) Labeling Program
- General
The purpose of EE Labeling Program is to promote sales of high efficiency products in the market. The program is applied mainly on home appliances, such as room Air Conditioner (AC), refrigerator, TV, lighting, and fan. In order to achieve the EE&C target in 2030, average efficiency of each home appliance is expected to increase more than 20% and near to 30%, because with the increase of economy, the number of home appliance, which are purchased by people will sure to increase in future. The program is the most effective measure to promote EE&C in residential sector.
Penetration of high efficiency appliances contributes to reduction of energy consumption (kWh) and also to reduction of electricity demand (peak load: kW).
Table 3.5-1 shows how the latest EE&C technology on home appliances/equipment is energy efficient compared with conventional ones.
Table 3.5-1 EE&C Technology of Home Appliances/equipment
EE&C technology Improvement of efficiency Large evaporation coil
Note: COP means co-efficient of performance; consumed kW/ input kW CFL means compact florescent lamp
Our country is joining BRESL (Barrier Removal and Cost Effective Efficiency Standards and Labeling) Program under UNDP, and has already started EE labeling program. However, the label has limited impact on the market, because elements of the program, as shown in Table 3.5-2, have not yet been sufficiently and suitably prepared. The elements should be developed and prepared promptly.
Source; BSTI
Figure 3.5-1 Bangladesh EE Label
Table 3.5-2 Elements for the EE Labeling Program
[...]
Program operation body
fairly. Measurement method includes EE indicator (unit), test protocol, test facility, measurement devices, and EE calculation method. The method should be issued as national standards (BDS) or quoted by international standards such as ISO/IEC.
Criteria for giving star numbers on measured EE performance are necessary. The criteria must be designed according to EE&C policy and market condition. MEPS (Minimum Energy Performance Standard) can be included in the criteria. The criteria should be issued as governmental notice or national standards.
Verification system to maintain credit of the labels is needed. EE data used in the labels should be checked by some authority.
Capable laboratories, which can conduct EE measurement tests, are needed for the program. National laboratories, international 3rd party laboratories and also manufactures in-house laboratories can also be candidates.
Authority that conducts the label certificates issue, monitors labels in the markets, provides programs information, reviews star rating criteria and follow-up EE products market penetration.
- EE Labeling Procedure and Verification System
EE labeling procedures are summarized in Figure 3.5-2. Verification system assuring reliability of the label and product EE performance are to be included.
Figure 3.5-2 EE Labeling Procedures
Actual procedure is as following:
- Manufacturers/importers get EE test on their products at accredited laboratories.
- Accredited laboratories should have been accredited by BAB throughISO17025, etc.
- Manufacturers/importers which have in-house laboratories can get EE test at their laboratories, provided laboratories are accredited by BAB
- Label certification body evaluates the EE test report and issue label certificate on the product with star rating, and delivers it to the manufacturer/importer
- Manufacturers/importers affix the label on the products or their packages, and deliver them to the markets.
- Label certification body carry out EE check test for the products sold in the market collecting samples at random, in order to maintain labels reliability.
- Anybody can claim challenge test to the label certification body, provided the test cost is backed by him/her
- Laboratories Capacity Development and Accreditation
Sustainable participation of the testing facilities must be accompanied with periodical maintenance, calibration, skilled personnel and demand of EE tests. Capacity development for skilled personnel needs long time and experiences, especially in case of refrigerator and AC. On the other hand, accreditation capacity of BAB should be also developed, since accreditation should be issued by testing. Therefore, BAB must be knowledgeable about testing procedures. Introduction of testing facilities, capacity of testing and accreditation bodies should be developed by SREDA and BAB.
- Products EE Database
In order to provide energy efficiency data of home appliances to customers, it is effective to construct a “product EE database”, which shows not only energy efficiency and stars in label, but also capacity, size, performance and other product information. The database should be maintained by SREDA.
3.5.4 Harmonization with International and/or Regional EE Labeling Programs Many countries have their own EE labeling program and label design. Some countries have 5 star rating, 4 star rating, and others have 7-10 star rating. Also EE measurement methods (standards) are different by country. To break through this chaos-like situation, regional and/or worldwide discussion to harmonize the standard and labeling program has started. Our country should join in this movement, analyzing
neighboring countries’ and world trends, to establish our EE labeling program. “Mutual recognition agreement (MRA)” between other countries on EE tests must be also studied for minimizing EE testing cost.
- Roles of Parties (Stakeholders)
Many parties are expected to take parts in the EE labeling program. Their roles are summarized in Table 3.5-3.
Table 3.5-3 Roles of Parties (Stakeholders)
Party (stakeholder) Roles
- Total management of the program
- Issue of star rating criteria
Directorate of National Consumer Rights Protection (DNCRP) of MOC
Manufacturers, importers
Retail shops, traders
Customers
- Label certification, as requested by manufacturers
- Provision of products EE database
- Analyze neighboring countries, and join in the harmonization
- Provision and maintenance of BDS on EE measurement
- Harmonization with other countries
- EE test in 3rdparty laboratory
- Promotion of EE products trading
- Join in the program
- Compliance on the regulation of the program
- Development of EE products
- Instruction (explanation) of EE performance to customers
- Understanding of the program
- Instruction (explanation) of EE performance to customers
- Understanding of the program
- Selection of EE products
Party (stakeholder) Roles
3rd party laboratory
- Obtain accreditation on EE tests
BAB ■ Accreditation of laboratories on EE test
EE labeling program committee
- Review of the program
- Recommendation on BDSs and renewal of star rating criteria
- Check and Review
Sales data of the labeled products and efficient products should be collected by market researches. The target monitoring items are shown in Table 3.5-4 and 5-5.
Table 3.5-4 Monitoring the Programs Implementation
Item Indicator Interval
EE Labeling Program
People’s conscious on EE label
Energy consumption at households
- Sales of labeled products
- Energy efficiency
- Is the label meaning understood?
- EE products procurement promotion
- Energy consumption by appliance and equipment
- Penetration of EE products
Every 3 years
Every 5 years
Every 5 years
Table 3.5-5 Check and Review Points on the Program
Item Point
EE measurement method ■ Comparison with other countries for harmonization
- Suitability of star rating criteria, relation to advanced EE technology, penetration of EE products, and domestic
Star rating criteria
manufacturers’ capacity.
- The criteria should be gradually up-graded.
- Roadmap up to 2030
The EE Labeling Program is initially starting as voluntary program, because mandatory program needs full provision of EE testing services, since it is requested by manufacturers and importers, who are obligated to get EE products data, and have not their own test facilities. It will require long time and budget for the provision of test facilities from the EE&C administration side. In case of the voluntary program, manufacturers and importers can join the program, if they have in-house laboratories or they can outsource EE test to some 3rd party laboratories. Roadmap up to 2030 for EE Labeling Program implementation is shown in Table 3.5-6. Targeted implementation ratio (energy consumption basis), which is expected to be achieved by introducing the regulatory measures below, is shown in Table3.5-7.
Table 3.5-6 EE Labeling Program Implementation Poadmap
Fiscal year 2014-15 2015-16 2016-17 2017-18 2018-19 2019-20 2020-25 2025-30
Regulation
Framework
▼Issue: Oct. 2015
Phase 1 : Room AC, refrigerator/freezer, 3 phase induction motor, CFL, electric fan, gas cook
- Standards
- Laboratory capacity
Development
Full-fledged for all market request
- Implementation
- Label penetration
- MEPS
- High efficiency product penetration
Voluntary ▼Jan. 2017 Mandatory
All products are labeled Provision of MEPS if necessary
Almost all appliances are efficient
Phase 2
: Water pumps, Electric water heaters, Microwave ovens, Television sets, Clothes irons, Rice cookers, Blenders/mixers, Washing machine
- Standards
- Laboratory capacity
Development Full-fledged for all market request
- Implementation
- Label penetration
- MEPS
- High efficiency product penetration
Voluntary
▼Jan. 2018 Mandatory
All products are labeled
Provision of MEPS if necessary
Almost all appliances are efficient
Phase 3: other appliances
Voluntary
Table 3.5-7 Targeted Introduction Ratio of EE Labeling by Appliance
COP: Coefficient of Performance, APF: Annual Performance Factor, SPF: Seasonal Performance Factor
ODP: Ozone Depletion Potential, GWP: Global Warming Potential, R32 & R600; refrigerant
- EE Building Program
3.6.1 Overview
The existing energy consumption ratio is not so large compared with industrial and residential sectors. Besides the energy consumption is rapidly increasing in buildings in Bangladesh. Especially new buildings construction is remarkable in city area. Therefore it is needed to implement an effective counter measures to mitigate this issue. And New Version of Bangladesh National Building Code (BNBC [Revised]) is going to be published by Ministry of Housing and Public Works (MOHPW), taking into consideration energy conservation in buildings as well. BNBC [Revised] is the core program for promoting EE buildings.
EE&C measures for buildings are as followings:
- Reduction of incoming heat from outside to inside by means of heat insulation, air-tight door/window and sun shine control
- Introduction of energy efficiency building equipment and appliances
- Appropriate use, operation and maintenance of the building and building equipment
However, these EE&C measures and rational energy use are not yet sufficiently implemented in Bangladesh.
Bangladesh National Building Code (BNBC) is the mandatory program which provides regulation and/or minimum requirement of building type (office, residence, commercial building, etc.), size (height, floor area), structure strength, indoor condition, construction material, etc.
Currently, addition of energy efficiency requirement of buildings in the code is on-going. BNBC [Revised], will be issued instead of the existing BNBC, by MOHPW. BNBC [Revised] will be the core program for promoting EE&C in Buildings and contain the following requirement on building energy efficiency:
- Heat insulation and/or ventilation performance of building envelope
- Energy efficiency of building equipment (HVAC, lighting, fans, hot water supply, lift, escalator, renewable energy options)
- Water efficiency and management
On the other hand, Green Building Guideline (GBG) is a voluntary program that provides recommendations not only on energy/water use efficiency but also on reduction of environmental impact caused by building construction, use and decommissioning. Development of green building guideline is an international movement. GBG is planned for the completion by 2025.
EE&C requirement issues in BNCB [Revised] are the minimum standards. On the other hand, EE&C requirement issues in GBG will be recommended and effective since it allows obtaining upper-grade EE&C performance than the buildings fulfilling BNCB [Revised].
- New Version of Bangladesh National Building Code (BNBC [Revised])
- EE&C requirement issues in BNBC [Revised]
Provisions of EE&C requirements in BNBC [Revised] consist of minimum requirement, standard specification and recommendations on the design and construction method. Table 3.6-1 shows outline of the requirement.
Table 3.6-1 EE&C Requirement Issues in BNBC [Revised]
Category Contents
- Roof insulation and green roofing system
- Window to wall ratio
Building envelope
HVAC(Heating, Ventilation and Air-Conditioning)
- Window opening
- Shading
- HVAC system
- Ceiling and wall mounted fans
Hot water supply ■ Solar hot water system
- Day lighting and supplementary lighting system
Lighting
- Lighting power density
- Occupancy sensors
Lift and escalator ■ Energy efficiency of lift and escalator
Renewable energy
Others
- Other renewable energy
- Water management (Reuse of gray water, efficient fittings in toilets)
Some requirements in BNBC [Revised] quote the criteria from foreign building codes and standards. To make them more compatible to our country’s climate, culture and manner and more acceptable for our laws and regulations, they will be reviewed and revised.
Also, EE&C requirements of building insulation materials will be introduced in association with EE&C materials and presented in the GBG.
- Application of BNBC [Revised]
In order to widely promote building EE&C in our country, application of EE&C requirement issues in BNBC [Revised] will be implemented and extended in a phased manner (under study by MOHPW). Table 3.6-2 suggests how the areas can be changed to expand the coverage of the code.
Table 3.6-2 BNBC [Revised] Coverage of Gloss Floor Area in m2 of Building Types
Categories 2015 2017 2019 2022
Hotel ≥5,000 ≥5,000 ≥3,000 All
Note: Year is a calendar year from January to December.
- Roles and responsibilities for BNBC [Revised] enforcement
For enforcing BNBC [Revised] and promoting EE&C in the buildings, all stakeholders should understand and carry out their roles and responsibilities as shown in Table 3.6-3. In order to disseminate the roles and responsibilities to all stakeholders, nationwide awareness raising program and capacity development program are needed.
Table 3.6-3 Roles and Responsibilities of Related Stakeholders
- Check and monitoring system to ensure building EE&C performance
Building permit under the existing BNBC is the procedure to check and verify that buildings are surely designed in accordance with rules and regulations and are constructed following the original plan and design. However actual EE&C performance of the buildings cannot be assured by the current procedure.
Additional check and monitoring system as shown in Table 3.6-4 will be provided in BNBC [Revised].. Submission of Notification and periodical report will be obligated for large scale building owners.
Table 3.6-4 Check and Monitoring Systems under BNBC [Revised]
Stage Check and monitoring systems
Local governmental agency checks if the plan and design are made in accordance with the building codes and the relevant regulations. If thebuildings are not planned and designed properly, the governmental organizations recommend and instruct their redesign. If the buildings are not redesigned, the local governmental agency does not permitconstruction of the buildings.
Design
Building owners report Notification on energy saving measures to the local governmental agency, prior to start of the construction. If theruction
[...]
Periodical Report for EE&C measures
EE&C measures are insufficient, the local governmental agency recommends or instructs the owners to improve measures. In case of disobedience to the instruction, publication of the company name and/or penalty are imposed.
Local governmental agency inspects if the buildings are constructed in accordance with the original plan and design. If the buildings are not constructed in accordance with the original plan and design, the local governmental agency recommends and instructs to modify them. If the buildings are not modified, the local governmental agency does not permit buildings use.
Building owners present Periodical Report to the local governmental agenciy. In the Periodical Report, the operation and maintenance conditions concerning the items described in the Notification are reported.
- Green Building Guideline (GBG)
- Application of the guideline
GBG is a voluntary program and is developing as a guideline for the design and construction of upper-grade EE&C and low environment impact buildings rather than the buildings under BNBC [Revised].. The objects of GBG are office, rental & mercantile (shopping mall), residential, hospital, school and hotel in new large scale projects by both public and private sectors. The Governments will carry out awareness rising of the guideline for building designers and developers.
- EE&C recommendation in GBG
GBG is developed to reduce not only energy and water consumptions but also environmental impacts during construction, use and decommissioning of the buildings. GBG, as a voluntary program, will give recommendation on use of energy and water, waste management, indoor environmental condition, material use at construction and other environmental issues.
- Other Programs for Promoting EE&C in Buildings
- Development of EE&C building manual
In order to encourage proper and effective EE&C implementation in BNBC [Revised]., EE&C building manual for local governments, building owners and users, designers and constructors, will be developed and published by MOHPW, in the initial BNBC [Revised] implementation stage. The manual shall include detailed explanations and concrete construction methods for EE&C measures described in BNBC [Revised].. Also the manual will include not only general measures applicable to all buildings but, also, a variety of recommended measures appropriate and economically beneficial depending on the specific conditions of the individual building and location.
- Development of Green Building Assessment System
Green Building Assessment System will be developed by MOHPW, in association with the GBG development and is compatible to our country’s climate, culture and manner and is acceptable for Bangladeshi laws and regulations. The system will start to be voluntarily applied for large scale development projects such as shopping mall, airport building, hotel and hospital.
In the future, the Green Building Assessment System with GBG will be used as an evaluation method for certification of “Green building” and/or “Net zero energy building”. Green building owners may be rewarded or incentives may be given.
- EE&C for existing buildings under Energy Management Program
In order to encourage energy efficient operation of existing buildings, retrofit with energy efficient technologies and other measures able to reduce energy consumption in existing buildings will be supported.
In the near future, large scale buildings classified as designated large consumers under the energy management program will implement EE&C activities or retrofitting under the program to be leaded by SREDA. SREDA will develop criteria and list buildings, classified as designated large consumers under the energy management program, in association with MOHPW and HBRI.
In the future, MOHPW and HBRI, in cooperation with SREDA, will expand EE&C measures in BNBC [Revised] and GBG to existing buildings.
- Check and Review of the Programs
- Check and review of the programs
MOHPW and HBRI will regularly check and review the progress situations for BNBC [Revised]. implementation and GBG development. If any delay and/or changes on the situations arise, MOHPW and HBRI, in association with SREDA, will prepare reschedules for them. SREDA will provide supports and cooperation to be needed for BNBC [Revised] implementation and GBG development.
- Preparation for statistical database
Building statistical database is necessary to check and review EE&C in buildings. However, the present database for buildings is not sufficient. Building statistical database is needed and properly maintained. The database will include not only existing & constructed floor areas and amount of buildings by building type but also the energy consumption and conditions of EE&C equipment and facilities, which will be researched by consultants and/or be collected through the documentation systems produced under BNBC [Revised], GBG and the other programs like the Energy Management Program.
- Roadmap up to 2030
Roadmap up to 2030 for Program Implementation of BNBC [Revised] and GBG is shown in Table 3.6-5. Expected energy savings in accordance with the predicted EE&C implementation ratio of BNBC [Revised] are shown in Table 3.6-6.
Considering that the current BNBC implementation ratio is low and BNBC [Revised] implementation is conducted in a phased manner, the predicted EE&C implementation ratio of BNBC [Revised] must be quite low at the being. Through the awareness raising and capacity development actions by the Government for local governments and the other stakeholders, it is possible to increase the implementation ratio step by step for full wide use of BNBC [Revised]..
The first largest issue is to conquer the existing buildings that neglect the rules under BNBC.
Table3.6-5 Program Implementation of BNBC [Revised] and GBG Roadmap
Note: Calendar year from January to December is used on a) “Recommendations for Green Building Code for Bangladesh, MOHPW/HBRI and b) “Development Green Building Code for Bangladesh, Development Design Consultants Ltd.”
Table 3.6-6 Expected Energy Savings in Accordance with Predicted EE&C Implementation Ratio of BNBC [Revised].
Note: Percentages in the table are the predicted EE&C implementation ratios for new construction buildings in each year, which are prepared based on the discussion in EE Building Programs WG held by SREDA and JICA and the follow-up discussion with HBRI in November, 2014, considering the increase of the BNBC [Revised]. compliance ratio and the increase of target buildings in a phased implementation manner
- EE&C Financial Incentive Programs
- Overview
Financial support is a key component to disseminate EE&C policies and activities. It motivates people to incorporate EE&C activities into their business and daily lives.
Financial incentives, in definition, are monetary rewards provided for performance of targeted objectives; and they can provide economic benefits for implementing EE&C projects to motivate people’s behavior. Also, financial incentives in general have good effects on raising the people’s awareness on EE&C. Financial incentives will bring a positive economic impact, which will help the government to adopt a market-based pricing system.
Figure 3.7-1 Virtuous Circle of Financial Incentives
For the nationwide dissemination of EE&C policies in our country, especially among industries, it is necessary to provide financial support which is feasible and thus able to be implemented in the local context. (See Figure 3.7-2)
Figure 3.7-2 EE&C Policies and Financial Support/ Incentives
- Types of Financial Incentives
One of the bottlenecks which have been preventing people from implementing EE&C activities is the fact that the prices of EE equipment are generally higher than those of the conventional technology. In order to facilitate the execution and dissemination of EE&C policies in our country, therefore, it is effective to provide financial support. The major financial incentives include subsidies, preferential taxation and low interest loans, the details of which are described below:
- Subsidies
For the quick diffusion of EE facilities and equipment, subsidies can be an effective financial incentive measure since they directly reduced the initial costs of purchasing EE equipment. Beneficiaries would be both individuals and establishments. By specifying the target EE appliances, subsidies could facilitate fast and quick nationwide installation. Subsidies are generally suitable for the application for a limited period of time, in order not to grant long-term privileges to early bird beneficiaries.
- Preferential taxation
Preferential taxation, tax reductions or exemptions, or accelerated depreciation, can be applied to individuals and establishments. Tax incentives will be effective to stimulate people to purchase EE goods, as long as such goods are taxable. One good point about tax incentive is that there is no need to change or add new procedures to the present taxation processes when introducing these incentives. Accelerated depreciation, which allows companies to place the bulk of the costs of an asset in the first few years of its useful life, is also profitable especially, for the industrial and commercial sectors, which are capital intensive.
- Low-interest financing (Loans)
In order to provide a long term financial support for the promotion of EE&C policies, concessional loans are the most suitable and effective. It is especially effective for establishments which plan to introduce or replace large amount of machines and equipment with highly energy-efficient ones. The target beneficiaries for such loan program will be limited compare to the other two financial incentives (namely, preferential taxes and subsidies); it has an advantage of easier implementation through ordinary bank loan procedures. Also, the administrator (such as the central and local governments) can adopt this incentive with less financial burdens compared with the other two financial incentives.
Table 3.7-1 shows major three types of financial incentives which are suitable for EE&C promotion. Their advantages and disadvantages are also summarized in Table 3.7-1.
Table 3.7-1 Types of Financial Incentives for EE&C Promotion
In a broad sense, preferential taxation and subsidy measures are implemented by the Government, whereas low interest loans are provided by financial institutions. Since loans are not gratuitous, and must be repaid thoroughly, beneficiaries are limited to those establishments that meet financial and technical eligibility criteria. This aspect of low interest loans is actually both disadvantage and advantage. Beneficiaries are limited in a sense that they are screened by eligibility criteria, but because of that, low interest loans can promote the intended policy more efficiently.
In contrast to this, the beneficiaries of both preferential tax and subsidy measures are not restricted by financial eligibility criteria. Any establishment and any individual can receive the support for their purchase of EE equipment and EE investments.
With regard to disadvantages, the economic impacts of tax measures such as accelerated depreciation and tax reductions on EE&C are hard to measure, since they both are simply an accounting procedure to reduce taxable income. As for the disadvantage of subsidy measures, implementing EE&C promotion measures require high administrative and transaction costs, which cannot necessarily be quantified.
- The Best Choice of Financial Incentives to Implement in Our Country
For the first step of effective and prompt implementation of EE&C activities in our country, low-interest loan program is the best choice. Here are the reasons:
- Long-term financial support for end-users: Encourage industries to work with energy efficient machineries with improved production quality and quantity (increasing industrial competitiveness)
- Easy to implement for banks and non-bank financial institutions (NBFIs): No need to create a new loan process - Adopting same credit appraisals as normal ones and using eligible lists/ criteria for technical appraisals)
- Less financial burden for the Government: The loan fund will be returned to the Government with interest from participating financial institutions (PFIs: banks and NBFIs)
- Low-interest loan program: “EE&C Promotion Loan Program”
EE&C Promotional Loan Program, low-interest loan program, will be implemented by setting goals below:
- Promotion of the nationwide adoption, execution and proliferation of EE&C programs such as energy management, EE equipment/ appliance labeling and EE building program.
- Creation of new markets for investments in (a) industrial sector EE&C , (b) EE equipment/ appliances and (c) green buildings.
To achieve the main goals, EE&C Promotional Loan Program will need to be designed into two phases, the first phase for implementing flagship EE&C projects to prove the economic viability of EE&C, and the second phase for the nationwide dissemination of EE&C investments.
Figure 3.7-3 Low-Interest Loan Program
The primary beneficiaries of each program are large energy consuming establishments, wholesaler/ distributors/ manufacturers, building owners and developers. For the details, see Table 3.7-4.
Table 3.7-2 Expected Beneficiaries by EE&C Policy
- Flagship Stage
Flagship project stage is necessary to show the economic benefits of EE&C investments to enlighten the general public, especially in the industrial and residential sectors, which are the largest energy consumers in this country. In addition, flagship projects will contribute to the creation of viable and bankable energy efficiency markets for EE equipment/ appliances, green buildings and industrial sector energy management, which is indispensable to convince private sector investors, namely, financial institutions and establishments. In order to meet these objectives, it is important that flagship projects shall be selected carefully in order to ensure their technical viability as well as financial profitability.
- Dissemination Stage
Dissemination stage will be implemented in order to facilitate the execution and nationwide proliferation of the three EE&C policy measures. In this stage, participating financial institutions, namely, banks and non-bank financial institutions including leasing companies and ESCOs (See BOX
1) are urged to provide finance for EE&C investments by end users. In order to make this stage successful, the following activities need to be provided:
- Education of financial institutions (both executives and loan officers) on the economic benefits of EE&C financing (based on the results of flagship projects), financial appraisals method of EE&C projects taking into account the value of energy-saving benefits and the concept of life cycle costs (see BOX 2)
- EE awareness-raising of establishments in industrial sector by introducing the economic benefits of flagship projects, the concepts of simple payback period (see BOX 3) and life cycle costs
According to our survey, average EE improvement of 36% and 30% between 2015 and 2030 can be expected in residential and industrial sector, respectively, considering the current levels of technology in the country. Even under the current low energy prices there is obviously a huge energy saving potential. Adequate financial incentives, therefore, will be needed to motivate financial institutions, establishments in industrial sector, owners of buildings and the households to save energy which unless otherwise will be wasted.
BOX 1 ESCO and quasi-ESCO services
ESCO (Energy Service Company) provides a comprehensive energy-saving services (including provision of energy-saving solutions, instalment of EE equipment, maintenance and operation of installed equipment). ESCO engages in a performance based contract with a client firm guaranteeing certain level of energy efficiency (EE) improvements (i.e. reduction of energy consumption and/or costs) and, in return, receives remuneration out of thus achieved energy savings.
The source of payments to such ESCO services derives from the energy-savings achieved, and the total payment amount will be arranged so as not to exceed the client’s current total energy bill.
There are two major types of models in ESCO business: 1) the guaranteed savings mode in which ESCOs provide clients with performance guarantees, but no financing; and 2) the shared savings model in which ESCOs provide performance guarantees as well as financing.
In the former model, clients themselves procure funds from banks based on their credibility and make repayments out of energy cost savings. And in the latter, energy cost savings will be split between the client and ESCO based on a pre-determined rate. There are also cases where ESCOs are in alliance with banks and leasing companies.
There also exists quasi-ESCO businesses to which no one provides performance guarantees, but financial institutions (such as banks, leasing companies and ESCOs) agree to provide financing based on cash flow expected to be generated from their energy-saving projects. In a quasi-ESCO project, a client firm may enjoy an advantage of introducing EE equipment without any additional financial burden, but at the same time, unlike an ordinary ESCO business, it will have no risk hedge against underperformance due to incidents such as electricity price falls which make it impossible to achieve expected energy cost reductions. In such a case it is important to involve well established and trusted manufacturers which can provide high quality EE products with long warranty and good maintenance services.
- Timing to Move on to the Dissemination Stage
With regard to the timing to move on to the Dissemination Stage, the Government shall wait until the market interest rates start to pick up again. Under the current market situation, where interest rates are constantly slipping downwards, end user interest rates will not be attractive enough to encourage EE&C investments. PFIs would need to ensure certain amount of interest margins to cover the risks involved in promoting EE&C loans which will make the end-user interest rate high when the market interest rate is on the down ward trend.
- Check and Review of the Loan Program
- SREDA’s Responsibility
SREDA is a nodal institution for identification, promotion, facilitation and overall coordination of all national renewable energy and energy conservation programs. In other words, SREDA has to ensure its monitoring authority over EE&C activities in this country by receiving reports from relevant ministries, financial institutions, and other organizations which are in charge of data collection related to EE&C. For example, financial institutions which provide policy promotion programs will report SREDA the total amount of money disbursed, what these incentives are used for, how the energy saving was achieved (e.g. replacing and/or installing EE equipment), etc. (See Figure 3.7-4)
Figure 3.7-4 EE Effects Reporting to SREDA
- Technical Standard Committee
It is recommended that SREDA will establish an independent Technical Standard Committee for the implementation of the EE&C policy promotion loan program. Main roles and responsibilities of the Committee will be to compile the eligible EE equipment list/ EE standards and criteria to PFIs in order to support their technical appraisals of EE&C projects. SREDA as the secretariat of the Standard Committee, will hold meetings on regular basis (for instance, every 6 months) to review and revise the list/standards/criteria reflecting the market trend by inviting technical experts from both private and public sectors.
- Roadmap up to 2030
The roadmap up to 2030 for the establishment of EE&C finance program is shown in Table 3.7-3. In order to execute and disseminate EE&C policies, it is highly recommended that the Government will provide an EE&C policy promotion loan program starting as early as possible. Idealistically an adequate timing for the start of this program would be the year 2016, taking into account the enforcement processes of EE Rule and Regulations, EE labeling program, energy management program and BNBC (Bangladesh National Building Code [Revised]).
With regard to the implementation of the EE&C policy promotion loan program, it is recommended that the program will be implemented in two parts: the introductory phase where selected flagship projects will be financed as showcases; and the dissemination phase where the nationwide EE&C investments will be stimulated through financing via participating finance institutions (PFIs).
It is considered effective to finance flagship projects for a short and limited period of time (for three years between 2016 and 2018) in order to show the actual economic benefits of EE&C investments to the private sector investors, both financiers and establishments. On the second phase, the data on EE&C effects collected from flagship projects will be disseminated to private sector investors through financing via PFIs which is expected to start as early as in 2019, following the completion of the three-year loan
disbursement for flagship projects. See Table 3.7-3 for the details of the establishment of EE&C policy promotion loan program.
During the nationwide EE&C policy dissemination phase, subsidy as a financial incentive can also be provided by utilizing the revolving loan fund (i.e. collected principal and interest payments from the first phase loans). Part of the fund earmarked for grants can be provided to support energy audits, EE electric appliances testing, interest subsidies for EE equipment investments, etc.
In addition, as a supplementary financial incentive measure, the Government can also consider the adoption of tax incentives (tax reduction/ exemption) targeted at specific industrial manufacturers sector, which produce high energy efficient products. As for the import duties of EE&C goods and materials, it is recommended that the Government will continue the already granted preferential treatment to industrial sector products (as low as 2%) as long as necessary.
Table 3.7-3 EE&C Finance Program Roadmap
To implement financial incentives, SREDA and the Government can utilize concessional loans and grants available from international donor agencies as well as its own tax revenues. In the future, for the country’s sustainable energy supply and demand management, the Government may create a new source of fund, such as tax on fossil fuels, part of which can be earmarked for promoting investments in EE&C activities as well as the overall reform of the energy supply and demand sectors.
- Government Own Initiative on EE&C Implementation
- Overview
The energy management program and EE building program mentioned above must be also applied on governmental organizations which include local governments, state-owned companies, semi-governmental organizations and other public sectors. The governmental organizations should surely comply with the regulations of the programs and implement EE&C. Also, the governmental organizations are expected to take part in the voluntary EE&C programs such as EE labeling program and GBC (Green Building Code) by adopting EE products on their purchase, design and construction of green buildings. The EE&C activities and results should be monitored and disclosed to all people, in order to inspire and promote them to take EE&C actions.
Government facilities and operations should include office buildings, schools, hospitals, military facilities, government provided or managed housing, vehicle fleets, roads, bridges, airports and other infrastructure.
- Planning
Firstly, SREDA will develop a typical EE&C action plan which can be applied to all governmental organizations. Secondly, governmental organizations must prepare their own EE&C action plan, and submit them to SREDA. The plan must include contents as shown in Table 3.8-1
Table 3.8-1 Governmental organizations’ EE&C Action Plan (examples of contents)
[...]
- EE&C Implementation
The governmental organizations must conduct EE&C actions according to the plan, and make efforts to achieve the EE&C target.
- Monitoring, Reporting and Disclosure
Governmental organizations must report their monitoring result on the EE&C action, and disclose it to the public annually. SREDA will analyze the reports. When some negligence on EE&C implementation is found, it must give necessary instruction to the governmental organizations.
- Support Services by SREDA
SREDA will provide information on energy efficient products recommended for government procurement, energy efficient design features for new buildings, good practices for energy management and retrofit, and or advisory services for EE&C planning and implementation including energy audits.
- Check and Review of the Program
Check and review of the program must be done by the governmental organizations individually. SREDA will check and review nationwide performance of the Government own EE&C initiative.
- Roadmap up to 2030
As shown in “Phase 1”, SREDA and the governmental organizations must start the program. Table 3.8-2 shows the roadmap of the program implementation for the governmental organizations up to 2030. Table3.8-3 shows the targeted implementation ratio by program.
Table 3.8-2 Program Implementation for Governmental organizations Roadmap
Table 3.8-3 Targeted Implementation Ratio by Program[...]
- Country’s Energy Consumption Data Collection Mechanism
- General
In order to curry out nationwide energy management is firstly necessary to grasp and monitor our country’s total energy consumption and also to break down the energy consumption by sector such as industry, business, transportation, residence and energy supply. Country’s total energy consumption can be relatively easy to grasp, through the amount of domestic energy production and energy import from foreign countries.
- Energy Data Collection in Our Country
The International Energy Agency (IEA) was founded in 1973 by 28member states. It has been working for to plan energy policy with the balance on environmental protection, energy security and economic development. And IEA performs statistical survey on manufacturing and energy around the world, and has issued various books and reports. “World Energy Outlook” is the typical one which shows the forecast of the energy market over the medium and long-term.
By analyzing the energy data of IEA, annual energy usage of each country including Bangladesh can be grasped. Our country’s energy balance in 2012, analyzed by IEA, is shown in Figure 3.9-1. Referring this IEA data and other useful existing data collecting mechanisms, our country’s energy data collecting mechanism will be designed and established.
Figure 3.9-1 Energy Balance in Bangladesh in 2012[...]
Source: Compiled by JICA Project Team based on IEA contry statistics
- Roles and responsibility
Table 3.9-1 shows the role share of planned and existing databases, for formulating effective energy consumption data collecting mechanism among the related governmental organizations.
Table 3.9-1 Role of Parties for Energy Data Collecting
[...]
- Roadmap up to 2030
Roadmap up to 2030 for the establishment of energy consumption data collection mechanism is shown in Table 3.9-2.
Table 3.9-2 Energy Consumption Data Collection Mechanism Roadmap
Global Warming Countermeasure
Overview
Carbon market
As discussed at the Introduction, policies and actions are already established in many countries, as a way to stimulate Climate Change mitigation. Figure 3.10-1 shows the geographical distribution of operational and near operational programs at the end of 2013. Some of them, as shown by the straight black arrow are international, in the sense that they may provide revenue for Climate Change mitigation actions occurring in other country.
By far the largest market for international carbon credit is the EU-ETS16, shown at Figure 3.10-1 as the big blue ball. According with these carbon market rules, which includes the Clean Development Mechanism (CDM), which associates projects developed in DC and LDC to a certain amount of carbon credits. These carbon credits have a value at the market. Other carbon markets or similar rewarding
16 EU-ETS means European Union Emission Trade Scheme
markets exist and new ones may grow soon, as is the case of the California Cap and Trade Program and the Japanese Joint Cooperation Mechanism also shon in Figure 3.10-1.
New agreements about Climate Change shall be set at the end of 2015, and dependent on the extension that the regulation covers a growing share of GHG emissions in all participating country, and on the level of the cap defined, it is possible that further carbon credits or some equivalent reward will show up. An increase in the value of 1 tonne of CO2eq avoided is widely expected if reductions on global GHG emission shall follow the suggestion of IPCC, which is a decline of 20% in the next few years and more than 50% by 2050.
Source: Mapping Carbon Pricing Initiatives – Development and Prospects 2013 World Bank Report2013.pdf
Figure 3.10-1 Map of Existing, Emerging and Potential Emission Trading Schemes
- Capacity development as “Carbon abatement project”
All carbon abatement project associated with Climate Change mitigation requires monitoring, reporting and verification (MRV), considering that its purpose is the real abatement of a quantified amount of GHG emission. Even before expenses with MRV occur, usually a complete document has to be prepared, explaining details of the project, which implies in more costs for the project owner. Furthermore, project implementation has its own cost. Table 3.10-1 lists all these costs for some of the most common project categories and it is important to comment that the values quoted may be underestimated since only a share of the presented projects are registry and qualifies for carbon credits. Finally, not only money is necessary to registry a project, but the availability of qualified personnel to design and implem is needed. Thus, the EE&C Master Plan proposes Capacity Development on this issue.
Finally, the Master Plan recognizes that considering our country’s extreme fragile situation regarding Climate Change impacts, a good control about all actions and projects performed in the country, yielding GHG emissions abatement, shall be fully monitored and used as a marketing activity at global level.
Table 3.10-1 Total Cost of New Carbon Abatement Projects Registry in EU-ETS (CDM projects), According with the Technology used.
Source: UNEP Risoe, CDM and PoA pipelines, March 2013
- Capacity Development and Carbon Abatement Awareness Raising
- Capacity development
All carbon value associated with Climate Change mitigation requires MRV. To perform MRV not only money is necessary, but the availability of qualified personnel to design and implem is needed.
- Awareness raising
It is necessary that the Government and major private establishments accurately understand about carbon impacts on Climate Change and the relevance to accurately quantify carbon abatement due EE&C projects. These evaluation can directly yield complementary resource of international money helping our country’s development. Thus, awareness rising will be obtained through seminars, folders, and notes prepared and distributed by SREDA.
- Cooperation with International Donor Agencies
There are several projects cooperated by international donor agencies (donors) for supporting the effort of EE&C from the demand side: for example, ADB, GIZ, JICA, USAID, World Bank etc.
The EECMP should mobilize donors’ access to EE&C activities. The donors are expected to communicate closely and cooperate with the Government in order to avoid duplication of their support and to create synergetic efforts.
Chapter 4 Economic Analysis of the EE&C Programs
- Background and Objectives
Economic viability and benefits of EE&C measures are already well introduced and tested 17 . Nevertheless, when it comes to a nationwide implementation of EE&C programs, it is not as easy and smooth as electricity supply side measures, such as the introduction of power plants utilizing renewable energy sources (i.e., wind, solar, geothermal and water). This is largely due to generally small investment size of each EE&C measure, which implies relatively high transaction costs, as well as to general sense of insecurity towards Negawatt (saved electricity by EE&C) or cash flow from EE&C which financiers (investors or lenders) do not know how to collateralize18.
In order to solve these problems and promote a nationwide EE&C implementation, economic viability and benefits of EE&C programs must be quantified in monetary terms and shared with all interested parties.
First of all, from the viewpoint of effective and efficient implementation, economic viability of each EE&C programs has to be verified by clarifying and comparing its costs and benefits (Cost-Benefit Analysis). In addition to energy consumption reduction, which is the primary and direct benefit of the EE&C implementation, secondary and indirect benefit shall, in some cases, be taken into consideration in order to justify the costs involved.
Secondly, from the viewpoint of effective allocation of limited resources, the Government has to compare candidate EE&C programs according to their cost effectiveness (or costs per unit of energy saved). After all, the Government has the responsibility to prioritize the allocation of limited resources to economically viable projects and to avoid implementation of those that seem to waste time and resources.
- Economic Impact of EE&C Implementation
The direct economic benefit of EE&C implementation is energy consumption reduction. In addition, EE&C programs could also bring about several other positive economic impacts to the electricity demand side (namely, residential, industrial and commercial sectors) as well as to the electricity supply side of the economy as shown in Figure 4.2-1.
- For the residential sector, reduction in consumption of energy (gas and electricity) implies extra pocket money, which contributes to poverty reduction that improves health and social conditions of daily life of the people.
- For the industrial sector, EE&C implies less energy costs per unit of production, which will increase industrial competitiveness and thus promote reinvestments in other productive activities that contribute to job creation.
- For the commercial sector, EE&C implies an efficient energy management of buildings, which contributed to appreciation of asset values.
17 There are several reports published from International Energy Agency (IEA) on economic benefits of energy efficiency improvements and policies to promote them. http://www.iea.org/topics/energyefficiency/
18 OECD/IEA (2012), by Ms. Lisa Ryan, Ms. Nora Selmet, Mr. André Aasrud, “Plugging the Energy Efficiency Gap with Climate Finance”
- For the electricity supply side, less electricity demand as a result of EE&C implies less fuel costs for electricity generation, which contributes not only to the improvement of trade balance through decreased fuel imports, but also to lower energy prices.
- For the Government, less energy demand implies less public budgets for electricity generation, which contributes to less energy subsidies and thus better management of limited resources as well as better fiscal management.
- Lastly, less energy demand implies less GHG emissions and thus climate change mitigation, which will contribute to the accomplishment of Millennium Development Goals.
Figure 4.2-1 Economic Benefits of EE&C Implementation
- Cost-Benefit Analysis
- Basic Concept
In general, economic evaluation of a policy measure is done by comparing the situation where the intended EE&C program is applied (With case) with those not applied (Without case). In concrete, the amounts of energy consumptions for “Without case” and “With case” are estimated and compared. “Without case” will also be referred to as the business as usual (BAU) case, while “With case” as EE&C case. (See Figure 4.3-1)
Figure 4.3-1 With (EE&C) vs. Without (BAU) Comparison (Image)
- Calculation Method and Data
How do you quantify EE&C programs? In principle, due to data limitations, each program will be independently quantified according to its data availability. In one case where time series data is available, energy consumption data before and after the adoption of the target EE&C program can be calculated and compared. In the other case where the target beneficiary (end user) is clearly focused, energy consumption of target and non-target beneficiaries can be calculated and compared.
As a matter of fact, all EE&C programs to be implemented under this MP are new and to be introduced for the first time in our country. Since there is no time sequential data available from the past, target vs. non-target comparisons will be conducted for the economic evaluation of each EE&C program. Publicly disclosed statistics and data will be utilized for the evaluation; and in some cases where adequate data is not available, raw data must also be collected independently through sample surveys.
- Secondary and Indirect Economic Benefits
The primary and direct economic benefit of EE&C programs is energy savings or economic value of reduced amount of energy consumption. This can be calculated by multiplying the total reduced amount of energy consumptions (converted into toe) by the unit price of energy (BDT/ toe).
In the country where energy prices (gas and electricity prices) are politically subsidized and kept lower than the market prices, however, direct economic benefit is sometimes not enough to cover the costs of the target policy measure. In such a case, secondary and indirect economic benefits (such as those listed in Figure 4.2-1) have to be taken into account in the calculation of economic benefits so as to justify economic viability of the target EE&C program.
- Identification of Cost and Benefit Factors
As the first step to quantify economic viability and benefits of EE&C programs, both cost and benefit factors must be identified and listed up. (See Table 4.3-1) In general, economic evaluation of regulatory measures (such as energy management, EE labeling and EE building) face more difficulty in identifying
cost factors, compared with the case of economic measures (such as low interest rate loans, subsidies and preferential taxes); It is generally troublesome to differentiate the administrative costs which are devoted solely to EE&C programs from those spent for other purposes. Therefore, for regulatory measures, administrative costs are often dismissed in cost calculations.
Table 4.3-1 Benefit and Cost Factors
[...]
- Comparison of Annual Benefits and Costs
For each EE&C program, annual benefits shall surpass annual costs.
[Annual Benefits – Annual Costs > 0]
Annual benefits are calculated as below:
- Calculate annual amount of energy reduced (kWh/year, m3/year, etc.)
- Calculate the annual benefit by multiplying the reduced energy amount by the unit price of energy. (BDT/year)
- Annual benefit will be sustained for the number of years as long as the energy saving effects will last (which is usually equivalent of the useful life of EE equipment); therefore, each new investment to be implemented under each EE&C program will generate an additional stream of benefits for its EE sustainable life (measured in years).
The total annual benefits of the EE&C program will be calculated by adding up the annual benefits derived from each investment (See Table 4.3-2).
Table 4.3-2 Calculation of Annual Benefits (Image calculation)
*Note: Investment 1~3 each represents the amount of energy (electricity/gas) to be reduced by one investment
Annual costs are calculated as below:
- Calculate total costs (See Table 4.3-2) to be included under each EE&C program.
- For amortizable assets, calculate annual costs by dividing the total costs by the legal useful life (10-30 years) of each machinery/equipment or by the average legal lives of buildings’ attachments (15 years in general), depending on the type of assets acquired. As for other costs, such as administrative costs of implementing EE&C program, use an average expected annual expense for the cost calculations.
- Sensitivity Analysis
In order to conduct the cost-benefit analysis of an EE&C program, several assumptions have to be established in order to calculate the future energy consumptions of target end users. For instance, in order to estimate the future electricity consumptions of the households which purchase specific electrical
appliance, several specific assumptions must be established for the future households’ aging structure, actual income and actual electricity prices. This implies the fact that calculation assumptions have direct impact on the result estimation. Therefore, it is important to conduct a sensitivity analysis to grasp the degree of error, for instance, between ageing and non-ageing of population, between assumed economic growth and lower-than-assumed economic growth, and between assumed electricity price and higher-than-assumed electricity price.
4.4 Cost Effectiveness Analysis
The Government aims to improve energy intensity (national primary energy consumption per gross domestic product/GDP) in 2030 by 20% compared to the 2013 level. This goal will not be attained without the Government’s strong leadership, peoples’ consciousness and actions to realize it. A total of 95 million toe (113 billion m3 of gas equivalent) will be saved in the period. Energy savings will amount to BDT 768 billion in total, or an annual average BDT 51 billion at the current weighted average natural gas price.
For the sake of effective utilization of limited public resources, it is important for the Government to prioritize implementation of EE&C programs and projects according to their cost effectiveness. Marginal Abatement Cost (MAC) curve can be drawn by plotting the data of costs (BDT) per unit of energy reduced (toe) and annual amount of energy reduced. In the MAC curve, the project which require the lowest costs (BDT) per unit of energy saved (toe) is placed at the lower left of the diagram and the project with the highest cost will be placed at the upper right of the diagram, as shown in Figure 4.3-2. In other words, those projects that appear below the horizontal axis can be implemented at a net benefit, while those above the horizontal axis can be implemented at a net cost. For the effective allocation of limited resources, it is wise for the government to prioritize the implementation of EE&C projects according to their cost effectiveness.
Source: Compiled by JICA EE&C MP Project Team based on independently collected data
Figure 4.3-2 MAC Curve of EE&C Flagship Projects
With regard to EE&C programs, namely, EE Building Program, EE Labeling Program and Energy Management Program, it is also recommended for the Government to prioritize their implementation
according to their cost effectiveness. Most of the projects to be promoted under these three Programs are cost effective and can be implemented with a net benefit..
Table 4.4-1 EE&C Projects (Examples) Representing Each EE&C Program
[..]
- Installment sales of EE type appliances to the residential sector
- Purchase of EE type industrial machineries and equipment in the industrial sector
- Production of EE type machineries and equipment in the industrial sector
- Construction of new green buildings and EE buildings in the commercial sector and government sectors
- Investments in EE retrofitting of old buildings in the government sector
Chapter 5 Capacity Development and EE&C Awareness Raising
- Overview
- Roles of the Government on capacity development and awareness raising Initially, the Government should lead and have a responsibility for capacity development and awareness raising to promote EE&C. Besides considering the importance of EE&C for our country, such roles are to be taken not only by the Government but also by relevant private sectors, NPO/NGO, individuals and other entities. Thus nationwide structure for EE&C awareness raising has to be formulated.
- Capacity development
For EE&C implementation, capacity development for governmental organizations, private sectors and energy experts is needed. It is important to cooperate with related organizations and programs to implement these activities effectively.
- Awareness raising
It is necessary that all the people accurately understand about the energy and natural resource issues, for nationwide EE&C implementation. In order to realize this, the Government should promote an awareness raising and information provision for all stakeholders more effectively. The final goal is that all the people and establishment take voluntary EE&C actions.
- Roles of the Government on Capacity Development and Awareness Raising SREDA should be the leading agency on capacity development and awareness raising. It carries out the following roles and actions in cooperation with the related governmental and/or private organizations and programs.
- Preparation of regulations and guidelines for EE&C implementation, specifying good practices and developing pilot and demonstration projects as a showcasing
- Capacity development of the other governmental organizations
- Capacity development of energy experts
- Capacity development of private sectors
- Awareness raising for residential sector
Other governmental organizations conduct capacity development and awareness raising for themselves and their sub-structuring organizations and related stakeholders, such as schools, industrial associations, etc.
- Capacity Development for the Government
- SREDA
SREDA should lead overall issues to promote EE&C in our country. And it has the responsibility to formulate capacity development programs for the governmental organizations (both central and local).
Nationwide EE&C cannot be realized only by SREDA, but by the comprehensive cooperation and partnership among other governmental organizations and local governments.
- Capacity Development for Energy Experts
Energy experts, who have knowledge, experiences and interest in EE&C, are the candidates for future certified energy managers, energy auditors and accredited energy auditors. SREDA should develop the capacity of these energy experts, through training programs. Besides because of the limitation of SREDA’s capacity, not only SREDA but also our country’s social systems should focus on the capacity development for energy experts; such as university curricula, internal training courses in establishments, publication of educational materials and introduction of success experiences from abroad etc.
- Capacity Development and Awareness Raising for Private Sectors
- Overview
Capacity development and awareness raising for private sectors will be implemented though National EE&C award, in accordance with the yearly electricity week, monthly seminar and monthly focus group seminar. Focus group seminars should be implemented focusing on the effective target sectors.
- National EE&C Award and Yearly Electricity Week
National EE&C award should be given for the establishments and energy managers, whose activities are worth being highly evaluated and to be good examples for the people. The targets of EE&C award consist of public buildings and commercial buildings.
National EE&C award ceremony, exhibition of energy technologies and equipment, and international seminars and workshop on EE&C is to be held in the yearly electricity week, which is held early December. Educational materials, such as leaflets, posters and booklets are to be distributed during the event.
- Monthly Seminar and Monthly Focus Group Discussion
SREDA is carrying out seminars and focus groups (important consumers to implement EE measures at time) discussion for target energy consumers on monthly basis . And these activities should be ifostered and continued.
- Efforts by Industrial Association
All industrial associations are conscious of cost reduction and sustainable operation of their business. In this context, the Government should communicate with them and make information exchanges on effective EE&C measures and imaginable future risks on energy supply etc. SREDA and related governmental organizations should lead to establish an EE&C focusing committee in each industrial sub-sector.
- Awareness raising for Residential Sectors
- Overview
Awareness raising for residential sector consists of EE&C school program initiative and media campaign.
- EE&C School/University Program Initiative
The EE&C school program initiative will be formulated focusing on students. Through the discussion with their parents and knowing their present energy consumption condition, the children can understand what the energy consuming appliances are, and how to save energy use from them etc.
The Government will conduct EE&C school/university program, which will be a joint program with SREDA and Ministry of Education. The target of this school program will be the students under 15 years old in primary and secondary school.
Educational curricula on efficient use of energy and its conservation for primary, secondary and higher educational institutions, universities or autonomous bodies will be prepared by SREDA, Ministry of Education and related organizations and fixed into their syllabus. The School/university Text Book Board will review the curricula periodically.
The following actions will be adopted in school/university curriculums:
- Exhibition of video clips and documentaries on energy efficiency and conservation practices and their benefits.
- Organizing spot quiz.
- Introduction of appropriate posters in schools.
- Organizing thematic art competition.
- Motivational talks by experts or professionals
- Media Campaign
Media campaign will be implemented through effective media, such as televisions, newspapers and advertising boards, discussions, street campaigns, school campaigns, competitions with prizes, etc. The Government will conduct media campaign in cooperation with related governmental and/or private organizations being coordinated by SREDA.
- Roadmap
Roadmap up to 2030 for awareness raising program implementation is shown in Table 5.7-1. Targeted people’s consciousness level is shown in Table5.7-2.
Table 5.7-1 Awareness Raising Program Implementation Roadmap
Table 5.7-2 Targeted People’s EE&C Consciousness Level