NOTE: Some content may not display correctly, including tables and figures. See PDF for full details.
MASTER PLAN
ON ASEAN CONNECTIVITY
One Vision, One Identity, One Community
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) was established on 8 August 1967. The Member States of the Association are Brunei Darussalam, Cambodia, Indonesia, Lao PDR, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and Viet Nam. The ASEAN Secretariat is based in Jakarta, Indonesia.
For inquiries, contact: The ASEAN Secretariat
Public Outreach and Civil Society Division 70A Jalan Sisingamangaraja
Jakarta 12110 Indonesia
Phone : (62 21) 724-3372, 726-2991
Fax : (62 21) 739-8234, 724-3504
E-mail : [email protected]
General information on ASEAN appears online at the ASEAN Website: www.asean.org
Catalogue-in-Publication Data Master Plan on ASEAN Connectivity
Jakarta: ASEAN Secretariat, January 2011
380.0959
1. Transportation – Communications
- Investment – Partnerships – ASEAN
First published: December 2010 1st Reprint: January 2011
ISBN 978-602-8411-62-2
The text of this publication may be freely quoted or reprinted with proper acknowledgement. Copyright Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) 2011
All rights reserved
HA NOI DECLARATION ON THE ADOPTION OF THE
MASTER PLAN ON ASEAN CONNECTIVITY
WE, the Heads of State/Government of Brunei Darussalam, the Kingdom of Cambodia, the Republic of Indonesia, the Lao People’s Democratic Republic, Malaysia, the Union of Myanmar, the Republic of the Philippines, the Republic of Singapore, the Kingdom of Thailand and the Socialist Republic of Viet Nam, on the occasion of the 17th ASEAN Summit;
RECALLING the ASEAN Leaders’ Statement on ASEAN Connectivity issued in Cha-am Hua Hin,Thailand, on 24 October 2009;
REAFFIRMING that enhancing intra-regional connectivity within ASEAN would benefit all ASEAN Member States through enhanced trade, investment, tourism, people-to-people exchanges, and development which would complement the ongoing regional efforts to realise a people-oriented ASEAN Community by 2015;
WELCOMING the work of the High Level Task Force on ASEAN Connectivity in developing the Master Plan on ASEAN Connectivity with the ASEAN Secretariat and relevant sectoral bodies, in cooperation with international organisations such as Asian Development Bank (ADB), Economic Research Institute for ASEAN and East Asia (ERIA), United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP) and World Bank;
RECOGNISING that the Master Plan on ASEAN Connectivity will promote economic growth, narrow development gaps, ASEAN integration and Community building process, enhance competitiveness of ASEAN, promote deeper social and cultural understanding as well as greater people mobility and connect its Member States within the region and with the rest of the world;
EXPRESSING appreciation for the support shown by our Dialogue Partners towards theASEAN Connectivity initiative and their readiness to partner with ASEAN in the implementation of the Master Plan;
DO HEREBY:
- ADOPT the Master Plan on ASEAN Connectivity, including a list of prioritised projects, which each ASEAN Member State will implement in accordance with the agreed-upon timelines.
- TASK concerned Ministers, the ASEAN Connectivity Coordinating Committee and the National Coordinators, supported by the ASEAN Secretariat, to coordinate and oversee the implementation the Master Plan on ASEAN Connectivity and to report to us the progress of its implementation on a regular basis through the ASEAN Coordinating Council in consultation with the ASEAN Political Security Community Council, ASEAN Economic Community Council and ASEAN Socio-Cultural Community Council.
ADOPTED in Ha Noi,Viet Nam on this Twenty Eighth Day of October in the Year Two Thousand and Ten, in a single original copy in the English Language.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY____ i
INTRODUCTION:
Background and Rationale for Developing the Master Plan____ I
CHAPTER 1:
Vision, Goals and Objectives of ASEAN Connectivity____ 5
CHAPTER 2:
Achievements of, and Challenges and Impediments to ASEAN Connectivity____ 11
CHAPTER 3:
Key Strategies for Enhanced ASEAN Connectivity____ 37
CHAPTER 4:
Mobilising Resources for Enhancing Connectivity in ASEAN____ 57
CHAPTER 5:
Implementation 65
APPENDICES____ 69
I.1 : ASEAN Leaders’ Statement on ASEAN Connectivity
2.1 : 47 Designated Ports and Their Respective Cargo Throughput 2008
2.2 : Status of Ratification of ASEAN Transport Facilitation Agreements
2.3 : Broader Development Challenges Faced by the BIMP-EAGA Sub-Regional Initiative
4.1 : Prioritised Projects for ASEAN Connectivity
MASTER PLAN
ON ASEAN CONNECTIVITY
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
- The vision of ASEAN Leaders to build an ASEAN Community by 2015 calls for a well-connected ASEAN that will contribute towards a more competitive and resilient ASEAN, as it will bring peoples, goods, services and capital closer together. An enhanced ASEAN Connectivity is essential to achieve the ASEAN Community, namely the ASEAN Political-Security Community, ASEAN Economic Community and ASEAN Socio-Cultural Community.
- In light of rapid developments in the region and the world resulting from globalisation, ASEAN must continue to strive to maintain its centrality and proactive role by being the driving force in the evolving regional architecture. To do so, ASEAN needs to accelerate its integration and Community building efforts while intensifying relations with external partners.
- As a key step towards realising the ASEAN Community of continued economic growth, reduced development gap and improved connectivity among Member States and between Member States and the rest of the world by enhancing regional and national physical, institutional and people-to-people linkages, ASEAN has developed this Master Plan on ASEAN Connectivity.
- Under the Master Plan, ASEAN has reviewed the achievements made and the challenges encountered or that are impeding each of these linkages. Key strategies and essential actions have been adopted with clear targets and timelines to address these challenges to further enhance ASEAN Connectivity in realising the ASEAN Community by 2015 and beyond.
- The Master Plan is both a strategic document for achieving overall ASEAN Connectivity and a plan of action for immediate implementation for the period 2011-2015 to connect ASEAN through enhanced physical infrastructure development (physical connectivity), effective institutions, mechanisms and processes (institutional connectivity) and empowered people (people-to-people connectivity).The three- pronged strategy will be supported by the required financial resources and coordinated institutional mechanisms. The Master Plan also ensures the synchronisation of ongoing sectoral strategies and plans within the frameworks of ASEAN and its sub-regions. Through an enhanced ASEAN Connectivity, the production and distribution networks in the ASEAN region will be deepened, widened, and become more entrenched in the East Asia and global economy.
- For the Physical Connectivity, the challenges that need to be addressed in the region include poor quality of roads and incomplete road networks, missing railway links, inadequate maritime and port infrastructure including dry port, inland waterways and aviation facilities, widening of digital divide, and growing demand for power. This calls for the upgrading of existing infrastructure, the construction of new infrastructure and logistics facilities, the harmonisation of regulatory framework, and the nurturing of innovation culture. Seven strategies have been drawn up with the view to establish an integrated and seamless regional connectivity through multimodal transport system, enhanced Information and Communications Technology (ICT) infrastructure and a regional energy security framework.
- With regard to Institutional Connectivity, ASEAN needs to resolve a number of key issues including impediments to movements of vehicles, goods, services and skilled labour across borders. To achieve this,ASEAN must continue to address non-tariff barriers to facilitate intra-ASEAN trade and investment, harmonise standards and conformity assessment procedures, and operationalise key transport facilitation agreements, including ASEAN Framework Agreement on the Facilitation of Goods in Transit (AFAFGIT), ASEAN Framework Agreement on the Facilitation of Inter-State Transport (AFAFIST), and ASEAN Framework Agreement on Multimodal Transport (AFAMT), to reduce the costs of moving goods
i MASTER PLAN ON ASEAN CONNECTIVITY
across borders. In addition,ASEAN Member States must fully implement their respective National Single Windows towards realising the ASEAN Single Window by 2015 to bring about seamless flow of goods at, between and behind national borders. An ASEAN Single Aviation Market and an ASEAN Single Shipping Market must be pursued in order to contribute towards the realisation of a single market and production base. Essentially, ASEAN should further open up progressively to investments from within and beyond the region. Here, ten strategies have been adopted to ease the flow of goods, services and investment in the region.
- Whereas for People-to-People Connectivity, two strategies have been formulated to promote deeper intra-ASEAN social and cultural interaction and understanding through community building efforts and, greater intra-ASEAN people mobility through progressive relaxation of visa requirements and development of mutual recognition arrangements (MRAs) to provide the needed impetus for concerted efforts in promoting awareness, collaboration, exchange, outreach and advocacy programmes to facilitate the ongoing efforts to increase greater interactions between the peoples of ASEAN.
- While recognising the tangible benefits of closer connectivity, the problems caused by transnational crime, illegal immigration, environmental degradation and pollution, and other cross-border challenges should be addressed properly.
- The Master Plan also identified prioritised projects from the list of key actions stipulated under the various strategies mentioned above, especially those, which implementation will have high and immediate impact on ASEAN Connectivity.These include:
(i) Completion of the ASEAN Highway Network (AHN) missing links and upgrade of Transit Transport Routes (TTRs);
(ii) Completion of the Singapore Kunming Rail Link (SKRL) missing links;
(iii) Establish an ASEAN Broadband Corridor (ABC);
(iv) Melaka-Pekan Baru Interconnection (IMT-GT: Indonesia);
(v) West Kalimantan-Sarawak Interconnection (BIMP-EAGA: Indonesia);
(vi) Study on the Roll-on/roll-off (RoRo) network and short-sea shipping;
(vii) Developing and operationalising mutual recognition arrangements (MRAs) for prioritised and selected industries;
(viii) Establishing common rules for standards and conformity assessment procedures;
(ix) Operationalise all National Single Windows (NSWs) by 2012;
(x) Options for a framework/modality towards the phased reduction and elimination of scheduled investment restrictions/impediments;
(xi) Operationalisation of the ASEAN Agreements on transport facilitation;
(xii) Easing visa requirements for ASEAN nationals;
(xiii) Development of ASEAN Virtual Learning Resources Centres (AVLRC);
(xiv) Develop ICT skill standards; and
(xv) ASEAN Community building programme.
- Critical to the Master Plan is the mobilisation of required financial resources and technical assistance to implement the key actions and prioritised projects stipulated under the adopted strategies. Recognising the scarcity of available resources, ASEAN will be exploring and tapping on new sources and innovative approaches, which include, among others, the possible establishment of an ASEAN fund for infrastructure development, public-private sector partnerships (PPP), and development of local and regional financial and capital markets, particularly to finance the key deliverables identified to be achieved by 2015.ASEAN will further strengthen partnership with external partners, including Dialogue Partners, multilateral development banks, international organisations and others for effective and efficient implementation of the Master Plan.
- To implement the Master Plan, relevant ASEAN sectoral bodies will coordinate the implementation of the strategies and actions under their respective purview while the National Coordinators and the relevant government agencies are responsible for overseeing the implementation of specific plans or projects at the national level.
- An ASEAN Connectivity Coordinating Committee will be established comprising Permanent Representatives to ASEAN or special representatives appointed by the ASEAN Member States. The Committee will report regularly to the ASEAN Coordinating Council, ASEAN Political-Security Community Council, ASEAN Economic Community Council and the ASEAN Socio-Cultural Community Council on the progress of and challenges faced in the implementation of the Master Plan. Partnership arrangements and regular consultations with the private sector, industry associations and the wider community at the regional and national levels will also be actively sought to ensure the participation of all stakeholders in developing and enhancing the ASEAN Connectivity.
- To monitor and evaluate achievements and constraints, a scorecard mechanism will be set up to effectively review, on a regular basis, the status of the Master Plan implementation and the impact of enhanced ASEAN Connectivity, and especially to ensure that all the list of priority measures and actions undertaken are responsive to the needs and priorities of ASEAN.
- To ensure cohesiveness and close collaboration among stakeholders or constituents, a communications strategy, aimed at achieving the objectives of ASEAN Connectivity, is envisaged for outreach and advocacy purposes.
- The desired outcomes emanating from the Master Plan would be to facilitate the deepening and widening of the production and distribution networks in ASEAN. Equally important, enhanced ASEAN Connectivity narrows development gaps in ASEAN and leads to increased opportunities for greater investment, trade, growth and employment in these areas. Finally, deeper intra-regional economic linkages and people-to- people interactions within ASEAN will contribute towards the achievement of an ASEAN Community by 2015, and which will reinforce the centrality of ASEAN in regional cooperation and integration.
• • • •
Background and Rationale for Developing the Master Plan
INTRODUCTION
MASTER PLAN ON ASEAN CONNECTIVITY
INTRODUCTION: BACKGROUND AND RATIONALE FOR DEVELOPING THE MASTER PLAN
- ASEAN is committed to build a Community by 2015. To realise this goal, a community of enhanced connectivity is essential because a well connected ASEAN, from its transportation networks to its peoples, will contribute towards a more competitive and resilient ASEAN as it will bring peoples, goods, services and capital closer together in accordance with the ASEAN Charter. This will ensure continued peace and prosperity for its peoples. This Master Plan on ASEAN Connectivity is a key step towards realising this vision.
- The development of this Master Plan drew impetus from the 15th ASEAN Summit in Cha-am Hua Hin, Thailand on 24 October 2009, where ASEAN Leaders adopted a Statement on ASEAN Connectivity, which appears as Appendix I.1. At the 16th ASEAN Summit in Ha Noi,Viet Nam on 8-9 April 2010, the Leaders emphasised the need to identify specific measures in the Master Plan on ASEAN Connectivity, with clear targets and timelines as well as the need to develop viable infrastructure financing mechanisms for the implementation of the Master Plan.
- Enhancing intra-regional connectivity within ASEAN and its sub-regional groupings would benefit all ASEAN Member States through enhanced trade, investment, tourism and development. As all of the overland transport linkages will have to go through the mainland Southeast Asian countries of Cambodia, Lao PDR, Viet Nam and Myanmar, these countries stand to benefit the most through infrastructure development, and the opening up of remote inland and less-developed regions. All these efforts would significantly narrow the development gap within ASEAN.
- In addition to the tangible economic benefits of ASEAN Connectivity, the linkages created would intensify and strengthen ASEAN Community building efforts, not only in terms of enhanced regional cooperation and integration, but also through people-to-people contacts. In this regard, the concept of ASEAN Connectivity would also complement the ongoing regional efforts to realise a people-oriented ASEAN Community by 2015 with a focus on fostering a sense of shared cultural and historical linkages.
- While recognising the tangible benefits of closer connectivity, the problems caused by transnational crime, illegal immigration, environmental degradation and pollution, and other cross-border challenges should be addressed properly. As we advance ASEAN Connectivity, the need to address climate change and its consequences should also be taken into account.
- The Master Plan should encompass various aspects of economic and social development to achieve a broad-based and inclusive outcome in line with the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). In this context, the Connectivity initiative should contribute towards promoting local economic and social development in the region.
The Driving Forces of ASEAN Connectivity
- The imperatives for enhancing connectivity in ASEAN are manifold. ASEAN is a region of around 600 million people with a combined gross domestic product of US$ 1.5 trillion.Within ASEAN, connectivity is necessary to facilitate the realisation of ASEAN integration, to accelerate ASEAN Community building and to reinforce ASEAN’s centrality and role as the driving force in charting the evolving regional architecture. Enhanced ASEAN Connectivity is required to achieve competitive growth, to facilitate economies of agglomeration and integrated production networks, to enhance intra-regional trade, to attract investments, to promote deeper ties between ASEAN peoples, and to foster a stronger sense of shared cultural and historical linkages. ASEAN Connectivity also spurs domestic connectivity through the economic development sustained by infrastructure and communications networks as well as the mobility of people, goods and services within.
- Beyond the region,ASEAN needs to collectively respond to the opportunities offered by its geographical and comparative advantages and to the competitive challenges brought about by global trade and investment environment. ASEAN is located at the heart of an economically vibrant and growing region bounded by India in the West; China, Japan and the Republic of Korea in the Northeast; and Australia and New Zealand in the South. Thus far, ASEAN has achieved considerable results in its economic integration efforts. Enhanced ASEAN Connectivity can potentially place ASEAN at the centre of growth and development and preserve the centrality of ASEAN in the evolving regional architecture, but only if it is able to reduce the costs of investment and international trade in goods and services.
- ASEAN has pursued regional integration and community building through various initiatives, strategies and action plans, in a plethora of sectoral and sub-regional modalities. Such efforts will benefit from a more focused and concerted approach, with the pursuit of ASEAN Connectivity viewed as an overall strategic vehicle to augment and accelerate the sectoral and sub-regional initiatives towards ASEAN Community and beyond.
Coverage and Definition of ASEAN Connectivity
- Connectivity in ASEAN refers to the physical, institutional and people-to-people linkages that comprise the foundational support and facilitative means to achieve the economic, political-security and socio- cultural pillars towards realising the vision of an integrated ASEAN Community. The key elements of ASEAN Connectivity include:
(i) Physical connectivity
- Transport
- Information and Communications Technology (ICT)
- Energy
(ii) Institutional connectivity
- Trade liberalisation and facilitation
- Investment and services liberalisation and facilitation
- Mutual recognition agreements/arrangements
- Regional transport agreements
- Cross-border procedures
- Capacity building programmes
(iii) People-to-people connectivity
- Education and Culture
- Tourism
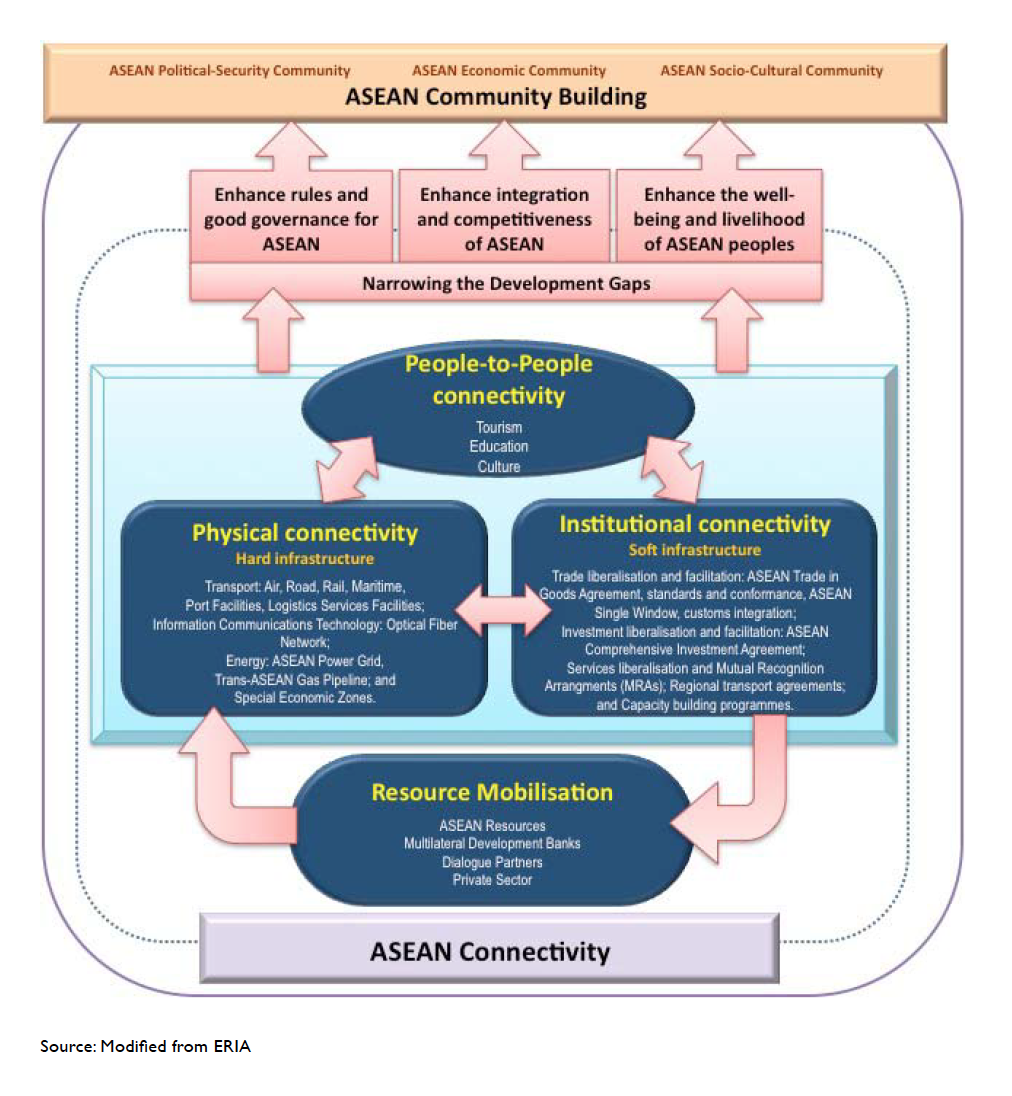
- Figure I.1 illustrates the interaction between ASEAN Connectivity and ASEAN Community building. ASEAN Connectivity can be achieved by enhancing physical connectivity and institutional connectivity thereby reducing the costs of investment and international trade in goods and services, including services link costs and network set-up costs. Enhanced physical and institutional connectivity can contribute to narrowing development gaps by expanding the frontiers of production/distribution networks and augmenting people-to-people connectivity, which will further nurture a sense of community in ASEAN.
Figure I.1: Interaction between ASEAN Connectivity and ASEAN Community
• • • •
Vision, Goals and Objectives of ASEAN Connectivity
CHAPTER 1: VISION, GOALS AND OBJECTIVES OF ASEAN CONNECTIVITY
- Enhancing intra-regional connectivity promotes economic growth, narrows the development gaps by sharing the benefits of growth with poorer groups and communities, enhances the competitiveness of ASEAN, and connects its Member States within the region and with the rest of the world.
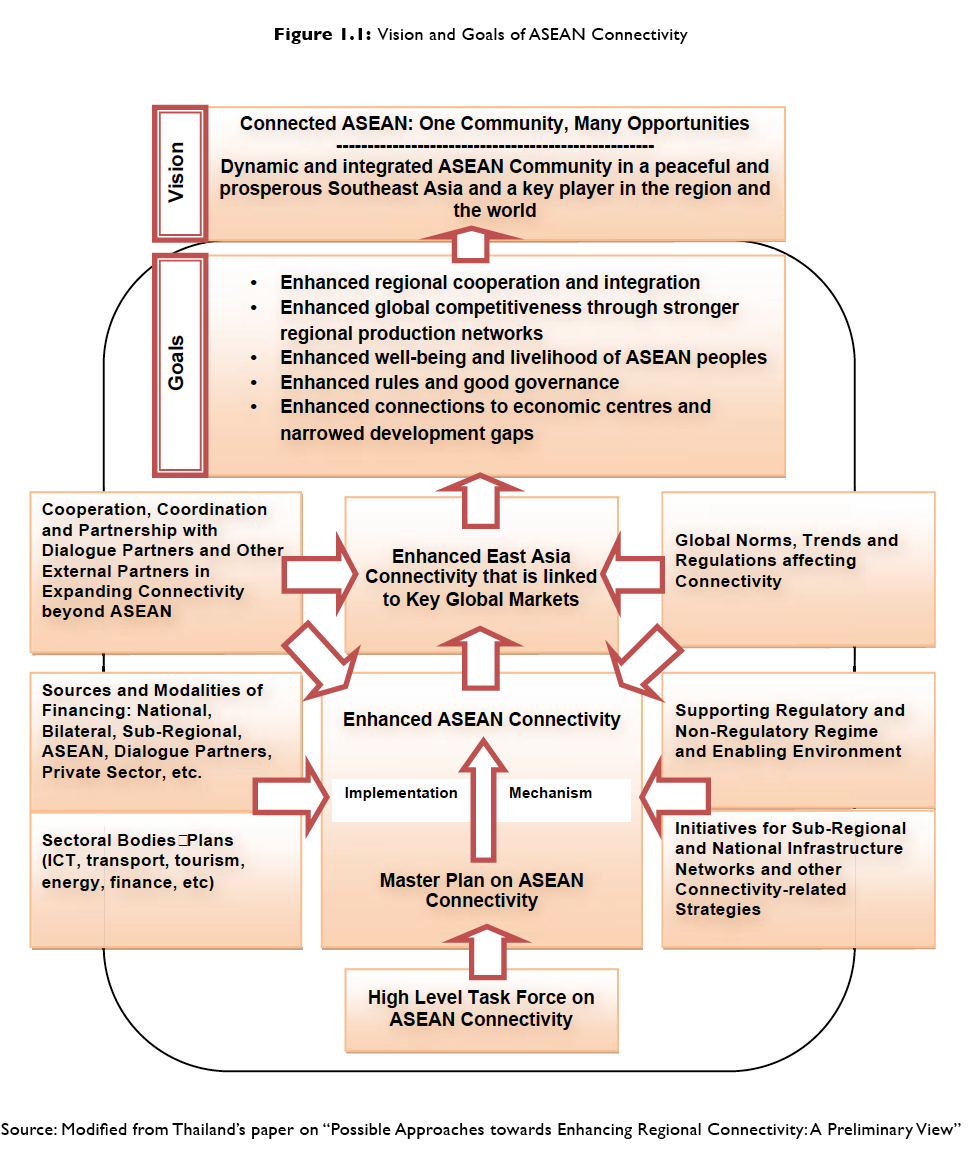
- The concept of ASEAN Connectivity would complement and support integration within ASEAN and within the broader regional framework in East Asia and beyond. The deepening and widening of connectivity in the region would reinforce ASEAN’s position as the hub of the East Asia region and preserve the centrality of ASEAN, which could further be strengthened through realising the potentials of a broader connectivity in the longer term with its partners in the wider region. Figure 1.1 below illustrates the vision and goals of ASEAN Connectivity.
Vision
- Consistent with ASEAN Vision 2020, ASEAN is envisioned as a concert of Southeast Asian nations, outward-looking, living in peace, stability and prosperity, bonded together in partnership in dynamic development and in a community of caring societies. Development and achievement of enhanced ASEAN Connectivity will need a common ASEAN vision with a long-term and sustainable approach for Connectivity, taking into consideration the need to promote local economic and social development and connectivity, mitigating environmental impacts, and synchronising domestic connectivity with regional connectivity. The vision of an enhanced ASEAN Connectivity will strengthen the ASEAN motto of “One Vision, One Identity, One Community” and address the baseline situation, the policy options, the funding mechanisms, and the implementation arrangements. It would also take into account the differentiated responsibilities and competencies of ASEAN and its Member States.
Goals
- The Master Plan on ASEAN Connectivity is envisaged to connect ASEAN through enhanced physical infrastructure development (physical connectivity), effective institutional arrangements (institutional connectivity) and empowered people (people-to-people connectivity). Building an enhanced ASEAN Connectivity requires not only the development of new strategies and institutions, but also investment in more effective implementation of existing and future initiatives.
- The goals of enhanced ASEAN Connectivity are:
(i) To enhance integration and cooperation of ASEAN;
(ii) To enhance global competitiveness of ASEAN through stronger production networks;
(iii) To enhance the well-being and livelihood of ASEAN peoples;
(iv) To enhance rules and good governance for ASEAN;
(v) To enhance connections to economic centres both within the ASEAN region and within individual Member States and narrow the development gaps;
(vi) To enhance local economic and social development;
(vii) To enhance efforts to tackle climate change as well as promote sustainable development; and
(viii) To address the negative impacts of Connectivity.
Figure 1.1: Vision and Goals of ASEAN Connectivity
- To achieve the goals, the Master Plan sets out the following objectives for an enhanced ASEAN Connectivity:
(i) To consolidate existing work plans related to connectivity and prioritise and enhance actions, taking into account related existing sub-regional cooperation frameworks;
Physical Connectivity
(ii) To develop an integrated and well-functioning intermodal transport, ICT and energy networks in ASEAN and the wider region;
Institutional Connectivity
(iii) To put in place strategies, agreements, and legal and institutional mechanisms to effectively realise the ASEAN Connectivity, including those to facilitate trade in goods and services, and the appropriate types of investment policies and legal frameworks to ensure that the investments are protected to attract the private sector investments;
People-to-People Connectivity
(iv) To develop initiatives that promote and invest in education and life-long learning, support human resource development, encourage innovation and entrepreneurship, promote ASEAN cultural exchanges, and promote tourism and the development of related industries;
Operationalisation of ASEAN Connectivity
(v) To establish the principles of funding, recommend appropriate funding mechanisms and provide an estimate of the required funding to develop and/or enhance the linkages identified in the Master Plan;
(vi) To forge win-win partnerships among the public sector, the private sector, ASEAN peoples and the international community;
(vii) To enhance the role of private sector and local communities in the implementation of the ASEAN Connectivity initiatives;
(viii) To draw up specific timetables for realising the goals of ASEAN Connectivity which will complement the work being undertaken to realise the ASEAN Community by 2015 as well as take into account the different levels of development of ASEAN Member States; and
(ix) To prepare capacity building cooperation arrangements in ASEAN such as the Initiative for ASEAN Integration (IAI) and other appropriate regional institutes in narrowing the development gap within the region, and in complementing ongoing regional efforts to realise a people-oriented ASEAN Community by 2015.
Key Principles for the Master Plan
- The Master Plan on ASEAN Connectivity is premised on the following key principles:
(i) Serve to accelerate, not hinder, existing ASEAN initiatives and complement ASEAN Community building process;
(ii) Foster a win-win solution to reflect the interest of all ASEAN Member States;
(iii) Ensure synchronisation of ongoing sectoral strategies or plans within the frameworks of ASEAN and its sub-regions;
(iv) Strive for balance between regional and national interests;
(v) Strengthen connectivity between mainland and archipelagic Southeast Asia;
(vi) Outward-looking and serve to promote healthy competitive dynamics among external partners and also help preserve ASEAN centrality; and
(vii) Feasible in practice with clear financial mobilisation models, including the involvement of private sector.
• • • •
Achievements of, and Challenges and Impediments to ASEAN Connectivity
CHAPTER 2
MASTER PLAN ON ASEAN CONNECTIVITY
CHAPTER 2: ACHIEVEMENTS OF, AND CHALLENGES AND IMPEDIMENTS TO ASEAN CONNECTIVITY
- ASEAN has continued to focus its efforts in implementing the ASEAN Charter and the Roadmap for an ASEAN Community. ASEAN Connectivity is a concept that presents the strengths, the potentials, and the challenges for building the ASEAN Community. It builds on the evolution of ASEAN regional cooperation and its achievements to date, and addresses the challenges that ASEAN encountered, including enhancing competitiveness, narrowing development gaps, and overcoming differences in social and cultural systems.
- The state of such regional cooperation in ASEAN, including initiatives at the sub-regional level, are examined below through the three dimensions of physical connectivity, institutional connectivity and people-to-people connectivity. ASEAN has put in place numerous programmes and initiatives for building and enhancing regional connectivity, and some good progress have been made. However, substantial work remains to be done to achieve the goal of a seamless regional connectivity.
2.1 Physical Connectivity
- Physical connectivity, encompassing both hard infrastructure in transport, ICT and energy infrastructure as well as the regulatory framework and the software necessary to deliver associated services and utilities, plays a crucial role in the process toward a more economically and socio-culturally integrated ASEAN region, through trade- and investment-facilitating infrastructure, potential reductions in trade- related costs, and by facilitating people-to-people contact.
2.1.1 Land, Maritime and Air Infrastructure Development
- Land Transport. ASEAN cooperation in roads and rail aims to establish efficient, integrated, safe and environmentally sustainable regional land transport corridors linking all ASEAN Member States and countries beyond. There are two flagship land transport infrastructure projects within ASEAN, namely the ASEAN Highway Network (AHN) and the Singapore Kunming Rail Link (SKRL).
- For road infrastructure, the ASEAN Transport Ministers (ATM) adopted a plan to develop the AHN with the following time-frame at its fifth meeting in Ha Noi,Viet Nam in September 1999:
- Stage 1: Network configuration and designation of national routes to be completed by 2000.
- Stage 2: Installation of road signs at all designated routes, upgrading of all designated routes to at least Class III standards, construction of all missing links and the operationalisation of all cross- border points by 2004.
- Stage 3:All designated routes to be upgraded to at least Class I standards and the upgrading of low traffic volume non-arterial routes to Class II standards would be acceptable by the year 2020.
- The AHN is an expansion of the ‘Trans-Asian Highway’ network within ASEAN.To date, while there have been significant progress made by the ASEAN Member States in terms of increasing the length and upgrading the road quality of the highway, there are still missing links and below
AHN Project
23 designated routes
38,400 kilometres
11 MASTER PLAN ON ASEAN CONNECTIVITY
standard roads in some Member States. As far as the missing links of the AHN are concerned, it is located mostly in Myanmar with total length of 227 kilometres.Whereas for the roads which are below Class III standards under the AHN, it stretches over 5,300 kilometres encompassing six Member States including Indonesia, Lao PDR, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines and Viet Nam.
Figure 2.1: ASEAN/Asian Highway Network Map
Source: ASEAN Logistics Network Map Study, JETRO 2008
- The AHN also identifies transit transport routes (TTRs) which are considered critical for facilitating goods in transit and have been prioritised for upgrading and construction. Below Class III roads of these TTRs include some 2,069 kilometres of transit transport routes in Lao PDR, Myanmar and the Philippines. Access to financing is the key challenge to the timely completion of the upgrading of the below Class III roads by 2004 as planned by the ASEAN Transport Ministers.
- As for rail infrastructure, the SKRL flagship project was proposed at the Fifth ASEAN Summit in December 1995 and targeted for completion by 2015. It covers several routes through Singapore–
Table 2.1: Designated Transit Transport Routes (TTRs) in ASEAN
Country | Total Length of TTRs (km) | Total Length of Below Class III TTRs (km) |
Brunei Darussalam | 168 | 0 |
Cambodia | 1,338 | 0 |
Indonesia | 4,143 | 0 |
Lao PDR | 2,170 | 391 |
Malaysia | 2,242 | 0 |
Myanmar | 3,018 | 1,467 |
Philippines | 3,073 | 211.5 |
Singapore | - 1/ | - |
Thailand | 4,477 | 0 |
Viet Nam | 577 | 0 |
Total | 21,206 | 2,069.5 |
Note: 1/ Designated TTRs for Singapore to be submitted at the time of deposit of Instrument of Ratification for Protocol 1 of the ASEAN Framework Agreement on the Facilitation of Goods in Transit.
Source:Thailand Report “The Updated Status of the AHN Project” Presented to 29th Senior Transport Official Meeting in Brunei Darussalam (1-3 June 2010), ASEAN Secretariat
Malaysia–Thailand–Cambodia–Viet Nam–China (Kunming) and spur lines in Thailand–Myanmar and Thailand–Lao PDR.
- Currently there are 4,069 kilometres of missing links or links which need to be rehabilitated in six Member States including Cambodia, Lao PDR, Malaysia, Myanmar, Thailand and Viet Nam. Due consideration should be given to CLMV countries with regard to securing both financial and technical assistance from ASEAN, its dialogue partners and other international organisations to help them in the undertaking of the SKRL project
- For inland waterways transport, which has large potential in reducing freight transport costs, the current utilisation rate within ASEAN is still very low. The ASEAN region is generously
Missing Links in the SKRL Project
- Vientiane –Thakek – Mu Gia, 466 kilometres ( 1 on the map)
• Mu Gia – Tan Ap – Vung Ang, 119 kilometres ( 2 on the map)
• Poipet – Sisophon, 48 kilometres ( 1 on the map)
• Phnom Penh – Loc Ninh, 254 kilometres ( 2 on the map)
• Loc Ninh – Ho Chi Minh, 129 kilometres ( 3 - 4 on the map)
• Thanbyuzayat – Three Pagoda Pass,110 kilometres ( 5 on the map)
• Three Pagoda Pass to Nam Tok, 153 kilometres ( 6 on the map)
endowed with some 51,000 kilometres of navigable inland waterways which can play an active role in transport development, especially in the CLMV countries and Thailand.The infrastructure issues related to this low utilisation are the underdeveloped waterways network, poor river ports and facilities, and poor intermodal connectivity. Considering the advantage for connectivity in economic activities, these infrastructure issues need to be addressed, together with improving rules and governance for managing the connected inland waterways transport systems.
- Maritime Transport. ASEAN has designated 47 ports as the main ports in the trans-ASEAN transport network as shown in Appendix 2.1. There are a number of challenges faced by the designated ports in providing a more efficient shipping network services given the varying levels of port infrastructure development. For example, the handling of cargo depends on the capacity of ship calling at the ports, cargo handling capacity, land transport and logistics capacity, and customs and administrative clearance procedures.
Figure 2.2: SKRL Networks and the Missing Links
Source: ASEAN Transport Strategic Plan 2011-2015 – Midterm Report, ERIA and Nippon Koei 2010
- Maritime transport is the most important mode of transportation in terms of the traffic volume in international trade. However, many ASEAN countries, with the exception of Singapore and Malaysia, rank poorly relative to China and Hong Kong in the UNCTAD Liner Shipping Connectivity Index. At
Key Challenges Port infrastructure Maritime services Port performance
the same time, most of the gateway ports of the ASEAN Member States are already “fairly full” which means that investments in capacity expansion would have to be made in order to meet the growth in trade expected from the deeper economic integration of the ASEAN Member States among themselves and with the rest of the world.
- Connecting the archipelagic regions of ASEAN requires efficient and reliable shipping routes in order to enhance intra-ASEAN connectivity. The results of the initial impact assessment of the Philippines Nautical Highway (also referred to as Roll-on/roll-off (RoRo)) System demonstrate significant benefits in terms of reduction in transport costs, the creation of new regional links and expansion of regional markets, more efficient shipment of goods and people that have particularly benefited the poorer provinces in the maritime routes, acceleration of local area development, realignment of logistical practices with more frequent deliveries, and greater competitive pressure on the domestic shipping industry (“Bridges Across Oceans: Initial Impact Assessment of the Philippines Nautical Highway System and Lessons for Southeast Asia”, ADB, 2010).
- Air Transport. In the area of air transport infrastructure, capital airports of ASEAN Member States are sufficient in terms of runway lengths to accommodate the existing operation of aircrafts. However, some of these airports still face problems in providing airport facilities,particularly runways and warehouses.
KeyChallenges
- Harmonisation of air navigation systems and procedures
- Identification of new routes
Aside from the development of airports, attention to harmonising ASEAN air navigation system and procedures including air routes should be given to anticipate the growing air traffic in the region. Failure to improve these facilities could result in limited growth potential. Some ASEAN Member States have recently implemented projects to improve airport facilities and services, including the construction of terminals for private low cost carriers (LCCs). However, lack of storage facilities at the airports of some ASEAN Member States remains.
2.1.2 ICT Infrastructure Development
- ICT infrastructure is fundamental to supporting trade, facilitating investments and enlarging markets through its ability to facilitate information exchange, to connect people, to support delivery of services and to reduce the cost of business and trade-related transactions. ICT infrastructure is broadly defined to include fixed, mobile, and satellite communication networks and the internet as well as the software supporting the development and operation of these communication networks.
- Developing ASEAN ICT infrastructure faces a number of challenges. The most important one comes from the extent of digital divide across the ASEAN Member States and how to overcome this. Bridging the digital divide requires commitment from the Member States to improve the competitiveness of their national ICT sectors.
- Other challenges, within the framework of ASEAN initiatives, include insufficient coordination to ensure connectivity amongst National Information Infrastructure (NII), the need to nurture technological innovation, as well as lack of financing schemes for infrastructure projects that involve significant participation of private capital, and improving access and affordability to reduce the digital divide.
KeyChallenges
- Extent of digital divide
- Insufficient NII coordination
- Need to nurture technological innovation
- Significant challenges also lie in the ability of ASEAN Member States to develop and harmonise ICT regulations necessary for connectivity projects (i.e., cross border transactions) and to encourage national and private investments in ICT infrastructure and services.
2.1.3 Energy Infrastructure Development
- Energy plays a crucial role in economic development and will remain critical to the continued economic growth of the ASEAN region. ASEAN cooperation in the energy sector has been guided by a series of Plan of Action including the ASEAN Plan of Action for Energy Cooperation (APAEC) 1999-2004,APAEC 2004-2009 and APAEC 2010-2015.
- Under the first Plan of Action (1999-2004), the conclusion of the Trans-ASEAN Gas Pipeline (TAGP) Master Plan by ASEAN Council on Petroleum (ASCOPE) and the ASEAN Interconnection Master Plan Study by Heads of ASEAN Power Utilities/Authorities (HAPUA) has paved the way for an enhanced regional energy security framework while promoting efficient utilisation and sharing of resources.
- In the second Plan of Action (2004-2009), significant achievements were realised including the signing of the Memorandum of Understanding for the ASEAN Power Grid (APG), the establishment of APG Consultative Council and the establishment of ASCOPE Gas Centre (AGC).
- The current Plan of Action (2010-2015) placed greater emphasis on accelerating the implementation of action plans to further enhance energy security, accessibility and sustainability for the region with due consideration to health, safety and environment, especially in relations to APG, TAGP, clean coal technology and renewable energy amongst others.
- APG is a flagship programme mandated in 1997 by ASEAN Leaders, which aims to help ASEAN Member States to meet increasing demand for electricity and improve access to energy services by enhancing trade in electricity across borders, optimising energy generation and development and encouraging possible reserve sharing schemes.The status of the APG project appears in Figure 2.3
- Challenges for the APG remain since a significant number of the future interconnection projects will either require marine/undersea cable interconnections or inland interconnections involving the grids
Figure 2.3: Status of the Development of ASEAN Power Grid Network
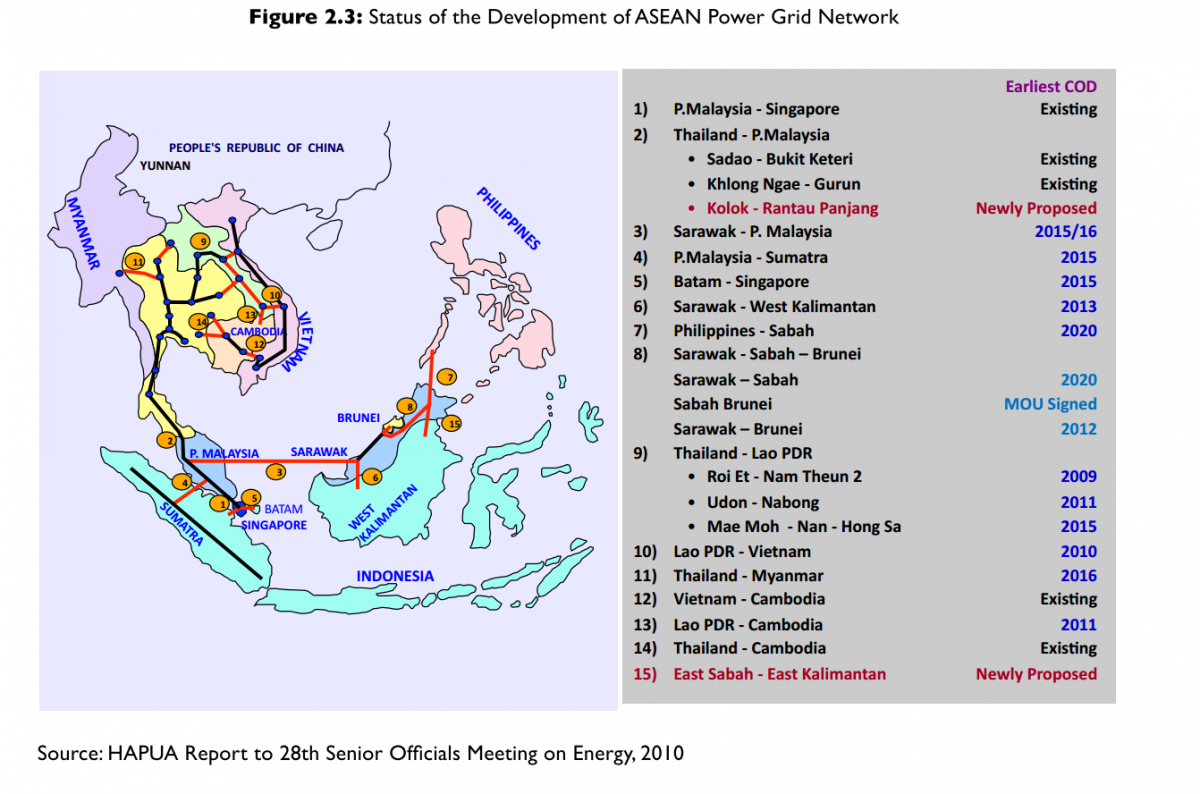
of the CLMV countries. The economic viability of the planned grid interconnection projects are yet to be established and accepted by participating economies even as the projects have been assessed by HAPUA to be technically feasible. In particular, economic viability will affect prospects for financial viability. Issues regarding the need to introduce an effective regulatory framework and a mechanism for raising capital also need to be addressed.
KeyChallenges
- Economic viability
- Effective regulatory framework
- Funding mechanism for low income countries’ participation
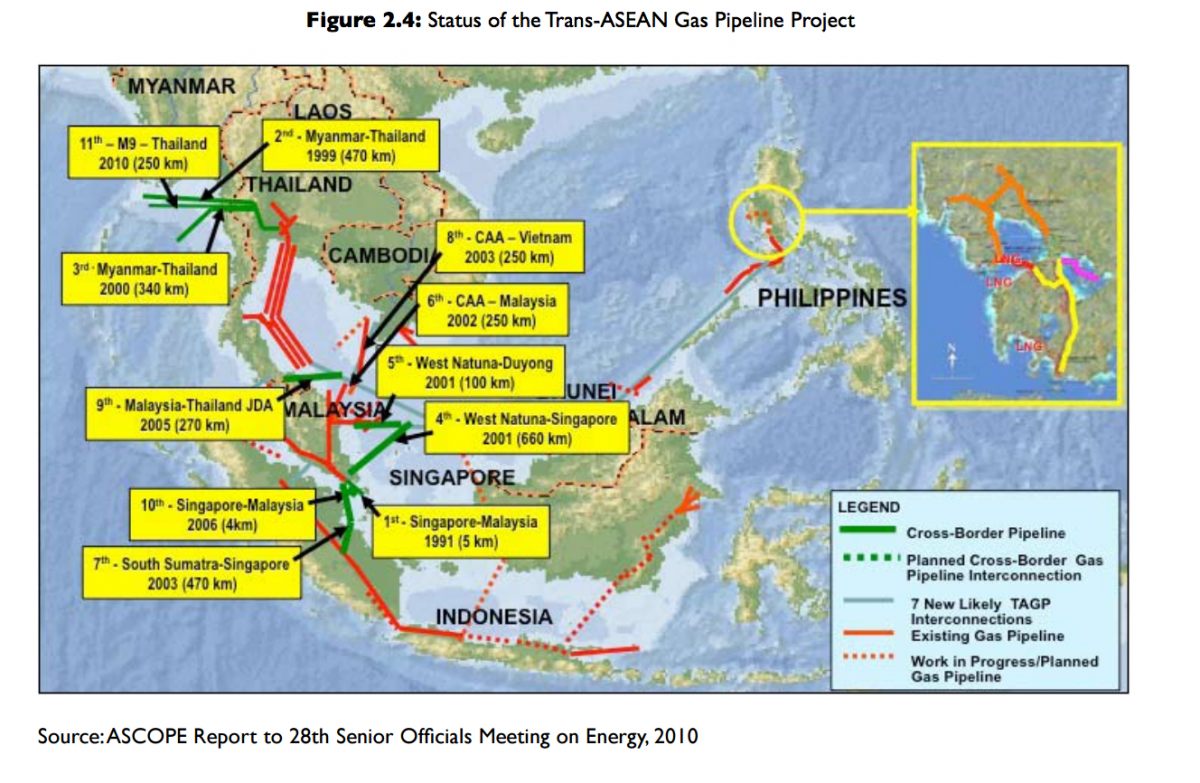
- TAGP aims to develop a regional gas grid by 2020, by interconnecting existing and planned gas pipelines of Member States and enabling gas to be transported across borders. By 2013, there will be a total of 3,020 kilometres of pipelines in place, with the completion of the M9 pipeline linking Myanmar to Thailand. The region is also looking into establishing infrastructure for the transportation of liquefied natural gas (LNG), as countries such as Malaysia, Singapore and Thailand undertake construction of LNG terminals. The challenges are in obtaining adequate supply of piped natural gas, increasing investment costs, synchronising national technical and security regulation requirements, and differences in the processes of supply, distribution, and management for natural gas across the countries. The status of TAGP project appears in Figure 2.4.
- The realisation of TAGP is expected to encounter substantial financial and legal complexities. The challenges here include increasing investment costs, synchronising national technical and security regulation requirements, and differences in the supply, distribution, and management procedure of natural gas across the countries. Rivalry between the pipeline-delivered natural gas and other energy
Figure 2.4: Status of the Trans-ASEAN Gas Pipeline Project
sources, such as coal and liquefied natural gas, also needs to be addressed. In addition, there is also a need to overcome the issue of political trust common in energy markets cooperation, which can be a huge barrier to trade of pipelined gas and electricity.
- To date, eight bilateral gas pipeline interconnection projects are currently operating, with a total length of some 2,300 kilometres. This is more than half of the total planned length for development (i.e., 4,500 kilometres). The developed projects link pipelines between Thailand and Myanmar, West Natuna and Duyong, West Natuna and Singapore, South Sumatera and Singapore, Malaysia and Thailand, and Singapore and Malaysia.
2.2 Institutional Connectivity
Eight bilateral gas pipeline interconnection projects in operation
- Institutional connectivity refers to linking various international or regional agreements and protocols to facilitate international transactions of goods and services as well as the movement of natural persons across borders.
2.2.1 Transport Facilitation
- ASEAN has introduced a number of transport facilitation initiatives over the years to create an efficient logistics and multimodal transport system for a seamless movement of goods, connecting land, maritime, and air transport. These include: (a) ASEAN Framework Agreement on the Facilitation of Goods in Transit (AFAFGIT),
(b) ASEAN Framework Agreement on Multimodal Transport (AFAMT), (c) ASEAN Framework Agreement on the Facilitation of Inter-State Transport (AFAFIST),
(d) Roadmap for Integration of Air Travel Sector (RIATS),
AFAFGIT Establish an efficient, effective, integrated and harmonised transit transport system in ASEAN
AFAMT Governs door-to-door delivery of goods using various modes of transport
AFAFIST Facilitates inter-state transport of goods, harmonisation of customs regulation and requirement for inter-state movement of goods
and (e) Roadmap Towards an Integrated and Competitive Maritime Transport in ASEAN (RICMT).
- All the agreements and roadmaps have the objective of complementing the hard transport infrastructure by creating efficient logistics and multimodal transport systems for a seamless movement of goods and by connecting land, maritime, and air transport. Many protocols of these agreements (e.g. Protocols 2, 6 and 7 of the AFAFGIT) have yet to be concluded or ratified as stated in Appendix 2.2. In this regard, the operationalisation of these agreements will be further delayed.
- The existing ASEAN initiatives on transport facilitation focus primarily on facilitating goods transportation. Due consideration should also be given to develop new initiatives to further facilitate intra-regional tourism and people-to-people connectivity through the movement of passenger vehicles.
RIATS Full liberalisation in air transport services towards realising Open Skies Policy in ASEAN
RICMT Promote progressive liberalisation of maritime transport services
- RIATS guides multilateral air services liberalisation in ASEAN by way of a series of milestones, in particular unlimited 3rd, 4th and 5th freedom of traffic rights for air freight among all ASEAN cities, and unlimited 3rd, 4th and 5th freedom of traffic rights for passenger services between all ASEAN capitals, by December 2008 and December 2010 respectively.
Unlimited 3rd, 4th and 5th freedom of traffic rights for scheduled passenger services in place
- To implement RIATS, ASEAN Member States concluded and signed both the ASEAN Multilateral Agreement on Air Services (MAAS) and the ASEAN Multilateral Agreement on the Full Liberalisation of Air Freight Services (MAFLAFS) and are now in the process of ratifying these agreements and their respective protocols. ASEAN Member States will also be signing the ASEAN Multilateral Agreement on the Full Liberalisation of Passenger Air Services (MAFLPAS) in November 2010. Under the MAFLPAS, passenger air services liberalisation will be extended to all ASEAN points via Protocol 1 On Unlimited Third, Fourth Freedom Traffic Rights Between Any ASEAN Cities and Protocol 2 On Unlimited Fifth Freedom Traffic Rights Between Any ASEAN Cities, to be implemented by 30 June 2010 and 30 June 2013 respectively. These multilateral air services agreements will form the basis for realising ASEAN Open Skies Policy.
- The key challenges facing further liberalisation of the air transport sector lie in the timely and full implementation of MAFLAFS, MAAS and MAFLPAS, and also the enhancement of ASEAN connectivity with its external partners.
- The Roadmap Towards an Integrated and Competitive Maritime Transport in ASEAN (RICMT) aims to further the goals enunciated in the Vientiane Action Programme (VAP) 2004-2010 and ASEAN Transport Action Plan (ATAP) 2005-2010, and the ASEAN Leaders’ call to institute new mechanisms and measures to strengthen the implementation of its existing economic initiatives.
- The Roadmap is a time-bound action plan for concrete actions that ASEAN Member States need to take in order to achieve a more open, efficient, and competitive ASEAN maritime transport system. It covers both passengers and freight maritime services. In addition, the Roadmap also deals with port and related services necessary for an efficient, secure, and reliable operation of maritime transport services. Most of the actions/measures stipulated in the Roadmap are currently being undertaken while there are some which have yet to be initiated. Implementation of the specific measures is subject to conformity with international conventions and/or the relevant national laws and regulations.
- There is a critical element in the Roadmap calling for the implementation of an ASEAN Single Shipping Market. Here there are a number of issues that need to be addressed prior to the implementation stage. These include the definition of a single shipping market, and the formulation of a strategy to realise such a market, bearing in mind the issue of cabotage principle.
2.2.2 Free Flow of Goods
Key Challenges
- Definition and strategy for ASEAN Single Shipping Market
- Adoption of cabotage principle
- For the past two decades, ASEAN Member States have intensified trade between themselves and also with the rest of the world including East Asia. Intra-ASEAN trade in goods is characterised by active participation of Member States in international production networks in East Asia, which can be attributed partly to substantial reduction in tariff.
- Intra-ASEAN trade as a share of total ASEAN trade increased from 19.4% during 1990-1991 to about 24% in both periods of 1995-1996 and 2000-2001, and to 27% during 2007-2008 (UNCTAD 2010). The intra-regional trade intensity index of ASEAN also increased from 3.65 during 1995-1996 to 4.55 during 2007-2008. This has led to ASEAN having the highest share of intra-regional trade to total trade (at 26.3% in 2008) among the regional economic groupings in the developing world. This reflects the high level of inter-dependence between regional production networks operated by both manufacturers and producers.
- In addition, the extent of reciprocal transactions in machinery and components in ASEAN-5 countries were larger than those in other countries, reflecting active participation of ASEAN Member States in East Asian regional production networks as shown in Figure 2.5 below.
Figure 2.5: Export and Import of Machinery and Components in 2008
Source: Global Trade Affairs
- ASEAN, through the Common Effective Preferential Tariff Scheme for the ASEAN Free Trade Area (CEPT-AFTA) and now embodied in the ASEAN Trade in Goods Agreement (ATIGA), is well on the way to the elimination of tariffs within the ASEAN region, with deadlines of 2010 for ASEAN-6 and 2015 (with flexibility to 2018) for the newer ASEAN Member States (CLMV countries). Beginning 1 January 2010, ASEAN-6 countries achieved zero tariffs for 53,457 tariff lines covering 99.11 % of the total tariff lines traded under CEPT.
- The way forward is to move beyond tariff reduction and increased productivity for a more sustainable growth.This is governed by ATIGA, which integrates all initiatives and measures related to trade in goods into one comprehensive framework. It focuses on non-tariff barriers, rules of origins (ROOs), customs, trade facilitation, standards and conformance, and it is expected to enhance the rules-based system of trade in goods in ASEAN.
- There has been a convergence towards more flexible and simpler ROOs under the CEPT-AFTA initiative. The utilisation rate of the CEPT-AFTA is, however, relatively low among the region’s firms. Moreover, there has been substantial variation in the ROOs in ASEAN’s free trade agreements (FTAs) with its trading partners. This is clearly not favourable because of the ‘noodle-bowl’ effects it creates.
- Low utilisation of preferential treatment under CEPT-AFTA
- • Tariffsfor top traded products are virtually or near zero
- Inconsistent implementation for ROOs
- Meanwhile, the non-tariff barriers essentially lower the extent of trade openness across the ASEAN Member States. Some studies have indicated that the percentage premia of products restricted by non- tariff barriers is very high, ranging from 50 to 70 percent of the world competitive price.
- ASEAN has adopted a work programme to reduce the protective measures that come from non-tariff measures (NTMs). The work programme includes the creation of a NTM database, identification of NTMs by the Member States, the setting of schedule for NTM elimination by the Member States, and the development of guidelines to govern, amongst others, the Import Licensing Procedure (ILP) that is consistent with the World Trade Organization (WTO) and ATIGA
Key Challenges
- HS 4 digits level NTMs database is outdated
- Adoption of voluntary disclosure mechanism
- Information on new NTMs not available
provisions. Other challenges include the lack of robust mechanism in the NTM reporting system and database.
- Trade facilitation initiatives in the area of standards and conformance through reduction of Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) focus on addressing differences between national laws, standards, and conformity assessment procedures towards a broader horizontal approach at the regional level.The approach taken, as outlined in ASEAN Economic Community (AEC) Blueprint, is to harmonise national standards with international standards and develop mutual recognition arrangements (MRAs) among Member States, especially for the priority integration sectors.
- Food safety is an important aspect of ASEAN cooperation with the aim to assure the safety and quality of foods entering internal as well as
TBT will be reduced for prepared foodstuff, automotive, electrical and electronic equipments, healthcare products, rubber-based and wood- based products
export markets. In the context of ASEAN integration, the main objective is to achieve freer movement of safe and healthy food within the region. Achievement of such objectives should also contribute to the enhancement of product competitiveness and regional market integration. Assurance of food safety, harmonisation of produce quality and standardisation of trade certification are among the priorities addressed, building upon the experience of some Member States and existing international standards such as Codex, World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE) and International Plant Protection Convention (IPPC).To facilitate trade between and among Member States while protecting human, animal and plant health, Member States commit to apply the principles of the WTO’s Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) Agreement in the development, application or recognition of any SPS measures. ASEAN has explored opportunities for further cooperation, technical assistance, collaboration, and information exchange on SPS matters consistent with commitments set forth in the AEC Blueprint. In addition, Member States are also considering development of equivalence arrangements and recommending equivalence decisions.
- Implementation of some measures is ongoing, under the direction of the ASEAN Consultative Committee for Standards and Quality (ACCSQ). These include harmonising standards, technical requirements, development of MRAs, setting up of technical infrastructure and harmonising technical regulations for some sectors. Notwithstanding the achievement, much is yet to be accomplished in terms of establishing the overarching framework for standards, technical regulations and conformity assessment procedures in ASEAN. Efforts to reduce TBT should not only be confined to the priority integration sectors but other sectors too.
- In its initiatives for ASEAN integration in the services sector, ASEAN has put in place several legal and institutional mechanisms. These include the ASEAN Framework Agreement on Services (AFAS), the AEC Blueprint, the Roadmaps for Priority Integration Sectors, and Services Liberalisation Modalities endorsed by the ASEAN Economic Ministers.
- In terms of liberalisation achievements,ASEAN Member States have undertaken five rounds of negotiations and have recently completed the seventh package of
ASEAN GATS-plus commitments
services commitments.The scope and depth of the commitments made so far are dictated by the targets for equity liberalisation and by the requirement to remove restrictions in Modes 1 (i.e., cross-border supply) and 2 (i.e., consumption abroad) and progressively remove market access limitations. In terms of coverage, commitments under AFAS exceed those made in the General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS).
- The Roadmap for Integration of Logistics Services (RILS) was endorsed in August 2008 to strengthen ASEAN as a single market and production base, and enhance its competitiveness through trade and transport facilitation. Under the liberalisation of logistics services which is an important element in achieving connectivity, the RILS calls for liberalisation of cargo handling services, storage and warehousing services, freight transport agency services, courier services, packaging services, custom clearance services, international freight transportation excluding cabotage, international rail freight transport services, and international road freight transport services, as stipulated in the RILS. In particular, challenges in transport logistics need to be addressed such as a well integrated physical transport infrastructure, substantial liberalisation for transport services and the development of human resources.
- There are however a number of challenges and impediments to move towards a more credible services sector liberalisation. The key challenge is to ensure that higher targets of services liberalisation are met so as to facilitate greater connectivity, not only for trade in services but also for trade in goods. Among others, domestic legal regulations often constrain further liberalisation, particularly for the liberalisation of Mode 3 (i.e., commercial presence). Strong views on protectionism from domestic stakeholders are also another challenge for progressive liberalisation. Finally, Mode 4 (i.e., movement of natural persons) has seen the least progress compared to the liberalisation plan of the other modes. Accordingly, alternative approach on how to move forward with a more liberalised Mode 4 is essential.
2.2.4 Free Flow of Investment
- ASEAN Member States have performed well in attracting Foreign Direct Investment (FDI). FDI inflows to the Member States as a group currently accounted for about ten percent of the total FDI inflows to developing countries. Intra-ASEAN FDI flows have also been increasing (refer to Figure 2.7), and indeed, intra-ASEAN FDI increased in 2008 when the general trend of FDI into ASEAN region was declining during this year.
- ASEAN has concluded a new investment agreement, namely the ASEAN Comprehensive Investment Agreement (ACIA), which contains more comprehensive provisions, covering investment
ACIA
Grants immediate benefits to both ASEAN investors and ASEAN-based foreign investors
liberalisation, protection, facilitation and promotion. ACIA puts together the two separate initiatives, namely the ASEAN Investment Guarantee Agreement (AIGA) and the ASEAN Investment Area (AIA). ACIA was concluded in 2008 and signed in 2009. ACIA grants immediate benefits to ASEAN investors and ASEAN-based foreign investors to achieve free and open investment by 2015.
Figure 2.7: Intra-ASEAN Foreign Direct Investment Inflow (US$ million)
Source: ASEANStat
- There are number of challenges to achieve a free investment flow by 2015 as set out by ACIA:
(i) Legal framework: The entry into force of ACIA needs to be expedited.
(ii) nvestment restriction: There is a need to ensure that restrictions are kept to the necessary minimum and are justifiable. In addition, in accordance with the AEC Blueprint targets, restrictions scheduled should be reduced and eliminated gradually. The
KeyChallenges
Legal framework Investment restriction Legal impediments Building
challenge is to ensure that this is undertaken in a phased, progressive manner ultimately leading to free flow of investments.
(iii) Legal impediments: Some national treatment limitations have been attributed to provisions under the relevant domestic laws and regulations, including relevant provisions in the Constitution. This may need a review of these laws to ensure that such limitations remain valid and are not unnecessary barriers to the free flow of investment.
(iv) Building awareness: ASEAN integration and the creation of a single market allowing investment connectivity should be accompanied by greater outreach and advocacy. There is a need for continuous efforts to promote the single market and the enhancement of the investment climate of ASEAN to ensure that ASEAN’s share of global FDI remains high.
2.2.5 Free Flow of Skilled Labour and Human Development
- The labour sector of the ASEAN Member States welcomes effort toward a greater ASEAN labour market integration. In moving toward this vision, the ASEAN Senior Labour Officials Meeting (SLOM) was of the view that the pre-requisite for any effort to enhance movement of labour is through the establishment of national skills frameworks as an incremental approach towards an ASEAN skills recognition framework. As some Member States are yet to establish national skills framework, further collaboration among Member States on the matter must be undertaken before addressing issues on the process of establishing regional skills recognition arrangements.
- Some efforts have been undertaken to help Member States establish the national skills framework. The efforts will be continued under the ASEAN Labour Ministers (ALM) Work Plan 2010-2015.
- In addition, the 2nd SLOM Working Group endorsed Indonesia’s Concept Note on ASEAN Guidelines on Development of National Framework for Skills Recognition Arrangement. The main objectives of the project are: (i) to harmonise National Competency Standard and its certification scheme within ASEAN countries; (ii) to determine concrete actions among ASEAN countries in realising harmonisation of competence standard and its implementation; and (iii) to achieve a qualified, competent and well prepared ASEAN labour force toward the AEC by 2015.
- Furthermore, in line with the Cha-am Hua Hin Declaration on Strengthening Cooperation on Education to Achieve an ASEAN Caring and Sharing Community, the enhancement of greater mobility of skilled workers in ASEAN should be accompanied by efforts to safeguard and improve educational and professional standards to meet the needs of industries in coordination with the ASEAN Labour Ministers. Moreover, developing a common standard of competencies for vocational and secondary education as a base for benchmarking with a view to promote mutual recognition needs to be encouraged.
- In relation to this, ASEAN has been working on mutual recognition arrangements (MRAs) to facilitate the free movement of skilled labour in the region. To date, eight MRAs have been concluded for the following professional groups:
(i) Engineering Services (signed in December 2005);
(ii) Nursing Services (signed in December 2006);
(iii) Architectural Services (signed in November 2007);
(iv) Framework Arrangement for the Mutual Recognition of Surveying Qualifications (signed in November 2007);
(v) Tourism Professionals (signed in January 2009);
(vi) Medical Practitioners (signed in February 2009);
(vii) Dental Practitioners (signed in February 2009); and
(viii) MRA Framework on Accountancy Services (signed in February 2009).
Eight MRAs Concluded
- However, there are a number of challenges which may affect the implementation of the concluded MRAs which currently differ in terms of the degree of cooperation in recognition of qualifications. One such challenge is the tendency of ASEAN Member States to impose nationality conditions prior to issuing the license. This was based on the notion that nationals are more familiar with local rules than foreign services providers. However, such regulation has gone out of synch as most countries have aligned their standards of practice with international standards.
- Another challenge is licensing. Certain ASEAN Member States require professionals to have a compulsory membership in professional association in domestic countries. This, however, might not be critical. The more important trade restrictiveness that comes from licensing does not emanate from the requirements themselves, but it comes from the divergence of these requirements across countries. In accountancy services, such divergence is pronounced. Reconciling differences in education and experience requirements has been proven difficult, which explains the lengthy negotiations before a mutual recognition arrangement can be forged. Moreover, among ASEAN Member States, only the Philippines has instituted reciprocity arrangements to allow foreign professionals to practice in the country provided they have the “equivalent” licensing requirements as the Philippines’ and their home countries accord reciprocal privilege to the Filipino accountants.
2.2.6 Cross-Border Procedures
- Physical connectivity per se cannot guarantee seamless movement of goods and people across countries. Inefficient and lengthy cross-border procedures, which add unnecessary friction and costs to transport, are serious challenges that need to be addressed. At the same time, enhanced connectivity, without appropriate safeguards from abuse, could lead to transnational crimes and other cross-border challenges such as pollution and pandemics.
- Greater connectivity within ASEAN poses its own challenges in terms of cross-border procedures, owing to negative externalities of substantially borderless countries (i.e., transnational crime). ASEAN addresses this issue through an initiative
Enhanced cooperation between Member States’ immigration authorities
to improve the cooperation between immigration institutions in the Member States, as well as through building and modernising the capability of the immigration institutions. All these are reflected in the ASEAN Plan of Actions for Cooperation in Immigration. Hence, cross-border facilitation and management is an essential component of enhanced ASEAN connectivity.The right balance must therefore be struck between encouraging and facilitating more efficient movement of goods and people on the one hand, and protecting the region and its peoples from transnational crimes and cross-border challenges and having secure supply chains throughout the region on the other. While the objective is clear, achieving it faces some challenges. The most critical one is in consolidating different policies, regulations, as well as institutions within a country, and across the Member States.
- Central to effective and timely cross-border facilitation and management are the Customs, Immigration, Quarantine (CIQ) mechanisms. The development of a well-functioning CIQ mechanism requires not only investment in the necessary infrastructure and technology at border checkpoints, but also the harmonisation of relevant rules and standards. In addition, human resource development through capacity building and training programmes designed to equip border management personnel with important knowledge and skills is also a prerequisite for effective cross-border management.
- ASEAN Framework Agreements, such as the (i) ASEAN Framework Agreement on the Facilitation of Goods in Transit (AFAFGIT), (ii) ASEAN Framework Agreement on the Facilitation of Inter-State Transport (AFAFIST) and (iii) ASEAN Framework Agreement on Multimodal Transport (AFAMT) are aimed at improving transport facilitation. Currently, many protocols of these agreements have not been ratified or implemented, thereby delaying the establishment of effective cross-border facilitation. Thus, ratification and implementation of these agreements are crucial in fostering effective cross-border facilitation. Integral to these efforts is the ASEAN Single Window, which is an environment where ten National Single Windows operate and integrate, enabling a single submission of data and information, a single synchronised processing of data and information, and a single decision-making system for customs clearance of cargo. This would be reinforced with the ASEAN Single Stop Inspection.
- Sub-regional initiatives also contribute to ASEAN efforts in improving cross-border facilitation and institutional connectivity. Of particular importance is the Greater Mekong Sub-region (GMS) Cross- Border Transport Agreement (CBTA), which emphasises key issues such as exchange of commercial traffic rights, single-stop inspection and single-window inspection at key border checkpoints. Such initiatives, together with international efforts such as the EU experience, offer useful lessons for efforts to enhance ASEAN connectivity through improved cross-border facilitation and management.
- The ASEAN-EU Border Management Project promises a new dimension for improving the extent of cooperation between the immigration institutions.The project aims to strengthen the regional network and cooperation among the Border Management agencies of the ASEAN Member States and the enhancement of operational Border Management capacities in selected Border Crossing Points (BCP). The main target groups are the immigration, law enforcement, border security and customs officials.
2.3 People-to-People Connectivity
- Since its inception in 1967, ASEAN has been guided by the Bangkok Declaration, which calls for a prosperous and peaceful community through a collective effort to accelerate economic growth, enhance social progress and intensify cultural development to increase the living standards of its people. To this end, ASEAN has embarked on a number of initiatives including education, culture, social welfare, youth, women, rural development and poverty eradication to name a few.
- Following the adoption of the ASEAN Socio-Cultural Community (ASCC) Blueprint in 2009, the ASCC Council has been the main body entrusted with the responsibility to ensure that all the aspirations and objectives under the ASCC Blueprint are effectively and expeditiously implemented. These include promoting ASEAN awareness and education, and enhancing people-to-people links.
- The awareness of the diverse cultural heritages within ASEAN needs to be promoted. Studies on ASEAN arts and cultures as well as of languages should be encouraged. This will also have the added effect of preserving our cultural heritages for future generations.
- In the area of education and human resource development,four areas of cooperation have been prioritised. These include promoting ASEAN awareness among its citizens, particularly the youth; strengthening the ASEAN identity through education; building ASEAN human resources in the field of education; and strengthening the ASEAN University Network (AUN). In this connection, educational cooperation in line with the Cha-am Hua Hin Declaration on Strengthening Cooperation on Education to Achieve an ASEAN Caring and Sharing Community, should be promoted to encourage regional cooperation on basic education and achieve universal access to primary education across the region by 2015, including the promotion of life-long learning to enhance capacity building of the people. The quality and compatibility of education, including technical and vocational, and skills training in the region should also be improved by developing technical assistance programmes at all educational levels, where appropriate.
- The ASEAN University Network (AUN) was established in 1995 to promote collaborative studies and research programmes among ASEAN scholars and scientists. It currently consists of 26 leading universities in ASEAN and is actively supporting the mobility of both staff and student in the region through two key programmes including the AUN Actual Quality Assessment (AQA) and the ASEAN Credit Transfer System (ACTS).
- Key challenges faced by the education sector include the lack of an agreed set of infrastructure in higher education to facilitate the mobility of students and staff, incompatible academic cycles, the need for quality assurance procedures, recognition of qualifications provisions and domestic regulations, and raising the quality of education to train workers for the knowledge economy and accessibility to education in low income countries.
KeyChallenges
- Academic cycles
- Recognition of qualifications
- The ASEAN Committee for Culture and Information (COCI) was established in 1978 to promote effective cooperation in the fields of culture and information for the purpose of enhancing mutual understanding and
Promote greater interactions between scholars, writers, artists and media practitioners
solidarity among ASEAN peoples and furthering regional development. Several activities are undertaken each year to nurture talent and promote greater interactions between scholars, writers, artists and media practitioners. Amongst others, the activities include the ASEAN Youth Camp, the AsiaVision ASEAN TV News Award, the Best of ASEAN Performing Arts series, and the ASEAN Newsmaker Project.
- Challenges arise from the growing interdependence between cultural growth and economic sustainability. It is important to create greater awareness of cultural role in sustainable development and to include cultural policies as one of the key components in Member States’ development strategies.
- Several ASEAN initiatives in the tourism sector have been undertaken over the years under the Roadmap for Integration of Tourism Sector 2004-2010 to further promote ASEAN as a tourist destination through the liberalisation of tourism and travel related services, upgrading of tourism infrastructure, enhancement of the skills of tourism related personnel and encouraging greater participation from the private sector in the development of the tourism sector.
- The successful undertaking of the Roadmap resulted in greater inflow of tourists from both ASEAN and third countries into the region.This has also led to growing demand for local products and services, jobs creation, foreign exchange and greater interactions between
local peoples and the tourists. ASEAN is in the process of drafting a strategic plan to succeed the Roadmap for adoption later this year. The plan is entitled ASEAN Tourism Strategic Plan 2011-2015.
Key Challenges
Further integrate the tourism sector
- Notwithstanding the achievements, there are a number of challenges ASEAN must address if it is to succeed in its efforts to integrate the tourism sector in the region. Amongst others, these include the harmonisation of visa requirements, the development of third party liability insurance, the standardisation of tourism related services, the upgrading of tourism related infrastructure, and facilitation for inflow of tourists across the region.
- Consistent with ASEAN’s vision of a caring and sharing community, the ASEAN Committee on the Implementation of the ASEAN Declaration on the Protection and Promotion of the Rights of Migrant Workers (ACMW) is intensifying efforts towards the development of an instrument to promote decent employment of migrant workers, curb trafficking in persons and promote capacity building by sharing of experiences and best practices.
2.4 Narrowing the Development Gaps through the Initiative for ASEAN Integration
- The Initiative for ASEAN Integration (IAI) was launched in 2000 with the objectives of narrowing the development gap (NDG) and accelerating economic integration in ASEAN, particularly Cambodia, Lao PDR, Myanmar, and Viet Nam (CLMV countries). ASEAN has continued to emphasise the importance of narrowing the development gap and the effective implementation of the IAI and other sub-regional frameworks, as it will ensure that the benefits of ASEAN integration are fully realised. The IAI provides assistance to the CLMV countries in meeting ASEAN-wide targets and commitments towards realising the ASEAN Community.
- ASEAN is now implementing the second IAI Work Plan (2009-2015) which is based on key programme areas in the three Community Blueprints: ASEAN Political-Security Community (APSC) Blueprint, AEC Blueprint and ASCC Blueprint. A priority list is being prepared by the IAI Task Force, which includes activities related to ASEAN Connectivity, taking into account existing sub-regional cooperation frameworks.
2.5 Sub-Regional Cooperation in Southeast Asia
- Parallel efforts under various sub-regional cooperation programmes which address in varying degrees physical, institutional and people-to-people connectivity are also being pursued individually and collectively by ASEAN Member States. These sub-regional initiatives complement ASEAN cooperation and are primarily supported by the Asian Development Bank (ADB) with its funding and coordinating role. ASEAN Dialogue Partners such as Australia, China, the European Union, Japan, the Republic of Korea and the United States have also made significant contributions.The sub-regional initiatives similarly play potentially critical roles in addressing both the development gaps and connectivity gaps between and within countries in the ASEAN region.
- The major three sub-regional initiatives in the ASEAN region include:
(i) The Greater Mekong Sub-region (GMS), comprising of Cambodia, Lao PDR, Myanmar, Thailand, Viet Nam, and China established in 1992;
(ii) The Brunei Darussalam, Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines-East ASEAN Growth Area (BIMP-
EAGA) established in 1994; and
(iii) The Indonesia, Malaysia and Thailand-Growth Triangle (IMT-GT) established in 1994.
- Other sub-regional initiatives related to connectivity include, among others, the ASEAN-Mekong Basin Development Cooperation (AMBDC), the Mekong River Commission (MRC), the Cambodia– Laos–Viet Nam (CLV) Development Triangle, the Cambodia-Lao PDR-Myanmar-Viet Nam (CLMV), the Ayeyarwady–Chao Phraya–Mekong Economic Cooperation Strategy (ACMECS), and the Heart of Borneo (Brunei, Indonesia and Malaysia). The sub-regional initiatives usually focus on less developed areas of the ASEAN region with less favourable infrastructure stock and weak intra-regional connectivity and hence, most projects involve infrastructure projects and trade and transport facilitation as well as investment promotion and facilitation.
- The GMS. The GMS strategic framework envisions a well-integrated, prosperous and harmonious Mekong sub-region through enhanced connectivity, increased competitiveness, and fostering a greater sense of community. The GMS programme also aims to help realise the potential of the sub-region through an enabling policy environment and effective infrastructure linkages for enhanced economic cooperation, development of human resources, and respect for environment and social interests to ensure sustainable and equitable development.
- GMS has made considerable progress in the implementation of high priority projects primarily in transport, power, and telecommunications, with completed or ongoing infrastructure projects supported by the Asian Development Bank, GMS governments and development partners reaching US$ 11 billion. The preponderant focus on transport, telecommunications and energy infrastructure cooperation is consistent with the phased corridor development strategy adopted for GMS, with initial emphasis on physical connectivity, followed by transport and trade facilitation, and eventual economic corridor development.
- The Economic Corridors Forum, established to coordinate all efforts toward economic corridor development, has now adopted strategies and action plan for all three GMS corridors (i.e., North- South, East-West and the Southern economic corridors). The 3rd GMS Summit also gave impetus for GMS to shift more emphasis on “software” aspects (after the initial focus on the “hardware” aspects).A consolidated and comprehensive Transport and Trade Facilitation (TTF) programme of action is in the process of formulation, which includes the GMS Cross Border Transport Agreement (CBTA) and other TTF measures. In this respect, there is a need to synergise the work of ASEAN and GMS in trade and transport facilitation.
- There is increasing interface between GMS and ASEAN transport connectivity initiatives. For instance, some of the sections of the AHN coincide or interface with the road projects in the GMS Transport Sector Strategy (2006-2015), particularly in the CLMV countries (e.g. Siem Reap-Stung Treng in Cambodia, Ha Noi-Haiphong in Viet Nam). Further, two GMS railway projects in Cambodia and Viet Nam form part of the SKRL. In addition to these infrastructure interfaces, GMS and ASEAN efforts in software development, such as in trade and transport facilitation, are also increasingly being aligned, e.g., the planned Single-Window/Single-Stop Inspection facility under the GMS CBTA and the ASW initiative. GMS efforts are also increasingly focused on mitigating the negative impacts of increased transport connectivity, such as the spread of HIV/AIDS, human and wildlife trafficking and environmental degradation.
- Full realisation of benefits from the development of GMS transport corridors has met with a number of challenges, including (i) the absence of road links or bridges, and the poor condition of some road spans limiting the effectiveness of the regional corridors; (ii) growth of international traffic on the GMS corridors has been restricted by the failure to fully implement the CBTA, delaying freight at key border
Key Challenge for
Connectivity in the GMS
- Transform transport corridors into economic corridors
- Ensure optimal use of the transport infrastructure
- Align the GMS initiative and ASEAN programmes and projects
- Establish appropriate policy, regulatory and institutional
frameworks
crossing points; and, (iii) the limited development of infrastructure supportive of economic activity along the corridors has contributed to slower than expected traffic growth. Current efforts to address these include (i) the focus on completing and rehabilitating such missing links; (ii) the TTF programme of action under development which is expected to address the various impediments to the effective implementation of CBTA measures; and (iii) encouraging more industrial estates along the corridors to benefit from the improved road links.
- In summary, therefore, apart from sustaining the progress in physical transport infrastructure, the key issue and challenge facing the sub-regional connectivity being pursued under the GMS programme is in transforming the transport corridors into economic corridors and ensuring optimal use of the transport infrastructure.This requires, among others, establishing the appropriate policy, regulatory, and institutional frameworks.
- In energy, while GMS countries have made big strides in interconnecting power systems to enable bilateral power trade, the regional power infrastructure is still a long way off from undertaking advanced (multi-country) power trading as envisioned under the GMS Inter-Governmental Agreement on Regional Power Trading (IGA).This is due to substantial gaps in the levels of power infrastructure development and differences in technical standards and practices in individual countries.The GMS countries are however addressing these challenges by slowly but continually working on interconnecting their respective power systems guided by the updated master plan on GMS power interconnections.
- The GMS initiative is well in line with the ASEAN Connectivity and AEC Blueprint. The challenge is in ensuring that GMS and ASEAN programmes and projects mesh together very well. This is not likely to be smooth sailing, especially since the two programmes have been pursuing parallel efforts and have sunk substantial investments in certain areas of cooperation, which although should ideally be consolidated may involve nuances and detailed issues that may be difficult to iron out. Wholesale subsuming of one programme to another is clearly not a feasible option. Rather, detailed and careful analysis of the individual programme’s specific protocols and resources and careful linking and alignment of these would be needed.
- BIMP-EAGA. BIMP-EAGA was established to address the economic and social development of the less developed and more remote areas of the Member States (except for Brunei Darussalam), with initial focus primarily through increased trade, investment, and tourism, and ultimately through economic diversification beyond resource extraction. In contrast to GMS, BIMP–EAGA is a sub-national growth area which is not contiguous and is significantly less physically connected as it consists mainly of island economies and trades much more with the rest of the world, usually via national capital ports, than within the sub-region. The BIMP-EAGA has designated two economic corridors in the sub-region; i.e., Western Borneo Economic Corridor (WBEC) and the Greater Sulu Sulawesi Corridor (GSSC), and ADB has approved a technical assistance programme to assess the viability of the two corridors.
- BIMP-EAGA has undertaken important policy initiatives. In 2007, the EAGA Leaders designated BIMP- EAGA as the test bed for the implementation of ASEAN agreements particularly with regard to transport and trade facilitation. The BIMP-EAGA Transport Ministers signed four important agreements on air, land and sea transport since 2007 to further connectivity within the sub-region. The air agreement in particular is considered a landmark agreement for the designation of secondary international airports as “fifth freedom traffic rights” (FFTR) airports. However, current market conditions for passenger and cargo traffic do not support the rapid development of intra-EAGA air connectivity. Despite the “open skies” agreement, the air traffic within the BIMP-EAGA region remains light. Intra-EAGA maritime transport has also not improved substantially. Many of the designated routes for land, air and sea transport have been explored and tested by commercial operators and some of them have been suspended due to low load factor. Cabotage restriction is another hindrance for transport operators to achieve economies of scale in improving their services.
- In trade facilitation, BIMP-EAGA has pioneered in phasing the implementation of relevant ASEAN programmes like ASEAN Single Window (ASW). The BIMP-EAGA Customs, Immigration, Quarantine and Security (CIQS) Task Force was established in 2006 and has mapped gaps and needed reforms in existing CIQS rules, regulations and procedures against
international standards and is coming up with a Memorandum of Understanding on CIQS Harmonisation to help achieve a streamlined and simplified CIQS processes as well as standardising CIQS agenda consonant with international and regional standards and best practices. However, implementation of CIQS reforms and trade facilitation programmes so far are often challenged by varying levels of compliance with international conventions and best practices both within and between the member countries and are mainly built on practical and short-gestating measures that are aligned with national programmes and priorities.
Key Challenges for Connectivity in BIMP-EAGA
- Low load factors of sea, land and air routes
- Little intra-sub-regional investment flow
- CIQS reforms and trade facilitation programmes
- Institutional gap in BIMP-EAGA structure supporting project planning
and implementation
- Despite being a test bed, institutional relations and linkages between BIMP-EAGA and ASEAN is limited to the holding of the EAGA Leaders Summit back to back with the ASEAN Leaders Summit. Relations between the secretariats have been ad hoc at best. If EAGA is to be truly a test bed for ASEAN agreements, institutional arrangements will have to be strengthened.
- In 2009, BIMP-EAGA Leaders endorsed a major shift towards “projectisation”, i.e., expediting the implementation of priority projects to fulfil its strategic visions and goals. Subsequent processing of the endorsed projects (under a new three-year rolling pipeline of priority infrastructure projects) revealed that infrastructure requirements of BIMP-EAGA are usually not taken up by the relevant national agencies and often excluded from the list of national infrastructure development priorities (and therefore receive no budgetary allocation). To address this institutional gap, BIMP-EAGA started discussions in 2009 to establish a mechanism to rationalise the identification, prioritisation of infrastructure projects in the short term and to monitor their implementation in the longer term.
- BIMP-EAGA also continues to be confronted with broader economic and development challenges which affect and is affected by connectivity issues, most of which have persisted since its inception in 1994. Some of the more pressing challenges are: (i) continued dependence on primary resource- based economic activities and little sub-regional investment flows in agro-industry which is the BIMP- EAGA focus; (ii) weak private sector with equally weak capacity to capitalise on opportunities; (iii) high incidence of poverty in the sub-region; and, (iv) lack of vital infrastructure particularly in the Indonesia and Philippines components of EAGA which are major bottleneck to private sector investments. These broader development challenges faced by the BIMP-EAGA sub-regional initiative are described in detail in Appendix 2.3.
- In support of the ASEAN Roll-on/roll-off (RoRo) concept, the 5th BIMP-EAGA Transport Ministers Meeting (TMM) welcomed the conduct of a study on BIMP-EAGA RoRo network which may form part of an ASEAN RoRo network.
- IMT-GT. The IMT-GT sub-region is an area of significant potential complementarities in a wide range of sectors, from agriculture to tourism, manufacturing, human resources, and medical services.Although not completely physically contiguous as the GMS, the IMT-GT sub-region is likely to be as equally physically integrated as GMS through the road and rail networks between Thailand and Malaysia and shipping services between Indonesia, most parts of Malaysia, and Thailand.
- The IMT-GT sub-region has seen substantial progress in intra-regional economic linkages and has arguably the most extensive and geographically spread out economic sub-regional linkages among the three sub- regional initiatives. The IMT-GT Roadmap for Development, 2007-2011 is also probably the most cogent, extensive, and specific of the roadmaps of the three sub-regional initiatives.The Roadmap has two anchors; namely, (a) a policy and regulatory anchor for an enabling policy and regulatory environment conducive to private sector activities, and (b) the development of five interconnecting economic corridors. The IMT-GT governments have notably agreed to take necessary steps such that the prioritised projects in the IMT-GT are given priority in their national public investment and expenditure programmes.
- Despite the significant progress in IMT-GT sub-regional cooperation, substantial challenges remain. Future needs for promoting enhanced connectivity will need to consider a modal approach especially for surface transport modes which should be sub-divided on a corridor basis. It is evident that the primary
Key Challenges for Connectivity in IMT-GT
- Modal approach to surface transport connectivity needs
- Internal or external focus of maritime connectivity
- Institutional transformation in managing implementation of new pipeline projects
demand for road infrastructure is in Sumatera, focusing on the north-south link between Banda Aceh and Palembang. Meanwhile, completion of planning studies and design of rail links in Sumatera will be needed to fully implement the Trans Sumatera Railway. The Southern Thailand-Northern Malaysia Railway link is also of high priority.
- A key issue on maritime connectivity in IMT-GT is whether the focus on port development should be on external connectivity i.e., of IMT-GT with international markets. Intra-IMT-GT maritime trade is quite small and much of the bilateral maritime trade is being handled by non-conventional vessels and is often integrated within ‘localised’ cross-border trading arrangements.This notwithstanding, improved maritime connectivity is needed through the (i) development of RoRo services among Indonesia, Malaysia and Thailand across the Strait of Melaka; (ii) improvement of container operations on the north and east coast of Sumatera; and, (iii) the development of Thailand’s Andaman Sea Ports particularly in Phuket on account of passenger and cruise facilities.
- With regard to air services, there is now extensive coverage throughout the region with the exception of Southern Thailand.The impressive growth in low cost carriers’ activities has resulted in greatly improved accessibility and coverage in much of the sub-region. In general, the aviation infrastructure is now of good quality and sufficient capacity is available to cover growth to 2016. The one ‘hardware’ issue still outstanding is the need to construct a new airport outside Medan, Sumatera.
- The IMT-GT and BIMP-EAGA programmes have focused on connectivity corridors since the early years of their inception but their efforts have shifted to higher gear in recent years as the impetus for integration became more pressing. The ADB foresees that managing the new pipeline of priority infrastructure projects developed to accelerate implementation under the two sub-regional programmes will require an institutional transformation. It calls for close monitoring and substantive follow-through and require a greater awareness of the larger ASEAN connectivity picture as a basis for identifying gaps and planning the missing links.
- Financing of sub-regional infrastructure projects faces far more complex challenges than national projects. Apart from the usual challenges associated with financing large infrastructure projects (e.g., long implementation period, sovereign risks), the development of regional investments also require the support of, and coordination between, two or more countries, which makes the process more complicated. Private sector finance is also important for the middle income countries of IMT-GT and BIMP-EAGA. A critical factor affecting the attraction of private sector finance for sub-regional projects is the lack of adequate project preparation which could deter public-private partnerships (PPPs).The lack of adequate and reliable technical and financial information on PPP projects can hamper the evaluation of risks, not only from the point of view of the private sector entity, but also from the point of view of the public sector. A sub-regional project development facility is hence seen as crucial in providing resources for the preparation of pre-feasibility and feasibility studies.
- Overall, there is a need to promote links and interface among the various sub-regions to broaden and deepen these partnerships, given the larger geographical coverage and synergy that can be generated among the sub-regions. ASEAN makes available a broader regional framework in which these sub- regional programmes can carry out their work since many ASEAN and GMS, BIMP-EAGA, and IMT-GT activities share the same purpose. Since the participating countries in these sub-regional programmes are members of ASEAN, there may exist overlapping country participation and geographical coverage in the sub-regional programmes. Many ASEAN programmes, especially those in infrastructure, human resources and the environment, could be implemented with greater focus and at a more rapid pace when carried out in the smaller area and context of the sub-regions. Enhancing coordination among the
33 MASTER PLAN ON ASEAN CONNECTIVITY
GMS, BIMP-EAGA and IMT-GT sub-regional programmes with ASEAN will help bridge the gap between project-driven “bottom-up” and policy-driven “top-down” approaches to economic integration and promote closer linkages between the sub-regional programmes and ASEAN. It will also be necessary to examine how to more closely coordinate the three sub-regional programmes in terms of sub-regional analyses and assessments, and programme and project planning.
- The sub-regions can be used as test beds for accelerating the implementation of relevant ASEAN agreements to contribute towards the acceleration of ASEAN economic integration especially the AEC by 2015. Conversely, the sub-regions can capitalise on the existing AEC initiatives in order to further strengthen their development agendas. The mapping of sub-regional action plans and sector roadmaps vis-à-vis the AEC Blueprint will be a useful start.This mapping exercise would assist in the identification of short-term and long-term measures for strengthening coordination and promoting links among these sub-regional programmes and with ASEAN mechanisms.
- In view of the above and to assist the Member States, aligning the sub-regions is required to accelerate the development of ASEAN’s regional market and connectivity. The synergies between ASEAN and the sub-regional economic programmes offer immense potential for growth and development. Governments will use these synergies to strengthen coordination between the ASEAN institutional processes and the sub-regional programmes. Furthermore it will have provided ASEAN with the mandate to work closely with the sub-regional platforms to initiate policy measures and develop technical assistance, and raise these with ASEAN’s decision-makers.
- Sub-regional cooperation initiatives with the participation of ASEAN’s external partners also play an increasingly important role in the architecture of economic relations in Asia. The implementation of these projects in the sub-regions together with those under the IAI would contribute to the narrowing of the development divide and enabling the sub-regions to link with the rest of ASEAN region and beyond.
• • • •
Key Strategies for Enhanced ASEAN Connectivity
CHAPTER 3
MASTER PLAN ON ASEAN CONNECTIVITY
CHAPTER 3:KEY STRATEGIES FOR ENHANCED ASEAN CONNECTIVITY
. As elaborated in Chapter 2, ASEAN’s fundamental framework for enhancing its connectivity consists of a three-pronged strategy of improved physical connectivity, better institutional connectivity and deeper people-to-people connectivity which will be supported by stronger financial mechanisms and institutions. The end result would be that the production and distribution networks in ASEAN deepen (in terms of the value chain), widen (with more commodities and countries or areas in the region engaged in the networks), and become more entrenched in the global and East Asia production and distribution networks. Equally important, enhanced ASEAN connectivity narrows development gaps in the ASEAN region because the ensuing increased connectivity of lagging countries and lagging regions within countries in ASEAN leads to increased opportunities for greater investment, trade and growth in these areas and their revealed comparative advantages flourish. Finally, at the heart of the ASEAN Economic Community are deeper intra-regional economic linkages and networks within ASEAN at the same time, the region becomes more integrated with the rest of the world.
- ASEAN, as a region, is more geographically dispersed and not physically contiguous compared to China and India. More importantly, compared to these two nations,ASEAN consists of ten Member States with disparate policies, priorities and institutions. Enhanced ASEAN connectivity helps address these relative disadvantages of the ASEAN region and at the same time engenders a more cohesive, competitive, investment-attractive, resilient, and dynamic economic community in the ASEAN region.
- There is an additional challenge for the ASEAN region, arising from its success in plugging into the fast growing Chinese and Indian economies, which would bring out the importance of ASEAN Connectivity. Specifically,ASEAN-China trade, at an average growth rate of 24 percent per year, grew twice the growth rate of intra-ASEAN trade during 2000-2009, so much so that the level of ASEAN-China trade reached 43 percent of intra-ASEAN trade in 2009 as against 19 percent in 2000. Similarly, ASEAN-India trade has picked up tremendous steam since 2004, also growing at 24 percent per annum during 2004-2009; although the ratio of ASEAN-India trade to the total intra-ASEAN trade was just at 11 percent by 2009. Intra-ASEAN trade did not only grow more slowly than ASEAN-China trade and ASEAN-India trade but also declined more during recessionary years including 2009 (refer to Figure 3.1).
Figure 3.1 Ratio of ASEAN-China Trade & ASEAN-India Trade to Intra-ASEAN Trade
Source: ASEANStat, ERIA
- In the light of the recent trends in ASEAN-China trade and ASEAN-India trade, intra-ASEAN trade needs to grow at least in step with ASEAN-China trade to reinforce ASEAN’s centrality and its role as the driving force in regional integration. This calls for greater connectivity among ASEAN Member States. Enhanced ASEAN connectivity and the road to an ASEAN Community can help engender greater dynamism into intra-ASEAN linkages at the same time that the ASEAN region becomes more deeply engaged with the rest of the world. Enhanced ASEAN Connectivity will strengthen ASEAN’s role at the centre of East Asian economic integration and the emergence of an East Asian economic community. ASEAN welcomes the commitments of its Dialogue Partners and other external partners to implement the Master Plan on ASEAN Connectivity.
3.1 Physical Connectivity
- Enhanced physical connectivity in the ASEAN region demands, first and foremost, better transport, improved ICT infrastructure and expanded interconnectivity.They are all vital for the seamless movement of goods and tradable services within the region and to the rest of the world. Energy infrastructure, including regional or sub-regional interconnection, which allows for reliable energy at reasonable cost in ASEAN, is important for production efficiency and reliability as well as for energy security in the region. The following are the key strategies to enhance physical connectivity in the ASEAN region:
Key Strategies to Enhance Physical Connectivity |
Strategy 1 | Complete the ASEAN Highway Network |
Strategy 2 | Complete the implementation of the Singapore Kunming Rail Link (SKRL) project |
Strategy 3 | Establish an efficient and integrated inland waterways network |
Strategy 4 | Accomplish an integrated, efficient and competitive maritime transport system |
Strategy 5 | Establish integrated and seamless multimodal transport systems to make ASEAN the transport hub in the East Asia region |
Strategy 6 | Accelerate the development of ICT infrastructure and services in each of the ASEAN Member States |
Strategy 7 | Prioritise the processes to resolve institutional issues in ASEAN energy infrastructure projects |
Strategy 1: Complete the ASEAN Highway Network
- In terms of traffic volume, road transport is the most important mode of transportation. Moreover, it is the integration of the lagging areas in the region under the ASEAN Highway Network (AHN) project that would have significant benefit to the poorer areas of continental ASEAN region. However, the implementation of the Ministerial Understanding on the Development of the ASEAN Highway Network Project (5th ASEAN Transport Ministers Meeting, Ha Noi, 1999) is behind schedule, which required ASEAN Member States to upgrade all designated routes to “Class III” or above and to install road signs by 2004.
Key actions:
(i) Upgrade all “below Class III” sections of AHN into at least “Class III”, with highest priority to the “below Class III” sections of the Transit Transport Routes (TTR), by 2012.
(ii) Install common road signs in all designated routes, with a specific priority on TTR by 2013.
MASTER PLAN ON ASEAN CONNECTIVITY 38
(iii) Upgrade “Class II or III” sections with high traffic volume to “Class I” by 2020.
(iv) Conduct a feasibility study on bridging archipelagic countries and mainland ASEAN by 2015.
(v) Upgrade the extension of AHN to China and India, particularly sections from Ha Noi via northern Lao PDR through Myanmar to the border with India, by 2015.
Strategy 2: Complete the implementation of Singapore Kunming Rail Link (SKRL) project
- The Singapore Kunming Rail Link (SKRL) project has been a priority agenda in ASEAN transport cooperation, and the political motivation to complete SKRL is significantly high. SKRL is expected to provide an alternative mode of land transportation, which is more environmentally friendly than road transportation. The SKRL has two lines, an “Eastern line” through Thailand, Cambodia and Viet Nam, with a spur line between Lao PDR and Viet Nam, and a “Western line” through Thailand and Myanmar. In view of the greater challenges in establishing the Western line, it is preferable to first complete the Eastern line in order to have a fully operational railway link between Singapore and China (via Kunming) as soon as possible.
Key actions:
(i) Construct the missing link sections.
a) Thailand: Aranyaprathet – Klongluk (6km) by 2014;
b) Cambodia: Poipet – Sisophon (48km) by 2013;
c) Cambodia: Phnom Penh – Loc Ninh (254km) by 2015;
d) Viet Nam: Loc Ninh – Ho Chi Minh (129km) by 2020;
e) Viet Nam: Mu Gia – Tan Ap – Vung Ang (119km) by 2020;
f) Lao PDR: Vientiane – Thakek – Mu Gia (466km) by 2020;
g) Myanmar: Thanbyuzayat – Three Pagoda Pass (110km) by 2020; and
h) Thailand: Three Pagoda Pass - Nam Tok (153km) by 2020.
(ii) Formulate a strategy for a seamless operation of SKRL by 2013.
(iii) Mobilise financial resources and technical assistance from external partners, either on a bilateral basis or with the coordination of ADB, to support the completion of SKRL in accordance with the agreed deadline.
(iv) Study the possibility of extending the SKRL to Surabaya, Indonesia.
Strategy 3: Establish an efficient and integrated inland waterways network
- Inland waterways transport plays a vital role in the mobility, welfare and economic development in several ASEAN Member States. It can provide a relatively cost-efficient and less environmentally harmful means of transport but has lacked adequate investment. There is a need to formulate and implement a regional policy framework for developing inland waterways transport services in ASEAN.
Key actions:
(i) Formulate a regional plan for developing inland waterways in ASEAN by 2012 and begin implementation thereafter.
Strategy 4: Accomplish an integrated, efficient and competitive maritime transport system
- In terms of the traffic volume in international trade, maritime transport is the most important mode of transportation. ASEAN needs to foster a competitive and efficient inter-state shipping service in ASEAN and take advantage of the full potential benefit of seamless integration with the global shipping system. In addition, efficient and competitive shipping routes to connect archipelagic regions needs to be established in order to enhance intra-ASEAN connectivity (refer to Figure 3.2). This will also contribute to narrowing the development gaps in the archipelagic ASEAN. Establishing a Nautical Highway System (RoRo) and inter-state shipping within the region will also boost tourism, including cruise tourism, in the region.
Figure 3.2: “Ring” Shipping Route
Source: ERIA/IDE GSM Team
Key actions:
(i) Enhance the performance and capacity of the 47 designated ports, with the priority set in the studies undertaken and being undertaken under Measures 6, 7 and 8 of the Roadmap Towards an Integrated and Competitive Maritime Transport in ASEAN by 2015. The enhancement of capacity can include the improvement in associated services like warehousing as well as dredging of the water channels where needed.
a) Establish efficient and reliable shipping routes (including RoRo) connecting mainland and archipelagic Southeast Asia including the related sub-regional initiatives such as BIMP-EAGA and IMT-GT. The emerging and/or potentially important international routes: Satun/Trang – Penang – Belawan, Malacca – Dumai, Davao – Bitung, Zamboanga - Sandakan, Muara – nearby ports;
b) Strengthen linkages with global and regional trunk routes and domestic shipping routes; and
c) Conduct a feasibility study on the establishment of an ASEAN RoRo network.
Strategy 5: Establish integrated and seamless multimodal transport systems to make ASEAN the transport hub in the East Asia region
- ASEAN is at the geographic centre of the emerging global centre of production and demand, the South Asia-Southeast Asia-Northeast Asia-Australia/New Zealand corridor. ASEAN needs to strategise on how its strategic location can make ASEAN function as the transport hub in the region. Considering that transport cooperation in ASEAN has been formulated and implemented separately by modes of transportation, it is important that ASEAN streamlines the sectoral strategies with reference to the concept of multimodal transport systems and dry ports in order to enhance intra- and extra-ASEAN connectivity. Although the full implementation of the strategy will take some time, it is important at the outset to have a clear strategy of multimodal development in the ASEAN region in consonance with developments in the broader East Asian region. Figures 3.3 and 3.4 illustrate the East West Economic Corridor (EWEC) Missing Link in Myanmar and the Mekong-India Economic Corridor (MIEC).
Figure 3.3: EWEC Missing Link in Myanmar Figure 3.4: Mekong-India Economic Corridor
Source: ERIA/IDE GSM Team
Key actions:
(i) Conduct a study on potential multimodal transport corridors to empower parts of ASEAN to function as land bridges in global supply routes.
(ii) Complete the East West Economic Corridor (EWEC).
a) Construct the missing link in Myanmar; and
b) Develop/upgrade terminal ports:Yangon, Da Nang.
(iii) Promote the Mekong-India Economic Corridor (MIEC) as a land bridge.
a) Construct the Mekong Bridge in Neak Loung (National road No.1 in Cambodia);
b) Develop the Dawei deep sea port (by 2020);
c) Build the highway between Kanchanaburi and Dawei (by 2020); and
d) Conduct a feasibility study and preliminary design for the railway spur line between Kanchanaburi and Dawei.
(iv) Identify and develop a network of ASEAN dry ports in accordance with existing ASEAN initiatives such as the ASEAN Highway Network and the SKRL.
Strategy 6: Accelerate the development of ICT infrastructure and services in each of the ASEAN Member States
- A robust ICT infrastructure in tandem with better human resources and regulatory environment is critical for enabling ICT as an engine of trade, economic growth, innovation and better governance in the ASEAN region. A number of countries in the region are gaining global reputation in ICT infrastructure, ICT-based industries and services. However, the digital divide within ASEAN remains, especially between the lagging regions and the urban areas on the one hand and between countries on the other hand.The digital divide needs to be reduced in order to narrow the development gaps within the region.
Key actions:
(i) Establish an ASEAN Broadband Corridor by identifying and developing locations in each ASEAN Member State to offer quality broadband connectivity.This will enable seamless usage of broadband services and applications across ASEAN to further connect and enhance the development of ICT and other sectors by 2014.
(ii) Promote the diversity of international connectivity among ASEAN Member States by 2015.
(iii) Establish an ASEAN Internet Exchange Network to facilitate peering amongst ASEAN internet access providers to reduce latency and increase speed as well as lower costs by 2013.
(iv) Promote network integrity and information security, data protection and Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT) cooperation by developing common frameworks and establishing common minimum standards where appropriate, to ensure a level of preparedness and integrity of networks across ASEAN by 2015.
(v) Review Universal Service obligations and/or similar policies to ensure that infrastructure covered under these policies are broadband Internet capable by 2015.
(vi) Prioritise and expedite roll-out of broadband Internet capable infrastructure to schools by 2015.
(vii) Conduct feasibility study on developing after 2015 an ASEAN Single Telecommunications Market, in the context of free flow of products, services, investments and skilled human resources by 2015.
Strategy 7: Prioritise the processes to resolve institutional issues in ASEAN energy infrastructure projects
- Physical energy infrastructures play a critical role to deepen the extent of regional integration and economic growth in ASEAN region. To enhance the current status of the Trans-ASEAN Gas Pipeline (TAGP) and ASEAN Power Grid (APG), there is a need to address the challenges of the technical and legal issues through harmonisation of standards. In addition, the complementary development of additional supply of piped natural gas and other energy sources such as coal and liquefied natural gas (LNG) also needs to be addressed.
Key actions:
TAGP
(i) Form a model for ASEAN Joint-Venture gas pipeline company.
(ii) Adopt common technical standards for design, construction and maintenance of infrastructure.
(iii) Adopt business model for TAGP.
(iv) Implement regional safety/security plan for TAGP infrastructure.
(v) Optimise and operationalise TAGP.
(vi) Study the feasibility of extending the TAGP to BIMP-EAGA.
APG
(i) Harmonise legal and regulatory framework for bilateral and cross-border power interconnection and trade (2008 – 2010).
(ii) Harmonise common technical standards codes or guidelines of the ASEAN Interconnection projects: Planning and Design, System Operation, and Maintenance (2008 – 2012).
(iii) Identify and recommend financing modalities for realising the APG (2008 – 2011).
(iv) Implement various bilateral/multilateral interconnection projects and reporting progress to Heads of ASEAN Power Utilities/Authorities (HAPUA) Council and ASEAN Senior Officials Meeting on Energy (SOME)/ASEAN Ministers on Energy Meeting (AMEM) (2008 – 2015).
3.2 Institutional Connectivity
- The second critical anchor of ASEAN connectivity, apart from physical connectivity, is institutional connectivity. Enhanced institutional connectivity in the ASEAN region raises the effectiveness of physical connectivity by easing the flow of goods and services (from the elimination of barriers to trade), reducing the cost of moving goods and services (from improved transport and trade facilitation services), and ensuring greater economic and social returns from greater physical connectivity and deeper economic linkages (through higher investments).
- This would entail much reduced policy and institutional barriers to the movement of goods, services and resources within the region, more harmonised rules, regulations, procedures and standards among ASEAN Member States, as well as improved institutional and infrastructural capability to provide the necessary transport and trade facilitation services (e.g.,Transport Facilitation Agreements and National Single Window) for a seamless movement of goods, services and resources in the ASEAN region.
The following are the key strategies to enhance institutional connectivity in the ASEAN region:
Key Strategies to Enhance Institutional Connectivity |
Strategy 1 | Fully operationalise the three Framework Agreements on transport facilitation |
Strategy 2 | Implement initiatives to facilitate inter-state passenger land transportation |
Strategy 3 | Develop the ASEAN Single Aviation Market (ASAM) |
Strategy 4 | Develop an ASEAN Single Shipping Market |
Strategy 5 | Accelerate the free flow of goods within ASEAN region by eliminating barriers to merchandise trade within the region |
Strategy 6 | Accelerate the development of an efficient and competitive logistics sector, in particular transport, telecommunications and other connectivity-related services in the region |
Strategy 7 | Substantially improve trade facilitation in the region |
Strategy 8 | Enhance border management capabilities |
Strategy 9 | Accelerate further opening up of ASEAN Member States to investments from within and beyond the region under fair investment rules |
Strategy 10 | Strengthen institutional capacity in lagging areas in the region and improve regional-sub- regional coordination of policies, programmes and projects |
Strategy 1: Fully operationalise the three Framework Agreements on transport facilitation
- A transport network is only as strong as the weakest link, and the weakest links can be found behind the national borders. In order to realise the vision of “single market and production base” as envisaged in the AEC Blueprint,ASEAN’s connectivity should be enhanced through transport facilitation initiatives to minimise (and eventually eliminate) the frictions at national borders that increase the transactions cost of moving goods between countries in the region. These initiatives include:
- ASEAN Framework Agreement on the Facilitation of Goods in Transit (AFAFGIT);
- ASEAN Framework Agreement on the Facilitation of Inter-State Transport (AFAFIST); and
- ASEAN Framework Agreement on Multimodal Transport (AFAMT).
Key actions:
(i) Expedite the ratification of the Agreements so as to enable their operationalisation in the region.
(ii) Expedite the finalisation of Protocol 2 (Frontier Posts) and Protocol 7 (Customs Transit) under AFAFGIT for eventual signing by ASEAN Member States by 2011.
(iii) Accelerate the conclusion of Protocol 6 (Railway borders and interchange stations) under AFAFGIT for eventual signing by ASEAN Member States by 2011.
(iv) Closely monitor the progress of implementation of AFAFGIT, AFAFIST and AFAMT in order to ensure that the three Agreements would be implemented by the ASEAN Member States by 2014-2015.
Strategy 2: Implement initiatives to facilitate inter-state passenger land transportation
- The expansion of road and rail connections within ASEAN would help to facilitate land travel between Member States (by private vehicles, tour buses and coaches) which could result in the development of new tour packages comprising tourism products from different Member States.
- However, there are a number of challenges which could impede the free movement of vehicles, goods, and people across international borders including (i) restrictions on the entry of motor vehicles; (ii) different standards requirements (vehicle size, weight and safety requirements, and driver qualifications); (iii) inconsistent procedures related to customs inspections, customs clearances, and assessment of duties; and (iv) restrictive visa requirements.
- In addressing these concerns, under the Greater Mekong Sub-region (GMS), the Cross Border Transport Agreement (CBTA) was signed to facilitate cross-border transport for both goods and people. BIMP- EAGA also signed and implemented the Memorandum of Understanding on Cross Border Movement for Buses and Coaches. Several ASEAN Member States have also entered into bilateral agreements to cater for greater cross-border mobility of passenger vehicles.
- ASEAN should capitalise on the existing sub-regional agreements with the view to develop it into an ASEAN-wide agreement to facilitate inter-state passenger land transportation in the region.
Key actions:
(i) Expedite the implementation of the existing bilateral and sub-regional arrangements on facilitation of inter-state passenger land transportation in the region by 2013.
(ii) Develop a regional ASEAN arrangement on facilitation of inter-state passenger land transportation, based on the assessment of the implementation of the bilateral and sub-regional arrangements by 2015.
Strategy 3: Develop the ASEAN Single Aviation Market (ASAM)
- In view of the rapidly growing importance of air transportation as well as the accelerated restructuring of the global aviation market,ASEAN needs to strengthen its aviation industry by establishing the ASAM. Low Cost Carriers (LCCs) have been rapidly growing in ASEAN, thereby facilitating intra-ASEAN tourism which in turn contributes to enhanced “people-to-people” connectivity.The Roadmap for Integration of Air Travel Sector (RIATS) has defined the timeline to establish the ASAM by 2015.
Key actions:
(i) Ratify and implement the Multilateral Agreement on the Full Liberalisation of Air Freight Services (MAFLAFS) and its Protocols 1 and 2 as soon as possible, in support of the establishment of the AEC by 2015, noting that the implementation timelines of the MAFLAFS and its Protocols 1 and 2 as agreed by ASEAN Transport Ministers are 31 December 2008.
(ii) Ratify and implement the Multilateral Agreement on Air Services (MAAS) and its Protocols 1 to 6 as soon as possible, in support of the establishment of the AEC by 2015, noting that the implementation timelines of the MAAS as agreed by ASEAN Transport Ministers are 31 December 2008 for Protocol 5 and 31 December 2010 for Protocol 6.
45 MASTER PLAN ON ASEAN CONNECTIVITY
(iii) Sign the ASEAN Multilateral Agreement on the Full Liberalisation of Passenger Air Services (MAFLPAS) by 2010 and ratify and implement MAFLPAS and its Protocols as soon as possible, in support of the establishment of the AEC by 2015, noting that the implementation timelines of Protocols 1 and 2 are 30 June 2010 and 30 June 2013 respectively.
(iv) Conclude the Air Transport Agreement (ATA) with China by 2010, India and ROK, and possibly other regional partners, not later than 2015, and thereafter consider the possible expansion to other partners.
(v) Formulate an ASEAN Single Aviation Market (ASAM) Roadmap and implementation strategy by 2011 and develop an ASAM by 2015.
Strategy 4: Develop an ASEAN Single Shipping Market
- Progressive integration towards the formation of an ASEAN single shipping market and intensified development of the maritime network infrastructure will lead towards a stronger ASEAN maritime sector, operating efficiently and delivering quality goods and services at competitive prices.
Key actions:
(i) Finalise the development of strategies by 2012 for an ASEAN Single Shipping Market and develop the relevant framework for its implementation no later than 2015.
Strategy 5: Accelerate the free flow of goods within ASEAN region by eliminating barriers to merchandise trade within the region
- The full play of comparative advantage and the deepening of regional production and distribution networks in the ASEAN region necessitate that goods flow as freely as possible within the region. This will allow for maximisation of complementarities and synergies among economies and production areas in the ASEAN region, which will lead to greater international competitiveness of the region in trade in the global arena.
- Given that tariffs on intra-ASEAN merchandise trade have virtually gone to zero in the original ASEAN-6 countries at present and will go virtually to zero in the newer CLMV countries by 2015 (with some exceptions), eliminating the barriers to merchandise trade within ASEAN in order to accelerate the free flow of goods in the region would entail the following:
Key actions:
(i) Rationalise and minimise non-tariff measures of ASEAN Member States.
a) Undertake a complete and up-to-date inventory of non-tariff measures of ASEAN Member States using the most updated international classification of non-tariff measures by 2015.
b) Expedite the operationalisation of the ASEAN Trade Repository (ATR) by 2015 so as to promote transparency and foster voluntary compliance while providing more certainty and predictability to business and industries.
c) Develop a set of guidelines for import licensing procedures, prohibitions and quantitative restrictions in a step by step basis with a view to eliminate the non-tariff barriers (NTB) component of these measures by 2014.
d) Eliminate non-tariff barriers and minimise the trade barrier effect of allowable non-tariff measures by 2015 .
e) Strengthen the capability of the ASEAN Secretariat to monitor effectively the implementation of the above-mentioned mandates by 2012.
(ii) Harmonise and develop regional standards and strengthen conformity assessment capability in the region, which may include the following:
a) Set common rules for standards and conformity assessment procedures.
- Formulate and establish regional infrastructure and institutional mechanisms supported by a legal framework for the development of regional standards by 2015.
The technical specifications of products meeting the essential requirements of safety and quality set out in the legislations, be it at the regional or national level, should be laid down in harmonised standards which remain as voluntary tools for compliance and uniformly applied in ASEAN to support the operations of a single market.
- Formulate a comprehensive regional policy and framework for conformity assessment procedures by 2015.
A comprehensive regional policy and framework for conformity assessment that will give the regulators the means to set up common procedures, for manufacturers to demonstrate product conformity, uniformly applied in ASEAN to support the operations of a single market.
- Formulate a legal framework for the application of principles of mutual recognition of products manufactured and/or marketed legally based on equivalence in national regulatory requirements by 2015.
Notwithstanding the harmonisation of regulatory requirements in ASEAN, policies and means should also be established to support the free movement of products which are legally manufactured and/or marketed in a Member State as long as the products meet the equivalent level of protection imposed by both exporting and importing Member States. This should be supported by overarching regional requirements for product safety and the circumstances when a Member State can refuse mutual recognition to ensure that no protectionism is imposed by any Member State.
b) Apply the ASEAN Conformity Mark by 2015.
The establishment of rules for the application of the ASEAN Conformity Mark to demonstrate compliance with harmonised regional legislations and that the product conforms to the applicable provisions of the overarching regional requirements for product safety and has been subject to the appropriate conformity assessment procedures as a mark of confidence that only products that meet the essential requirements of safety are placed in the ASEAN market.
1 Flexibilities up to 2018 for CLMV countries.
c) Specify the industries and products where national standards are to be set to international standards within the region, which industries and products where regional standards are to be established, and which industries and products will have essentially national standards by 2015.
d) Set out a timetable, and implement accordingly, the implementation of the alignment of national standards to international standards as well as the establishment of regional standards which will become national standards by 2015.
e) Accelerate operationalisation of MRAs in priority and selected industries and products in the region by 2015.
(iii) Enhance the rules of origin (ROO) continuously, including the introduction of facilitative processes such as the electronic processing of certificate of origin (COO) by 2012 and harmonisation or alignment of national procedures to the extent possible by 2015.
(iv) Determine areas for further alignment of ROOs of Dialogue Partners to the ATIGA ROOs, in order to strengthen production processes in the region and expedite the movement of goods within ASEAN and between ASEAN and Dialogue Partners by 2015.
Strategy 6: Accelerate the development of an efficient and competitive logistics sector, in particular transport, telecommunications and other connectivity related services in the region
- The competence, efficiency and cost effectiveness of logistics services industry in a number of ASEAN Member States can be further improved, as reflected in the wide variation in the ranking of the ASEAN countries in the “competence of service providers” sub-component of the World Bank’s Logistics Performance Index (2010). As ASEAN Member States develop their logistics development plans, the liberalisation of the logistics services industry can be expected to contribute to the improvement of logistics in the region. In addition, the transport services component of connectivity and logistics would also need to be improved significantly in a number of ASEAN countries. Similarly, the geographic breadth and efficiency of telecommunications infrastructure and cost competitiveness of telecommunications services in a number of ASEAN countries leave much to be desired. A more liberalised and competitive environment can entice more investment and continuing technology improvements to the region’s telecommunications, logistics and transport services industries.
Key actions:
(i) Remove substantially all restrictions on trade in services for logistics services by 2013.
(ii) Expedite the liberalisation of the telecommunications services as soon as possible noting that the deadline in the AEC Blueprint is 2010.
Strategy 7: Substantially improve trade facilitation in the region
- There is no doubt that many ASEAN Member States need to substantially improve the quality of customs services and the timeliness of delivery of goods before the region can become truly an integrated production hub for the world. At present, the international ranking on the quality of customs services of ASEAN Member States as reflected in the World Bank’s Logistics Performance Index 2010 is divergent (from the world’s number 2 to the world’s number 146 out of a total of 155 countries). Among the ASEAN Member States, the percentage of imports subjected to physical inspection ranges from 1 percent to 50 percent while the percentage of imports subjected to multiple physical inspection ranges from 1 percent to 15 percent of imports. The extremely wide range of performances of customs services in the ASEAN region, among others, effectively illustrates the significant challenge of providing institutional connectivity towards an integrated and interconnected ASEAN region.
- The implementation of the National Single Windows and the ASEAN Single Window together with the reform and modernisation of customs will jointly redress the highly disparate customs environments in the region, thereby engendering faster and more predictable flow of goods within the region and from the region and the rest of the world. This initiative requires a change of essential features of customs control, expressed in customs procedures and practices. Foremost of all, making them compatible and interoperable is a key to enhanced ASEAN connectivity. Indeed, the deepening and widening of the regional production networks in the region, which means larger volume of time sensitive imports moving within the region, necessitates more efficient and consistent customs service in the ASEAN Member States. However, a more efficient and consistent customs service demands a more efficient and effective coordination of related government agencies with the customs service in each of the ASEAN Member States. The implementation of the National Single Windows and the ASEAN Single Window facilitates the streamlining of processes and procedures, engenders tight coordination of related government agencies and trade-related service providers in the private sector, and fosters greater transparency and predictability on trade-related rules, regulations and procedures. All these redound to faster, easier, more predictable, and more cost effective movement of goods that would ultimately benefit the ASEAN Member States and lead to deeper ASEAN economic linkages.
- The development and operationalisation of the National Single Windows has proven to be more complex than earlier anticipated; hence, the delays in the implementation in the original ASEAN-6 countries beyond the original target. Nonetheless, given the critical importance of the National Single Windows and the ASEAN Single Window for ASEAN Connectivity, there is a need to forge ahead on the implementation of the Single Window initiative in the whole ASEAN region with greater resolve.
Key actions:
(i) Accelerate the full implementation of the National Single Windows (NSWs) for ASEAN-6 as soon as possible, noting that the deadline for the establishment of NSWs in ASEAN-6 was 2008, and for CLMV in 2012.
(ii) Activate and operate the ASEAN Single Window in selected ports as early as possible for Member States who are ready to implement it, and for all ASEAN Member States, by 2015.
(iii) Simplify customs procedures, formalities and practices of all Member States with priority on those serving to a single market and single production base (such as design and operation of outward processing, inward processing, temporary admission) by 2013 with the target of reducing processing costs by 20 percent by 2013 and by 50 percent by 2015.
(iv) Develop a comprehensive and compatible regulatory framework on customs procedures and border management operations by 2014.
(v) Promote partnership and active engagement of businesses and industries into the process of policy making in fostering its speedy and smooth implementation.
(vi) Develop the human resources necessary to complement the above actions by 2013.
Strategy 8: Enhance border management capabilities
- Synchronising activities of control at border among related agencies in charge of border management is the first step to improve the connectivity among Member States. Mutual recognition arrangements constitute a comprehensive upgrade to enable goods, means of transport and passengers to cross border without interruption. At present, the cooperation in the area has started and if accelerated, outputs of this cooperation will assist in enhancing ASEAN Connectivity. In this regard, appropriate measures need to be explored and developed as necessary, in accordance with national laws and regulations, in order to ensure a safe region for the peoples of Southeast Asia and secure supply chains throughout the region.
Key actions:
(i) Develop procedures of border management (Customs, Immigration, Quarantine, or CIQ) in managing cross-border movement of passengers and goods by 2013.
(ii) Synchronise procedures, formalities and practices in border management and its harmonisation to the extent possible by 2013.
(iii) Promote joint border management in pursuing “One Single Inspection and Processing Point” by 2013.
Strategy 9: Accelerate further opening up of ASEAN Member States to investments from within and beyond the region under fair investment rules
- Benefits from the initiatives toward an interconnected ASEAN are best enhanced with increased investments from domestic investors, foreign investors from within the region, and from the rest of the world. Increased investments have been key enablers of robust economic and trade growth in virtually all the economic success stories in the developing world in recent decades.Thus, it is important for the ASEAN Member States to be attractive investment destinations. At present, ASEAN Member States vary widely in terms of investment attractiveness, with international rankings on global competitiveness and ease of doing business ranging from one of the world’s best to among one of the world’s lowest. One pressing challenge is how to substantially improve the investment attractiveness of the investment lagging countries in the region, thereby ensuring that the benefits from ASEAN Connectivity become more widespread within the region.
- Greater physical connectivity as well as regulatory and institutional improvements in order to ease the flow of goods and services in the region is expected to improve the attractiveness of the ASEAN region as an investment destination. The further opening up of the ASEAN Member States to foreign investments from the region and the rest of the world as well as ensuring a fair investment regime for both domestic and foreign investors will also improve further the investment attractiveness of ASEAN Member States.
- ASEAN needs to remain committed to fully implement the three-phased investment liberalisation programme by 2015.
Key actions:
(i) Establish a modality for the phased reduction/elimination of investment restrictions and impediments, in order to achieve a free and open investment regime with minimal investment restrictions within ASEAN by 2015. The reduction and elimination of investment restrictions and impediments is preferentially accelerated in the ASEAN priority integration sectors.
(ii) Establish a review process at the level of Ministers to ensure effective implementation of the phased reduction of the investment restrictions and impediments in each ASEAN Member State by 2015.
Strategy 10: Strengthen institutional capacity in lagging areas in the region and improve regional-sub-regional coordination of policies, programmes and projects
- Effective implementation of the initiatives in the Master Plan on ASEAN Connectivity that would provide a more balanced development impact on the region necessitates the strengthening of the institutional capacity in lagging areas or countries in ASEAN as well as good coordination of the policies, programmes and projects of the sub-regional initiatives in ASEAN (e.g. GMS, BIMP-EAGA, IMT-GT, Heart of Borneo) with the corresponding national policies, programmes and projects of the ASEAN Member States.
- The Initiative on ASEAN Integration (IAI) has provided some resources for capacity building in the CLMV countries. However, much more resources are needed especially in the CLM countries in order for the significant initiatives in the Master Plan to be effectively implemented. A key example is the National Single Window. Both technical expertise and financial resources are needed in order for the CLM countries to be able to undertake all the preparatory work and the actual implementation of the National Single Windows by 2015.
- The sub-regional initiatives in the ASEAN region focus primarily on the lagging areas or countries in the region. Thus, they complement the national programmes of ASEAN Member States under the various ASEAN regional initiatives and roadmaps such as the AEC Blueprint and the Master Plan on ASEAN Connectivity. Thus, it is important to ensure strong coordination and complementarities between the sub-regional initiatives and the ASEAN regional initiatives.
Key actions:
(i) Facilitate the flow of technical assistance, including from the donor community, to CLMV countries and sub-regional groupings for capacity building needed to effectively undertake the initiatives under this Master Plan by 2012.
(ii) Set up a coordinating mechanism and structure between the ASEAN Secretariat on the one hand and the respective secretariats of the sub-regional initiatives and the ADB on the other hand, so as to ensure the consistency and complementarities of the policies, programmes and projects of the sub-regional initiatives with the policies, programmes and projects of ASEAN by 2011.
(iii) Strengthen the capability and resources of the ASEAN Secretariat and the secretariats of the sub-regional initiatives in monitoring and evaluating the implementation of the above-mentioned mandates by 2011.
3.3. People-to-People Connectivity
- People-to-people connectivity is the socio-cultural glue that supports and anchors the various initiatives toward greater physical connectivity as well as the regulatory and institutional reforms that are needed to ensure institutional connectivity in the ASEAN region.
- With an area spanning over 4.43 million km2 and a population of some 591 million, ASEAN hosts one of the richest cultural heritages in the world. At the same time, ASEAN has seen a growing sense of inter-relatedness and community over the years. In light of the Leaders’ decision to establish an ASEAN Community by 2015, it is imperative that ASEAN as a region continues to draw strength from its unity amidst cultural diversity to address the challenges while reaping the benefits arising from the rapid globalisation process we witness today. The following are the key strategies to enhance people-to- people connectivity in the ASEAN region:
Key Strategies to Enhance People-to-People Connectivity |
Strategy 1 | Promote deeper intra-ASEAN social and cultural understanding |
Strategy 2 | Encourage greater intra-ASEAN people mobility |
Strategy 1: Promote deeper intra-ASEAN social and cultural understanding
- Cultural diversity, which has been shaped by customs and beliefs, can provide the much needed impetus for creativity, innovation and development when opportunities are created for greater interactions between peoples in ASEAN. Such interactions could be pursued or facilitated through awareness, collaboration, exchange and outreach programmes. Despite the many years of efforts in ASEAN for greater socio-cultural, athletics, and educational interchanges among the peoples in the region, there remain substantial opportunities for more concerted regional efforts towards greater people-to-people connectivity.
Key actions:
(i) Establish coordinated but distributed Virtual Learning Resource Centres on the People, Culture, History, Places of interest, and Economy of each ASEAN Member State by 2012.
The advent of Internet presents an opportunity for each ASEAN Member State to share information through dedicated website(s) about its people, culture, history, economy, and places of interest. The websites are interlinked and coordinated through the ASEAN Committee on Culture and Information (COCI).
The ASEAN virtual learning resource centres can become major reference tools to students and peoples in the ASEAN region in their studies or information gathering requirements on other ASEAN countries. The benefits from the virtual learning resource centres will increase much more if ASEAN Member States would also encourage actively the curricular development or modular sections on the ASEAN region in their respective high schools and colleges.
(ii) Encourage the establishment of curricular offerings or education modules on ASEAN and on the ASEAN countries by 2012, where appropriate.
(iii) Encourage the development of ASEAN-related content in school curricula at all educational levels and instructional materials of ASEAN Member States. The concerted approach to develop a common curriculum framework should also be supported to promote greater awareness of ASEAN and strengthen the ASEAN regional identity among children and youth in the region.
(iv) Encourage the study of languages of ASEAN countries as the third language, after the native language and English.
(v) Education institutions would be supported to develop common content on ASEAN for schools as a reference for teacher training and teaching; and be a good platform to create ASEAN awareness, cultural understanding and greater awareness of each other’s culture in order to create deeper mutual understanding and forge a sense of commonality for students of all ages and levels.
(vi) Encourage the development of ASEAN-related content in school curricular to enhance learning opportunities. In this light, educational cooperation in developing a common curriculum framework of ASEAN, containing the wide-area aspects of ASEAN such as geography, demographics, history, culture and society should be promoted as a crucial element for cultivating regional identity, related to social justice and equity, diversity, and sustainable development and to enhance collaboration and cooperation across the ASEAN region and internationally.
This effort can be further supplemented through regular features in local media such as radio, television and newspapers for the benefit of the rural communities which have limited access to the Internet.
(vii) Establish a major concerted ASEAN Community Building Programme, to be jointly but proportionately funded principally by ASEAN Member States by 2013.
(viii) Promote awareness of ASEAN through active implementation of the Communication Plans of all three ASEAN Communities.
(ix) Promote understanding of common cultures and history of ASEAN through regular cultural events.
Over the years, ASEAN Member States have been implementing their respective community building programmes on an ad-hoc basis. It is evident that a more concerted approach is required to provide the much needed impetus for the realisation of the ASEAN Community by 2015.
Apart from the curricular offerings/education modules and virtual learning resource centres, the building of a sense of community in the region is best facilitated by direct people-to-people interaction and cooperative endeavours. There are many possible areas for such people-to-people cooperative endeavours.
One programme to consider is the expanded collaboration among higher education institutions, research institutions, and centres of excellence in ASEAN Member States to jointly undertake research on the ASEAN region,ASEAN countries, and how ASEAN could further progress in key areas which will foster greater regional integration. Such entities, as well as the broader civil society and the business sector, could also benefit from visiting scholars who will enrich the institutions’ intellectual and research endeavours through the delivery of lectures, seminars, research and internal discussions on their respective from the region areas of expertise. Educational institutions could further facilitate the exchange of students to complete their final year in neighbouring countries’ institutions to provide them with an opportunity to study in a new environment, learn new languages, and experience new culture and self-reliance.
On the cultural front, each Member State enjoys traditional performing arts which have been passed down from one generation to the next, ranging from music, dance, drama, theatre and martial art. It would be desirable for local arts and theatre companies to jointly organise a tour of the performing artists to perform in all ASEAN countries in August each year which will coincide with the anniversary of ASEAN.This will certainly help to create greater awareness of ASEAN among peoples from all walks of life. Furthermore, exchange of best practices with a view to preservation and promotion of local culture can also be encouraged.
ASEAN also needs to be vigilant of the global developments which may hamper its ongoing efforts to create a dynamic and resilient community to weather through both political and economic uncertainty. Key regional movers and shakers from private sector, academic, non-government organisations or local community, can be invited to retreats to brainstorm on how ASEAN region could continue to be relevant in the rapidly developing world. Such views should then be presented to the ASEAN Leaders for their consideration.
The programme mechanics and operational focus will be finalised by a committee to be created under the aegis of the ASEAN Socio-Cultural Community Council. ASEAN Member States will be the primary provider of resources of the programme. ASEAN Member States can also encourage their private business and philanthropic sectors as well as the international donor community to participate in providing co-funding to the programme.
(x) Optimise the use of ICT as a tool to promote ASEAN people engagement and empowerment in the context of ASEAN Community building and identity by 2015.
ICT can be harnessed to assist ASEAN in facilitating policy coordination, enhancing its coordination with stakeholders, and creating a regional identity. Through the use of ICT, ASEAN Member States can facilitate communication among and between their peoples and stakeholders and effectively manage information regarding ASEAN and its initiatives in a manner that is not bounded by physical restrictions such as distance.
Strategy 2: Encourage greater intra-ASEAN people mobility
- Despite the growing number of people visiting ASEAN over the years, there are still a number of limitations and restrictions deterring private individuals from visiting ASEAN for business or leisure. Amongst others, these include visa requirements, inadequate infrastructure and facilities which tend to limit accessibility, and also the quality of services rendered.
Key actions:
(i) Undertake a study on the possibility of progressively liberalising visa restrictions towards full implementation of a visa exemption regime for intra-ASEAN travel by ASEAN nationals within ASEAN by 2012.
(ii) Explore the possibility of establishing ASEAN Immigration Lanes for ASEAN nationals in major international ports of entry in ASEAN by 2011.
(iii) Carry out a study on the possibility of implementing progressive visa relaxation for foreign tourists visiting ASEAN by 2015.
(iv) Further encourage intra-ASEAN tourism through the concerted development of tourism products (e.g. heritage sites, cruise, home stay, health/medical tourism, eco-tourism), easier access to tourism areas, affordable packages, and assurance of consistent quality by 2012.
Currently there are over 35 protected areas listed under the ASEAN Declaration on Heritage Parks which was signed in 2003.A study should be undertaken to develop heritage circuit packages to provide tourists with unique lifetime experiences of the rich heritage ASEAN has to offer.The study should also look into developing standards for basic amenities facilities, supporting infrastructures, training for tour guides, language and interpretation skills, and memorable programme for the visitors.
Cruise tourism has also slowly gained momentum as an alternative transportation means for visiting different countries in the region. Such potential should be further developed for it will provide another distinctive experience for the tourists. A study should also be undertaken to look into how public and private sectors could collaborate to address some of the key obstacles including inadequate infrastructure and facilities, the development of tourism corridors, and the facilitation of land travel, as well as transnational crime, for example, piracy and armed robbery at sea.
Affordable and hassle-free tourism within ASEAN will lead to greater people-to-people connectivity and greater understanding of ASEAN peoples, societies and countries.
(v) Enhancing stakeholders’ involvement on skills development by sharing best practices among ASEAN Member States through instructors training, raising skill standards, skills competitions, development of vocational training modules and curricular in ASEAN, and teaching technologies for workforce potential development. Furthermore, ASEAN Member States will facilitate several channels of people-to-people connectivity in order to achieve the stated key actions.
(vi) Encourage more intra-ASEAN movement of skilled labour through the development of further MRAs by 2012 and the full implementation of all completed MRAs by 2015.
In addition to the eight existing MRAs, an MRA for skills certification in ICT will be developed.
(vii) Develop MRA for skills certification to ensure quality of ICT talents and facilitate movement of ICT human resource within ASEAN by end 2015.
(viii) Undertake a study of a pilot project in establishing an ASEAN regional mobility pool for ASEAN skilled labour by 2015.
(ix) Strengthen the social services network and the Consortium of social welfare practitioners, educators and schools of social work to improve social welfare for the peoples of ASEAN.
(x) Implement the 2007 ASEAN Declaration on the Protection and Promotion of the Rights of Migrant Workers.
• • • •
Mobilising Resources for Enhancing
Connectivity in ASEAN
CHAPTER 4
MASTER PLAN ON ASEAN CONNECTIVITY
CHAPTER 4:MOBILISING RESOURCES FOR ENHANCING CONNECTIVITY IN ASEAN
- Achieving the Master Plan goals of improving physical, institutional, and people-to-people connectivity will require the mobilisation of significant financial resources and technical assistance. A variety of internal and external financing sources will need to be made available to address the different financing and technical assistance needs across the ASEAN membership, both over the short- and the medium- term, to help match the needs for enhanced connectivity with the financing that is available.
- This chapter reviews the potential financing and technical assistance sources, modalities and arrangements, including the public-private partnership (PPP), to help implement the Master Plan on ASEAN Connectivity. The emphasis is on how to mobilise available resources to finance key priorities of physical and institutional connectivity infrastructure encompassing hard infrastructure in intermodal transport, ICT, and energy networks, as well as the regulatory framework and related transport and trade facilitation software necessary to deliver associated connectivity-related services and utilities. Some of the resources identified could also be used to fund education, culture and tourism-related priorities as outlined under people-to-people connectivity of the Master Plan.
Financing of Enhanced Connectivity: Traditional Sources
- A variety of traditional funding sources and modalities are available to contribute to the financing of ASEAN Connectivity related projects. These include multilateral development banks (e.g. Asian Development Bank (ADB), World Bank, and Islamic Development Bank), bilateral development partners, and national Governments. The amounts, modalities and terms of traditional sources of finance vary according to the types of lending institutions, levels of development of borrowing countries, and nature of projects.
- With regard to multilateral development banks, the ADB, for example, offers: (i) sovereign and non-sovereign loans at near market terms to better off borrowing member countries from its Ordinary Capital Resources (OCR), recently augmented by the Fifth General Capital Increase; (ii) sovereign loans at concessional rates and terms and grants to poorer member countries from its Asian Development Fund (ADF); and (iii) technical assistance, mostly in grant form, to help identify, prepare and implement projects and foster regional economic integration. The World Bank offers a variety of funding, including International Development Assistance (IDA) and International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) loans. The International Finance Corporation (IFC) offers support for the private sector.
- Reflecting the nature of their modalities and operations, including loan guarantees, adherence to best practice safeguards, strong credit ratings, and the provision of specialised technical assistance, the ADB and World Bank also act as effective catalysts for attracting co-financing from bilateral donors and aid agencies, and the private sector.
- The Islamic Development Bank specialises in mobilising financial resources for member countries and for Muslim communities in non-member countries from a variety of specialised funds and in the form of Shari’ah-compliant instruments (in accordance with the principles of Islamic Law), including in infrastructure, human resource and private sector development.
- Several regional and global funds and facilities have been established to foster infrastructure and related software development.These include the Regional Cooperation and Integration Fund (RCIF) and Climate
57 MASTER PLAN ON ASEAN CONNECTIVITY
Change Fund (CCF), both financed and administered by ADB; the Investment Climate Facilitation Fund (ICFF), financed by the Government of Japan and administered by ADB; the Regional Cooperation and Poverty Reduction Fund (RCPRF), financed by the Government of the People’s Republic of China and administered by the ADB; and the Clean Energy Financing Partnership Facility (CEFPF) and the Public-Private Infrastructure Advisory Facility (PPIAF), financed by multiple donors and administered by the ADB and the World Bank, respectively. There are also other regional and global funds that will be identified during the implementation of the Master Plan.
- A variety of infrastructure financing initiatives have also been established by the external partners of ASEAN, such as the Facility for Asia Cooperation and Environment (FACE) and the Leading Investment for Future Environment (LIFE), financed by Japan and administered by Japan Bank for International Cooperation (JBIC); the Asia Infrastructure Financing Facility (AIFF), financed by the Republic of Korea and administered by ADB; and the China-ASEAN Investment Cooperation Fund (CAICF). In this context, Japan has cooperated with ASEAN Member States and contributed towards the development of competitive economic corridors which has led to the improvement of infrastructure networks and regional economic integration in ASEAN.
- To complement “hardware” improvements and ensure that the “software” components of connectivity of goods, services and people support the full effective use of physical infrastructure, many of the external partners mentioned above and others offer a wide range of connectivity- and institutional development- related technical assistance, such as for transport and trade facilitation, sanitary and phyto-sanitary (SPS) standards, and logistics. In addition, to support the delivery of priority connectivity projects and deepen the physical connectivity pipeline over the coming years, technical assistance is needed to help with project identification and preparation in the first instance, including pre-feasibility studies, which are especially important for determining potential PPPs, and the implementation, monitoring and evaluation to ensure that selected projects achieve their objectives and act as concrete building blocks towards the realisation of ASEAN Community. Table 4.1 provides an indicative list of funding sources for technical assistance.
Table 4.1: Indicative List of Funding Sources for Technical Assistance
No | Possible Sources of Available Funding |
1. | ASEAN Development Fund (ADF) |
2. | ASEAN Cultural Fund (ACF) |
3. | ASEAN Information Communications Technology (ICT) Fund |
4. | ASEAN Energy Endowment Fund |
5. | ASEAN-China Cooperation Fund (ACCF) |
6. | Japan-ASEAN Integration Fund (JAIF) |
7. | ASEAN-ROK Special Cooperation Fund (SCF) |
8. | ASEAN-ROK Future Oriented Cooperation Programme Fund (FOCP) |
9. | ASEAN Plus Three Cooperation Fund |
10. | ASEAN-Australia Development Cooperation Programme Phase II (AADCP II) |
11. | ASEAN-India Fund |
12. | ASEAN Economic Integration Support Programme (ASEAN-EU) |
13. | ASEAN Air Transport Integration Project (ASEAN-EU) |
14. | ASEAN Development Vision to Advance National Cooperation and Economic Integration (ADVANCE) Programme (ASEAN-US) |
15. | Economic Research Institute for ASEAN and East Asia (ERIA) |
16. | Asian Development Bank (ADB) |
17. | World Bank |
18. | Other Technical Assistance Programmes within ASEAN and with ASEAN External Partners |
- National Government budgets will continue to be an important source of financing of infrastructure, institutional and people-to-people connectivity projects. However, it is understood that the effects of the global economic crisis and the current lack of available fiscal space over and above the recent fiscal stimulus response measures represent a serious public financial constraint to infrastructure development in many ASEAN Member States, especially for the developing member countries where available public resources are scarcer than in the more advanced member countries. Meanwhile, the global economic crisis has also negatively impacted on aid development budgets. While some ASEAN Member States could gradually increase financing from the issuance of Government securities, including, in some countries, Sukuk (i.e., Islamic Law compliant) bonds, the amount of financing mobilised in such a manner would need to be consistent with the pace of local and regional capital market development and public debt sustainability. Finally, most ASEAN Member States, understandably, have been reluctant to finance infrastructure investment through foreign borrowings because of appropriate caution in incurring large commercial debts in foreign currencies to invest in assets that generate revenues in local currency.
Financing of Enhanced Connectivity: New and Innovative Sources
- While multilateral and bilateral development partners, various types of regional and global funds, and national Governments are able to fill part of the total resource needs for priority connectivity infrastructure, the total amount of the resources mobilised from these traditional sources may not be sufficient to close the infrastructure deficit. Moreover, the centrality of ASEAN suggests that ASEAN’s aspirations of greater physical, institutional and people-to-people connectivity could also be financed from tapping part of the region’s large aggregate private savings and where appropriate from foreign exchange reserves, consistent with relevant national laws and foreign exchange management guidelines, which have been built up over time from impressive overall economic growth and sustained prudent macroeconomic management, including through the most recent global economic crisis.
- Such new and innovative resource mobilisation initiatives will need to take into account the important reality. Private individuals and businesses, who hold most of ASEAN’s excess savings are looking to invest them in ventures with high financial returns and low levels of risk, have a vital role to play in the success in regional infrastructure funding. Infrastructure projects, particularly sub-regional ones, require special attention because of their long implementation periods, uncertain financial returns and inherent risks. As a result, most infrastructure projects are financed by Governments, and/or multilateral and bilateral institutions, at concessional terms for developing member countries, while PPP projects usually require Government guarantees.
- In an effort to clearly signal ASEAN’s self-reliance and centrality as part and parcel of an ASEAN Connectivity package, the ASEAN Member States are working towards the establishment of an ASEAN Infrastructure Fund (AIF) with the objective to mobilise financial resources within ASEAN to support regional infrastructure development.The ADB has been requested to support this establishment of the AIF. It is envisaged that the proposed AIF will reduce infrastructure deficit, provide the resources to support growth and poverty reduction, facilitate private sector participation and development, promote regional economic integration, and support social and environmental aspects of infrastructure. More concretely, the proposed AIF would help ensure best practice designs and execution arrangements for priority infrastructure projects, and help ensure that these priority projects are approved and implemented.
Role of the Private Sector in ASEAN Connectivity
- Involvement of private sector as a source of private capital and expertise in developing sustainable infrastructure projects will also support the aims of the Master Plan on ASEAN Connectivity. In particular, PPPs represent an innovative way for the governments to work with the private sector in providing high-quality service delivery and in closing the gaps in fund requirements of the infrastructure sector.
- With the exception of telecommunications projects, there are few successful PPPs in infrastructure, especially for sub-regional projects, as both domestic and international project financiers feel constrained by their perceptions of the high degree of risks involved in long-tenure infrastructure transactions.Thus, the main reasons for the low success rate is not merely the scarcity of available private sector financing, but also the ability of Governments to identify and prepare attractive, sound and bankable2 projects, which meet the requirements of the private sector. Some countries have established PPP units, but not all of these have been as successful as initially hoped for. To help the Governments and the private sector prepare bankable projects to attract private sector funding, the ADB has proposed the establishment of a Special Project Development Facility (SPDF). Under the first phase of the proposed SPDF, the ADB could help finance pre-feasibility studies for some of the priority connectivity projects identified in the IMT-GT and BIMP-EAGA sub-regional project pipelines. Such pre-feasibility studies would help clarify the specific criteria according to which projects could be prepared under a PPP modality to help maximise the chances of successful PPPs.
- To leverage private capital in financing ASEAN’s infrastructure development in a way that will support the aspirations and goals of the Master Plan on ASEAN Connectivity, actions at the country and regional levels would be required to implement PPP projects.
- At the country level, the private sector engagement strategy aims to support governments in the region in mobilising and channelling private financing into infrastructure development through market-based instruments. This strategy requires the following key components:
(i) Issuance of PPP Financing Framework by combining different sources of financing – public finances, Official Development Assistance (ODA), and private investments – through PPPs, in line with their respective risks allocation.
(ii) Preparing PPP projects to internationally acceptable standards to receive the infrastructure financing mobilised from different sources, and structuring the projects so that the risk exposure to concerned parties is well-aligned to the financing provided.
(iii) Establishing credit culture in public infrastructure operations to access financial market through bond issuance, bond rating and improved standing of public agencies as credible partners for the private sector.
(iv) Leveraging on initiatives by multilateral development banks and other development partners in the region which offer tailored technical expertise on infrastructure financing and other specific models which have attracted private sector financing for PPP projects.
2 A “bankable” project can be defined as one that has sufficient collateral, future cash flow, and a high probability of success so that it is acceptable to institutional lenders for financing.
- At the regional level, the private sector engagement strategy aims to achieve a well-functioning infrastructure finance market set against changing global financial and macroeconomic realities. This strategy requires the following key components:
(i) Sharing information and working towards harmonising procedures on infrastructure finance, including PPPs, and related financial sector mechanisms to facilitate cross-border private investments in infrastructure and connectivity.
(ii) Providing technical support to individual countries in developing policies and mechanisms for private financing of infrastructure through regional knowledge exchange and capacity building platforms such as the World Bank-ASEAN Infrastructure Finance Network (IFN).
(iii) Establishing a Private Sector Consultative Group to position the regional PPP development agenda as a strategic partnership between public and private sectors, as well as to solicit ideas and seek technical support through meetings and consultations of PPP units in the respective ASEAN Member States and the private sector.
The Role of Developing Regional and Domestic Capital Markets
- Financing of infrastructure requires the availability of long-term capital, on reasonably competitive terms, and preferably in local currency – requirements that are rarely met in developing countries. The high savings rates in the ASEAN region, at 30 percent to 35 percent of GDP, are encouraging; yet the absence of institutional interlocutors constrains channelling these monies into infrastructure. Priorities for the development of the domestic debt market include: (a) the need to increase availability of local currency debt financing, and with longer tenor; (b) banking sector reforms to address long-term debt financing needs of infrastructure; (c) development of flexible financing/refinancing options; (d) bond market development, along with market-based tools like credit ratings to help investors assess the level of risk associated with a given fixed-income investment; and (e) tapping institutional investors, pension funds to invest long-term capital in infrastructure.At the same time, equity markets require: (a) the need for a strong regulatory and oversight body; (b) the establishment of clear corporate governance principles in the law; (c) the need for greater disclosure, clearly established accounting rules; (d) the increase in the number of listed companies; and (e) clarity on the role of private equity and infrastructure funds, and associated oversight.
- An even more important shift would require the use of market-based tool, such as credit ratings, to assess the performance of public entities which are (or plan to be) engaged directly with the financial market as issuers of debt.A new credit ratings scale, known as the ASEAN regional ratings scale (ASEAN scale), has been introduced to assign credit ratings on issuers located in Southeast Asia. The scale is designed to enable investors participating in national or regional ASEAN capital markets by providing finer distinctions of credit quality, allowing an assessment of the relative creditworthiness of issues and debt issuers, based on credit assessment measures that are consistent across the ASEAN region. The new ratings scale will complement the work on creditworthiness of public infrastructure utilities and state-owned enterprises (SOEs), and extend it on the regional level, facilitating regional comparisons of creditworthiness of a range of agencies and institutions. This is expected to have a positive impact on
(a) making more and better information available on the creditworthiness of a wider pool of public and private agencies; and (b) providing stronger incentives to public agencies for better financial management and espousing credit culture.
Moving Forward with Financing Connectivity Projects
- This Master Plan has identified relevant projects of priority to substantiate the ASEAN Connectivity initiative (refer to Appendix 4.1). These projects, some of which are national projects that help establish and operationalise critical sub-regional links, would provide key building blocks to ASEAN physical connectivity.
- As these projects are successfully implemented and the sub-regional pipelines of connectivity projects deepen over time, longer-term financing options will also need to be available. While Governments, multilateral and bilateral institutions would still contribute to physical infrastructure projects, an increasing share of the additional resources required could be generated by the deepening of regional and local financial and capital markets.
- In the longer term, channelling regional private savings into regional investment in physical infrastructure projects will also be made easier by greater regional capital market integration, a process that is being facilitated by the ASEAN Capital Markets Forum (ACMF) since its establishment in 2004 under the auspices of the ASEAN Finance Ministers. ASEAN Finance Ministers have endorsed the Implementation Plan to promote development of an integrated ASEAN capital market, while taking steps to strengthen the region’s resilience to exogenous shocks. More specifically, the establishment of the Credit Guarantee Investment Facility (CGIF), developed under the ASEAN+3 Asian Bonds Market Initiative, has been proposed to help develop deeper and more liquid local currency and regional bond markets.The CGIF is to be set up as a US$ 700 million trust fund, including capital contributions of US$ 130 million from the ADB. The pilot CGIF, due to start in 2011, will provide guarantees on local currency denominated bonds issued by companies in the region. Such guarantees will make it easier for firms to issue local bonds with longer maturities.This will help reduce the currency and maturity mismatches and make the regional financial system more resilient to volatile global capital flows and external shocks.
• • • •
Implementation
CHAPTER 5
MASTER PLAN ON ASEAN CONNECTIVITY
CHAPTER 5: IMPLEMENTATION
- ASEAN is resolved to embark on a bold and long-term strategy to enhance its Connectivity so that it can operate in an efficient and seamless manner. For ASEAN Connectivity to be effectively implemented, necessary mechanisms and resources shall be put in place.
- An implementation mechanism, involving the establishment of an ASEAN Connectivity Coordinating Committee, comprising the Permanent Representatives to ASEAN or any other special representatives appointed by ASEAN Member States, shall be put in place to ensure the effective implementation of the strategies and policies put forward. The ASEAN Connectivity Coordinating Committee shall coordinate the overall implementation of the Master Plan together with the National Coordinators who should be appointed by the Governments of respective ASEAN Member States, with the support of a dedicated unit with adequate funding in the ASEAN Secretariat.
- Relevant ASEAN sectoral bodies will coordinate the implementation of the strategies and actions while the National Coordinators and the relevant government agencies are responsible for overseeing the implementation of specific plans or projects at the national level. Partnership arrangements and regular consultations with the private sector, industry associations and the wider community at the regional and national levels will also be actively sought to ensure the participation of all stakeholders in developing and enhancing the ASEAN Connectivity. Figure 5.1 illustrates the implementation arrangements for the Master Plan on ASEAN Connectivity.
Figure 5.1: Implementation Arrangements for the Master Plan on ASEAN Connectivity
Communications Strategy
- A communications strategy, consisting of a comprehensive set of coherent communications activities aimed at achieving the objectives of ASEAN Connectivity, is envisaged for outreach and advocacy purposes as implementation requires close collaboration among stakeholders or constituents, which could cover the mass media, relevant representatives of the public and private sectors as well as national and local authorities. In addition, it is also important to assess stakeholders’ or constituents’ concerns, expectations, interests, and perceptions of Connectivity activities. It is also essential that the communications strategy takes into account processes that have been initiated and established, giving special attention to lessons learned and existing channels of dissemination.
Monitoring, Evaluation and Review
- The implementation of the Master Plan on ASEAN Connectivity shall be monitored and overseen by the ASEAN Connectivity Coordinating Committee.
- A scorecard mechanism, detailing the strategies and key actions with relevant timelines and responsible bodies, will be set up to effectively monitor and evaluate the implementation on a regular basis.
- The Master Plan shall be reviewed periodically to ensure that all the activities are responsive to the needs and priorities of ASEAN.
• • • •
APPENDICES
MASTER PLAN ONASEAN CONNECTIVITY
APPENDIX I.1: ASEAN Leaders’ Statement on ASEAN Connectivity, Cha-am Hua Hin,Thailand, 24 October 2009
! ASEAN Leaders’ Statement
on ASEAN Connectivity, Cha-am Hua Hin, Thailand, 24 October 2009
- The Heads of State/Government of the Member States of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) discussed the concept of ASEAN Connectivity at the 15th ASEAN Summit in Cha-am Hua Hin on 24 October 2009.
- They observed that ASEAN was located at the crossroads of an economically vibrant and growing region bounded by India in the west; China, Japan, and the Republic of Korea in the Northeast; and Australia and New Zealand in the South.ASEAN thus has the potential to physically anchor itself as the transportation, Information and Communication Technology, and tourism hub of this region.
- Enhancing intra-regional connectivity within ASEAN and its subregional grouping would benefit all ASEAN Member States through enhanced trade, investment, tourism and development. As all of the overland transport linkages will have to go through the mainland Southeast Asian countries of Cambodia, Laos, Vietnam and Myanmar, these countries stand to benefit the most through infrastructure development, and the opening up of remote inland and less-developed regions. All these efforts would significantly narrow the development gap within ASEAN.
- In addition to the tangible economic benefits of ASEAN Connectivity, the linkages created would intensify and strengthen ASEAN Community building efforts, not only in terms of enhanced regional cooperation and integration, but also through people-to-people contacts. In this regard, the concept of ASEAN Connectivity would also complement the ongoing regional efforts to realize a people-oriented ASEAN Community by 2015 with a focus on fostering a sense of shared cultural and historical linkages. In order to do this, the Leaders hereby agreed that:
- It is vital to complete the physical road, rail, air, and sea linkages within ASEAN. Development of infrastructure and multi-modal transport projects such as, inter alia, the ASEAN Highway Network and the Singapore-Kunming Rail Link, should be expedited in parallel with addressing software related issues within relevant existing work plans of ASEAN. Given the importance of the Internet in business, education and development, it is also crucial to complete the ASEAN ICT Master Plan in 2010 to enhance intraregional Information and Communication Technology linkages.
- The deepening and widening of connectivity in the region would reinforce ASEAN’s position as the hub of the East Asian region, which could further be strengthened through realizing the potentials of a broader connectivity in the longer term with its partners in the wider region. In this regard, the Leaders were of the view that this concept of ASEAN connectivity would complement and support integration within ASEAN and within the broader regional framework in East Asia.
- ASEAN should seek the support of all its Dialogue Partners and other international agencies and development partners to realize the vision of ASEAN Connectivity, including the establishment of an infrastructure development fund for ASEAN.ASEAN should also explore ways to effectively capitalize on existing cooperation funds for infrastructure development with its Dialogue Partners and remain open to future cooperation with other interested parties, as appropriate.
- An ASEAN High Level Task Force, comprising relevant experts, supported by the ASEAN Secretariat and relevant sectoral bodies, in cooperation with relevant international organizations such as the Asian Development Bank (ADB), the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP), the Economic Research Institute for ASEAN and East Asia (ERIA), shall be established to study ASEAN’s internal and external connectivity, and to develop an ASEAN Master Plan on regional connectivity, that include, among others, innovative infrastructure financing mechanisms, taking into account the work done and planned to ensure optimum synergy rather than duplication of work. In devising the Master Plan, the Task Force should ensure that the limited resources from ASEAN, Dialogue Partners and International Development Banks and Agencies are employed in the most efficient and effective manner to realise our vision.The ASEAN High Level Task Force should consult with the APSC Council, the AEC Council and the ASCC Council before submitting their recommendations to the 17th ASEAN Summit in 2010 through the ASEAN Coordinating Council.
. . . . . .
Issued on 24 October, 2009 in Cha-am Hua Hin,Thailand.
Appendix 2.1: 47 Designated Ports and Their Respective Cargo Throughput 2008
Source: JICA Study on Guidelines for Assessing Port Development Priorities 2009
Appendix 2.2: Status of Ratification of ASEAN Transport Facilitation Agreements
AGREEMENT/PROTOCOL | DATES OF SIGNING | DATES OF RATIFICATION BY MEMBER STATES | DATE OF ENTRY INTO FORCE |
BRN | CAM | INA | LAO | MAL | MYM | PHI | SIN | THA | VNM |
ASEAN Framework Agreement on the Facilitation of Goods in Transit (AFAFGIT) | 16/12/98 | 15/8/00 | 30/4/99 | 13/1/00 | 21/12/99 | 2/3/99 | 16/12/98 | 20/5/99 | 2/10/00 | 17/2/99 | 24/6/99 | 2/10/00 |
Protocol 1 | 8/2/07 | 19/10/09 | 27/10/09 | | | | | 13/11/07 | | | | |
Protocol 2 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Protocol 3 | 15/9/99 | 8/9/04 | 9/5/07 | 23/6/00 | 19/1/00 | 24/7/09 | 21/8/00 | 25/11/99 | 2/5/06 | 19/4/10 | 15/11/99 | 1/6/10 |
Protocol 4 | 15/9/99 | 8/9/04 | 9/5/07 | 23/6/00 | 19/1/00 | 24/7/09 | 21/8/00 | 26/11/09 | 2/5/06 | 19/4/10 | 15/11/99 | 1/6/10 |
Protocol 5 | 8/4/01 | 8/4/02 | 30/1/02 | 30/7/02 | 6/11/02 | 26/3/02 | 16/10/03 | 22/9/03 | 29/8/02 | 8/1/03 | 2/7/01 | 16/10/03 |
Protocol 6 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Protocol 7 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Protocol 8 | 27/10/00 | | 23/5/03 | 31/12/02 | 9/5/01 | | 10/9/02 | 26/11/09 | 3/3/06 | 23/8/03 | 29/3/01 | |
Protocol 9 | 20/9/02 | 30/3/04 | 9/5/07 | 29/8/03 | 19/5/03 | | 25/4/03 | 5/5/03 | 12/9/07 | | 15/11/02 | |
ASEAN Framework Agreement on Multimodal Transport (AFAMT) | 17/11/05 | | 27/10/09 | | | | | 30/6/08 | | 11/7/08 | | 11/8/08a |
ASEAN Framework Agreement on the Facilitation of Inter-State Transport (AFAFIST) | 10/12/09 | | | | | | | | | | | |
Source: ERIA,ASEAN Secretariat
Note. a AFAMT’s entry into force is on the 30th day after the deposit of the second instrument of ratification or acceptance, and is effective only among ASEAN Member States that have ratified it or accepted it.
Appendix 2.3: Broader Development Challenges Faced by the BIMP-EAGA Sub-Regional Initiative
BIMP-EAGA continues to be confronted with major challenges, most of which have been there since its inception in 1994. Some of the more pressing challenges are:
i) Continued dependence on primary resource-based economic activities with the manufacturing sector contributing less than 20% of the regional gross domestic product. EAGA, hence, has maintained its position as mere supplier of raw materials. A key objective of the economic cooperation is to increase the processing of natural resource products within the sub-region – that is, increase the value added that in turn will increase employment opportunities within the sub-region. Efforts to establish production networks and/ or value chains in selected commodities have started since 2006, but progress has been slow mainly because of other factors such as the lack of efficient intra-EAGA transport services that allow for better movement of goods across borders. Moreover, there is little intra-sub-regional investment flow in agro- industry, which is the focus of attention of the sub-region.
ii) Weak private sector with equally weak capacity to capitalise on opportunities. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) dominate the business sector in BIMP-EAGA and impediments to the growth of SMEs in EAGA are plentiful.These include rising costs of production and inputs, inadequate framework of policy and programme support, and competition from foreign imports. Moreover, SMEs often lack access to credit and finance for working capital and investment, appropriate technology, markets, and market information. The private sector has been designated as the sub-region’s engine of growth, but this engine is not sufficiently well-oiled to spur investments and growth. There is need for increased emphasis on SME development if growth in the sub-region is to be private sector-led.
iii) High incidence of poverty in the sub-region. There does not seem to be a clearly defined overall strategy for poverty reduction to complement and/or supplement the national poverty reduction strategies. Sustained high economic growth will be needed in order for BIMP-EAGA to reduce poverty and narrow the development gaps. But policies for sustained strong growth will have to be complemented by targeted interventions and will require increased investments in basic infrastructure as well as in healthcare and education. To facilitate progress in reducing intra-regional and inter-regional inequalities, consideration would have to be given to extending the national MDG targets to the BIMP-EAGA focal areas. New initiatives such as the community-based ecotourism development programme are a step in the right direction.Similar programmes with a pro-poor slant should be identified and implemented in the sub-region.
iv) Lack of vital infrastructure.There is agreement that inadequate infrastructure particularly in the Indonesia and Philippines components of EAGA, is a major bottleneck to private sector investments. When BIMP-EAGA was created, there was some basis for believing that development of the sub-region could be accelerated through close attention to policy coordination across national boundaries, emphasis on further development of infrastructure, and vigorous promotion of substantial private investment in the sub-region. Public sector investment in infrastructure development in BIMP-EAGA is currently being assessed, although it is widely accepted that for most parts of the sub-region, infrastructure investment has seriously lagged behind other parts of the respective member countries, particularly after the 1997 financial crisis. Given the widely dispersed population and centres of production, infrastructure, transport and logistics development are vital to the marketing and distribution of production inputs and outputs. It is recognised that BIMP-EAGA could not expect to receive significantly larger public sector resources for its development. For development to happen, conditions have to be created to encourage increased private sector investments in infrastructure development.
Appendix 4.1: Prioritised Projects for ASEAN Connectivity
Project Title | Project Description | Type of Intervention/ Sources of Financing | Remarks/Justification |
A. Physical Connectivity |
1. Completion of the ASEAN Highway Network (AHN) Missing Links and Upgrade of Transit Transport Routes [LAND TRANSPORT] | The ASEAN Highway Network (AHN) is a flagship land transport infrastructure project which forms the major road (interstate highway) component of the overall trans-ASEAN transportation network. The AHN will help provide access to an enlarged market, reduce transportation and trade cost, establish linkages with regional and global supply chains, and facilitate greater regional economic cooperation and integration. The AHN’s current implementation state still shows missing links and ‘below Class III’ roads within ASEAN’s designated Transit Transport Routes (TTRs). The subset of projects below will complete these missing links and prioritise the upgrade of ‘below Class III’ roads in designated TTRs by 2015. Missing links: (i) Myanmar:AH112 (Thaton – Mawlamyine – Lahnya – Khlong Loy, 60 km) (ii) Myanmar: AH 123 (Dawei – Maesamepass, 141 km) Upgrading of ‘Below Class III’ TTRs: (i) Lao PDR:AH12 (Vientiane – Luang Prabang, 393 km) (ii) Lao PDR:AH15 (Ban Lao – Namphao, 98 km) (iii) Myanmar:AH1 (Tamu – MDY – Bago – Myawadi, 781 km) (iv) Myanmar: AH2 (Meikthila – Loilem – Kyaington – Tachikeik, 593 km) (v) Myanmar:AH3 (Kyaington – Mongla, 93 km) | CAPITAL ASSISTANCE POSSIBLE SOURCES OF FINANCING: Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs), Bilaterals, National Budgets, China-ASEAN Investment Cooperation Fund and the US$15b China-ASEAN credit, Japan | The AHN sections identified for priority implementation here are those that will result in the completion of the missing links in the AHN and will upgrade designated TTRs to the barest minimum road class standards. Focus on implementing this subset of projects appears to be more achievable by 2015, as compared to the completion of all the construction and/or upgrading required for the entire AHN by 2015. Moreover, priority to the completion of the AHN by 2015 is stipulated in the ASEAN Leaders’ Statement on ASEAN Connectivity (October 2009) as well as the AEC Blueprint. Completion of the missing links and other infrastructure projects could contribute towards the development of economic corridors which are already in progress in ASEAN. |
2. Completion of the Singapore Kunming Rail Link (SKRL) Missing Links [LAND TRANSPORT] | THE Singapore Kunming Rail Link (SKRL) is another flagship project for land transport infrastructure intended to link seven ASEAN Member States and China through Singapore–Malaysia–Thailand–Cambodia–Viet Nam–China (Kunming) and spur lines in Thailand–Myanmar and Thailand–Lao PDR. To complete the mainline SKRL and to demonstrate ASEAN’s resolve to complete this rail link, the following links need to be prioritised for construction: (i) Thailand: Aranyaprathet – Klongluk, 6 km (ii) Cambodia: Poipet – Sisophon, 48 km (iii) Cambodia and Viet Nam: Phnom Penh – Snuol – Loc Ninh, 254 km (iv) Viet Nam: Loc Ninh – Ho Chi Minh City, 129 km | CAPITAL ASSISTANCE POSSIBLE SOURCES OF FINANCING: MDBs, Bilaterals, ASEAN Member States’ (AMS) assistance to other AMS, National Budgets, Private Sector Participation (PSP), ASEAN Infrastructure Fund (AIF), China- ASEAN Investment Cooperation Fund and the US$15b China-ASEAN credit | The railway sections prioritised here correspond to the sections that will complete the mainline SKRL.The first three - items (i), (ii) and (iii) - are scheduled for completion by 2015. Item (iv), which is a 129 km connection between Loc Ninh and Ho Chi Minh City, is currently scheduled for completion by 2020.The full benefits of SKRL will only be realised if all the links - (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) - are completed by 2015. |
Project Title | Project Description | Type of Intervention/ Sources of Financing | Remarks/Justification |
3. Establish an ASEAN | The ASEAN Broadband Corridor (ABC) project has two main objectives: (i) to | CAPITAL/TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE | As information infrastructure is fundamental |
Broadband Corridor | provide the infrastructure backbones to enable ICT services to all communities | | to improving economic efficiency through |
(ABC) | in ASEAN; and (ii) to put in place the required enabling policies and legislation to | POSSIBLE SOURCES OF FINANCING: | providing access to information and |
| attract businesses and investments to the region. | AIF, PSP, Dialogue Partners, Bilaterals, MDBs, | knowledge, it is necessary to establish an |
| | National Budgets | ABC. The ABC will be significant as it can |
[ICT] | The project will focus on development of the “next generation infrastructure” (which | | boost business and social development |
| refers to both wired and wireless technologies) and set the minimum standards and | | throughout the region. It also can allow |
| quality of broadband connectivity in ASEAN. It will also identify and develop the | | individuals to build a sense of community |
| locations in each ASEAN Member State which offer quality broadband connectivity | | and awareness beyond their immediate |
| and enabling environment for the seamless usage and ICT applications across | | surroundings. |
| ASEAN and enhance the development of ICT and other sectors (e.g. broadband to | | |
| all schools), and promote the diversity of international connectivity among ASEAN | | |
| Member States. [2015] | | |
4. Melaka-Pekan Baru | This project involves a 600 MW high voltage direct current (HVDC) interconnection between Peninsular Malaysia and Sumatra, Indonesia consisting of: (i) Submarine cable (52 km) through the Straits of Malacca from Telok Gong in Malaysia to the Island of Rupat in Indonesia; (ii) Overhead transmission lines (30 km) crossing the Rupat Island; (iii) Submarine cable (5 km) crossing the Rupat Straits up to Dumai; (iv) 275 kV overhead transmission lines (200 km) from Dumai to Garuda Sakti in Central Sumatra to be built by Indonesia’s state electricity firm - Perusahaan Listrik Negara (PLN); and, (v) Converter stations in Telok Gong and Garuda Sakti including harmonic filters and other necessary transmission facilities. The project will be implemented in two phases. The first phase will consist of a 300 MW single pole configuration and the second phase will add a second 300 MW pole allowing the interconnection to operate on a bipolar configuration. [2012] | CAPITAL ASSISTANCE | The rationale for the project is based |
Interconnection | | on a win-win deal where each country |
(IMT-GT: Indonesia) | POSSIBLE SOURCES OF FINANCING: | will share their peaking capacity and the |
| AIF,Asian Development Bank (ADB) | spinning reserve due to (i) the one hour |
[ENERGY] | | time difference between the two countries; |
| | and (ii) the difference in peak hours and |
| | load curve pattern (Malaysia has a day peak, |
| | while Sumatra has a night peak). |
Project Title | Project Description | Type of Intervention/ Sources of Financing | Remarks/Justification |
5.West Kalimantan-Sarawak Interconnection (BIMP-EAGA: Indonesia) [ENERGY] | The project will consist of 120 km high voltage 275kV AC interconnection called theWest Kalimantan-Sarawak Interconnection and Bengkayang substation.The line will connect Bengkayang Substation in West Kalimantan to Mambong Substation in Sarawak. PLN will build an 82 km line in West Kalimantan side while the length of line in Sarawak side will be around 38 km. In addition, to allow the power to reach the load centre in West Kalimantan, PLN will build 60 km of 150 kV AC line from Bengkayang substation to Singkawang substation. [2013] | CAPITAL ASSISTANCE POSSIBLE SOURCES OF FINANCING: AIF,ADB | The interconnection will increase the reliability of the West Kalimantan system. The rationale for the project is based on a win-win deal where: (i) West Kalimantan will reduce the oil consumption since most of the existing plants are diesel-based; and (ii) each country will share their peaking capacity and the spinning reserve due to (a) the one hour time difference between the two countries; and (b) the difference in peak hours and load curve pattern (Sarawak has a day peak, while West Kalimantan has a night peak). |
6. Study on the Roll-on/roll off (RoRo) Network and Short-Sea Shipping [MARITIME TRANSPORT] | The project will involve a technical and feasibility study on adopting a roll-on/roll- off (RoRo) network in ASEAN and an assessment of options available for ASEAN Member States to encourage the development of short-sea shipping. | TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE POSSIBLE SOURCES OF FINANCING: National Budgets, USAID, Asia Foundation | This study will be a first step in exploring one of the options to implement one of the key principles in the Master Plan on ASEAN Connectivity on bridging archipelagic ASEAN with mainland ASEAN. |
Project Title | Project Description | Type of Intervention/ Sources of Financing | Remarks/Justification |
B. Institutional Connectivity |
1. Developing and | This project will assist ASEAN Member States to (i) develop more Mutual | TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE | Technical assistance is required to |
Operationalising | Recognition Arrangements (MRAs), in particular, for the priority integration | | implement this. As of 2010, ASEAN has |
Mutual Recognition | sectors; and (ii) adhere to the general principles and conditions stipulated in | POSSIBLE SOURCES OF FINANCING: | only developed MRAs for the electrical |
Arrangements (MRAs) for | the ASEAN Framework Agreement on MRAs and to facilitate the recognition | National Budgets, Dialogue Partners, ASEAN | and electronic sector, and cosmetic sector. |
Prioritised and Selected | of results of compulsory certification required by a Member State where the | Economic Integration Support Programme | More MRAs would need to be developed, |
Industries | certificate is issued by conformity assessment bodies in the territory of another | (EU), MDBs | in particular, for the priority integration |
| Member State, especially for the prioritised sectors. | | sectors as ASEAN works towards the |
[FREE FLOW OF GOODS] | | | creation of a single market and production |
| | | base by 2015. |
2. Establishing Common | This project will undertake a stock-take of regulatory regimes/legislative | TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE | In 2005, ASEAN prepared a policy |
Rules for Standards and | framework, an assessment of the feasibility of establishing a set of common rules, | | guideline on standards and conformance |
Conformity Assessment | and the development of a roadmap to implement these rules across ASEAN as | POSSIBLE SOURCES OF FINANCING: | which provides the guiding principles |
Procedures | a region. | National Budgets, Dialogue Partners, ASEAN | for harmonising standards, implementing |
| | Economic Integration Support Programme | relevant conformity assessment schemes, |
[FREE FLOW OF GOODS] | | (EU), MDBs | and their adoption in technical regulations. |
| | | As ASEAN strives to achieve free flow of |
| | | goods by 2015, it is imperative for such a |
| | | study to be undertaken. |
3. Operationalise all | Technical assistance should be provided to helpASEAN Member States,particularly | TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE | ASEAN Leaders agreed that ASEAN-6 and |
National Single Windows | the newer Member States (i.e., CLMV countries), to accelerate the technical, legal, | | CLMV countries should implement their |
(NSWs) by 2012 | institutional and infrastructural preparations toward the operationalisation of | POSSIBLE SOURCES OF FINANCING: | NSWs by 2008 and 2012 respectively with |
| National Single Windows (NSWs) for selected ports. | Dialogue Partners, ADVANCE ASEAN Single | the view to shorten the processing time, |
[FREE FLOW OF GOODS/ | | Window Project (US), National Budgets, | expedite the clearance of goods, lower |
ASEAN SINGLE WINDOW] | | MDBs, Bilaterals | transaction costs and also lower barriers |
| | | to trade for new businesses. To date, not |
| | | all ASEAN-6 countries have operationalised |
| | | their respective NSWs. |
Project Title | Project Description | Type of Intervention/ Sources of Financing | Remarks/Justification |
4. Options for a Framework | With the objective of attracting and retaining investments in the region,ASEAN has | TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE | Implementation of the Master Plan |
Modality towards the | in recent years taken bold steps in creating a more open and facilitative investment | | involves investment in physical and other |
Phased Reduction and | environment in the region with the signing of the ASEAN Comprehensive | POSSIBLE SOURCES OF FINANCING: | connectivity projects. The investment |
Elimination of Scheduled | Investment Agreement (ACIA), a comprehensive agreement that builds upon and | Dialogue Partners, ASEAN-Australia | environment in ASEAN Member States |
Investment Restrictions/ | improves on the two investment agreements signed in 1987 and 1998. ACIA is | Development Cooperation Programme | needs to be enhanced to ensure that |
Impediments | based upon international best practices and is forward looking. | Phase II | FDI flows will be further encouraged to |
| | | augment other sources of funding. This |
[FREE FLOW OF | Under ACIA, ASEAN adopted a negative list approach and set a definitive | | project will complement ASEAN’s efforts |
INVESTMENTS] | timeline of 2015 to open investment in ASEAN which shall be achieved through | | under the AEC Blueprint to undertake |
| progressive liberalisation. In fulfilling the target of 2015,ASEAN needs to develop | | phased reduction/elimination of investment |
| a framework/modality in which Member States will undertake a phased approach | | restrictions by proposing options for a |
| in removing the remaining investment measures that restrict free flow of | | modality for such reductions. |
| investments in the region. A technical assistance project needs to be provided | | |
| to draw up and implement a liberalisation programme taking into account the | | |
| need for the framework/modality e.g. formula with clear criteria and timeline that | | |
| would outline the phased reduction and elimination schedule of restrictions for | | |
| individual Member States until 2015. The technical assistance would also include | | |
| the formulation of a set of guiding principles and criteria that would guide the | | |
| proposed phased reduction schemes. | | |
5. Operationalisation of the | This involves the technical assistance and related studies to implement the specific | TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE | Three transport facilitation agreements |
ASEAN Agreements on | Protocols of the ASEAN Framework Agreement on the Facilitation of Goods in | | covering inter-state transport, multimodal |
Transport Facilitation | Transit (AFAFGIT). This priority project focuses on one of the three ASEAN | POSSIBLE SOURCES OF FINANCING: | transport and goods in transit are crucial |
| transport facilitation agreements which ASEAN concluded as early as 1998 so | National Budgets, Dialogue Partners, MDBs, | in fostering cross-border facilitation. |
[TRANSPORT | that critical elements to put in place an effective and seamless transit transport | ASEAN Economic Integration Support | Currently, many protocols of these |
FACILITATION] | system in the ASEAN region can be implemented. | Programme (EU), Japan-ASEAN Integration | agreements have yet to be finalised, ratified |
| | Fund (JAIF). | or implemented, thereby delaying the |
| | | establishment of effective cross-border |
| | | facilitation and seamless transit transport |
| | | system in ASEAN, including movement of |
| | | cross-border passengers and goods under |
| | | the development of procedures for cross- |
| | | border management (CIQ). |
Project Title | Project Description | Type of Intervention/ Sources of Financing | Remarks/Justification |
C. People-to-People Connectivity |
1. Easing Visa Requirements for ASEAN Nationals [MOVEMENT OF PEOPLE, TOURISM] | This project will facilitate mobility of people and tourists, possibly involving visa exemption for intra-ASEAN travel by ASEAN nationals in all ASEAN Member States. The possibility of implementing progressive visa relaxation for foreign tourists visiting ASEAN by 2015 will also be explored. | POLICY/ IMPLEMENTATION OF AGREEMENTS; TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE POSSIBLE SOURCES OF FINANCING: National Budgets, Dialogue Partners, MDBs | This addresses basic people-to-people connectivity issues as well as tourism facilitation. It sends a strong signal on ASEAN’s resolve to harmonise its procedures as one community. |
2. Development of ASEAN Virtual Learning Resource Centres (AVLRC) [CULTURE] | This is a two-part project.The first is a study to identify key factors related to the development of the ASEANVirtual Learning Resource Centres (AVLRC), including technical issues and web management. The study is important at this stage since there will be several sectors involved in the management of the AVLRC, including culture, education and tourism. Outcomes gathered from this study will form the basis of part 2 of the project, that is, the development of AVLRC. | TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE POSSIBLE SOURCES OF FINANCING National Budgets, Dialogue Partners, MDBs | ASEAN has one of the richest cultural heritage in the world with a population of some 590 million people living in an area spanning over 4.43 million km2. With the advent of ICT, greater interaction could be fostered among the peoples of ASEAN through sharing of information on the people, culture, history, places of interest and economy of each Member State by establishing and hyperlinking Virtual Learning Resources Centres. |
3. Develop ICT Skill Standards [ICT] | The project involves developing a Mutual Recognition Arrangement (MRA) for the ICT skill standards in ASEAN and will have two phases: (i) Develop an ICT Certification and Skills Upgrading programme which will focus on adoption of the certification of ICT skill sets, promotion for movement of certified ICT experts and develop a competitive ICT workforce through skills upgrading to meet the demand for ICT resources; and (ii) Establish MRA for skill certification which focuses on the development of ICT skill standards for ASEAN and promotion of the movement of ICT human capital within ASEAN. [2015] | TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE POSSIBLE SOURCES OF FINANCING: AIF,ADB | An MRA for ICT skill certification will be necessary for developing consistency in the ICT skill standards required for different certifications across ASEAN. By doing so, businesses in every ASEAN country can be assured of the quality of ICT manpower and ICT experts can be viewed as legitimate wherever they go in the ASEAN region. |
Project Title | Project Description | Type of Intervention/ Sources of Financing | Remarks/Justification |
4. ASEAN Community | One main activity under this programme is a tour of performing artistes in all | TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE | Promoting a sense of regional identity |
Building Programme | ASEAN countries in August each year, coinciding with ASEAN’s anniversary. At | | requires a basic awareness of the cultural |
| each stop (preferably, the performance should take place in the provincial capital), | POSSIBLE SOURCES OF FINANCING: | heritage of the region.The objective of the |
[CULTURE, EDUCATION] | cultural exhibitions will be held to further promote understanding of the region’s | National Budgets, Dialogue Partners, MDBs, | project is intended to showcase ASEAN’s |
| cultural diversity.The local media will be invited to broadcast the performance. | JAIF | best arts and cultural performances that |
| | | will allow the public, both ASEAN and |
| The second activity brings together key movers and shakers from private sector, | | international communities, to know and |
| academic, non-government organisations, youth groups and local community for | | understand more about the history and |
| exchange programmes. A related activity involves expanding collaboration among | | cultures of ASEAN Member States, and |
| higher education institutions, research institutions, and centres of excellence | | the work of ASEAN. In order to have |
| in ASEAN Member States to jointly undertake research on the ASEAN region, | | optimum achievements, it is expected that |
| ASEAN countries, and how ASEAN could further progress in key areas which will | | the local/international media be involved to |
| foster greater regional integration. | | broadcast the event to all ASEAN Member |
| | | States and on the ASEAN website. |
| | | The need for a major scale participation |
| | | of ASEAN think-tanks to evaluate and |
| | | review the work of ASEAN and on how to |
| | | improve and expand its activities is needed |
| | | to be held regularly, either annually or twice |
| | | a year. |
| | | The ASEAN University Network (AUN) |
| | | is currently promoting student mobility |
| | | and academic exchange. As such, relevant |
| | | activities could be part of the AUN |
| | | Secretariat’s Strategic Plan. |
www.asean.org